Understanding Startup Database: Key Features and Importance

Understanding Startup Database: Key Features and Importance
Overview
The article highlights the key features and significance of startup databases, underscoring their role as essential tools for investors, entrepreneurs, and researchers navigating the entrepreneurial ecosystem. These databases offer comprehensive information, which enables market analysis and facilitates informed decision-making. This capability is crucial for identifying trends and investment opportunities in a competitive landscape. By leveraging the insights provided by these databases, users can enhance their strategic planning and execution, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes in their ventures.
Introduction
The rapid growth of the entrepreneurial landscape has led to an increasing reliance on startup databases. These databases serve as vital repositories of information about emerging businesses, compiling essential details such as funding history and market segments. By empowering investors and entrepreneurs to make informed decisions, these databases can significantly influence their success. However, with so much data available, how can organizations effectively navigate this wealth of information? This question invites consideration of strategies to uncover actionable insights and gain a competitive edge.
Define Startup Database: Core Concepts and Functions
An emerging company repository serves as an organized collection that compiles comprehensive details about new businesses, including their founding teams, funding history, product offerings, and industry segments. These data repositories are vital resources for investors, entrepreneurs, and researchers, providing access to a wealth of information that can guide decision-making and strategic planning. The primary functions of a new venture information system include information storage, retrieval, and analysis, enabling users to recognize trends, evaluate market opportunities, and assess competitive environments. By consolidating information from multiple sources, these systems offer an extensive perspective of the entrepreneurial ecosystem, facilitating connections between new ventures and potential investors or collaborators.
The size of new venture information systems can vary significantly, with some encompassing thousands of records that reflect the dynamic nature of the entrepreneurial landscape. For instance, the U.S. is home to over 82,000 new businesses, underscoring the vast amount of data available for analysis. Efficient business information systems, such as Crunchbase and PitchBook, exemplify how organized data empowers investors and entrepreneurs to make informed choices. These platforms not only provide insights into funding rounds and valuations but also track industry trends and emerging technologies.
The significance of the startup database is immense. They act as essential tools for investors seeking promising opportunities and for entrepreneurs striving to understand industry dynamics through the startup database. As industry leaders note, accessing extensive information is crucial for navigating the competitive landscape. For example, Michael Burtov states that approximately 90% of new businesses fail before reaching the venture capital phase, highlighting the necessity for thorough market research and data analysis. Moreover, the average cost of launching a business stands at $40,000 in the initial year, emphasizing the financial considerations for new ventures. By leveraging entrepreneurial information sources, stakeholders can enhance their strategic planning and increase their chances of success in a challenging environment.
Explain the Importance of Startup Databases in Market Research
Startup databases serve as vital tools in industry research by providing access to essential data that can significantly influence business strategies. These systems allow companies to:
- Identify emerging trends
- Evaluate competitive dynamics
- Discover potential investment opportunities
For instance, a new information system can aid enterprises in pinpointing innovative firms within their sector, thereby enabling them to stay ahead of industry shifts. Additionally, these data collections facilitate the examination of consumer behavior and preferences, which is essential for tailoring products and services to meet market demand. By leveraging insights gained from entrepreneurial information sources, organizations can make data-informed decisions that enhance their market position and drive growth.
How can your organization harness these insights to improve its strategic approach?
Trace the Evolution of Startup Databases: From Concept to Necessity
The development of new business information systems over the last several decades has been extraordinary. Initially, information about new businesses was scattered across various platforms, making it challenging for investors and entrepreneurs to obtain thorough insights. However, the advent of digital technology and the growing emphasis on data-driven decision-making highlighted the necessity for a startup database as a centralized repository. Today, the startup database, which includes over 3.7 million startups and companies worldwide, serves as an essential resource that consolidates extensive information. This enables users to conduct in-depth market analyses and discover growth opportunities.
This shift underscores a significant trend in the business landscape, where data is increasingly viewed as a crucial asset for achieving success. Statistics show that companies using data-informed decision-making are 5-6% more productive than their rivals. This highlights the concrete advantages of employing these data resources. Additionally, with platforms such as Crunchbase featuring over 75 million users in 2025, the dependence on these resources is clear.
As the entrepreneurial environment continues to progress, especially in 2023—which emphasizes resilience and adaptability—the role of startup databases in enabling informed choices and strategic planning grows increasingly vital. How can you leverage these insights in your own business strategy? The implications are clear: harnessing the power of data can lead to significant competitive advantages.
Identify Key Features of Effective Startup Databases
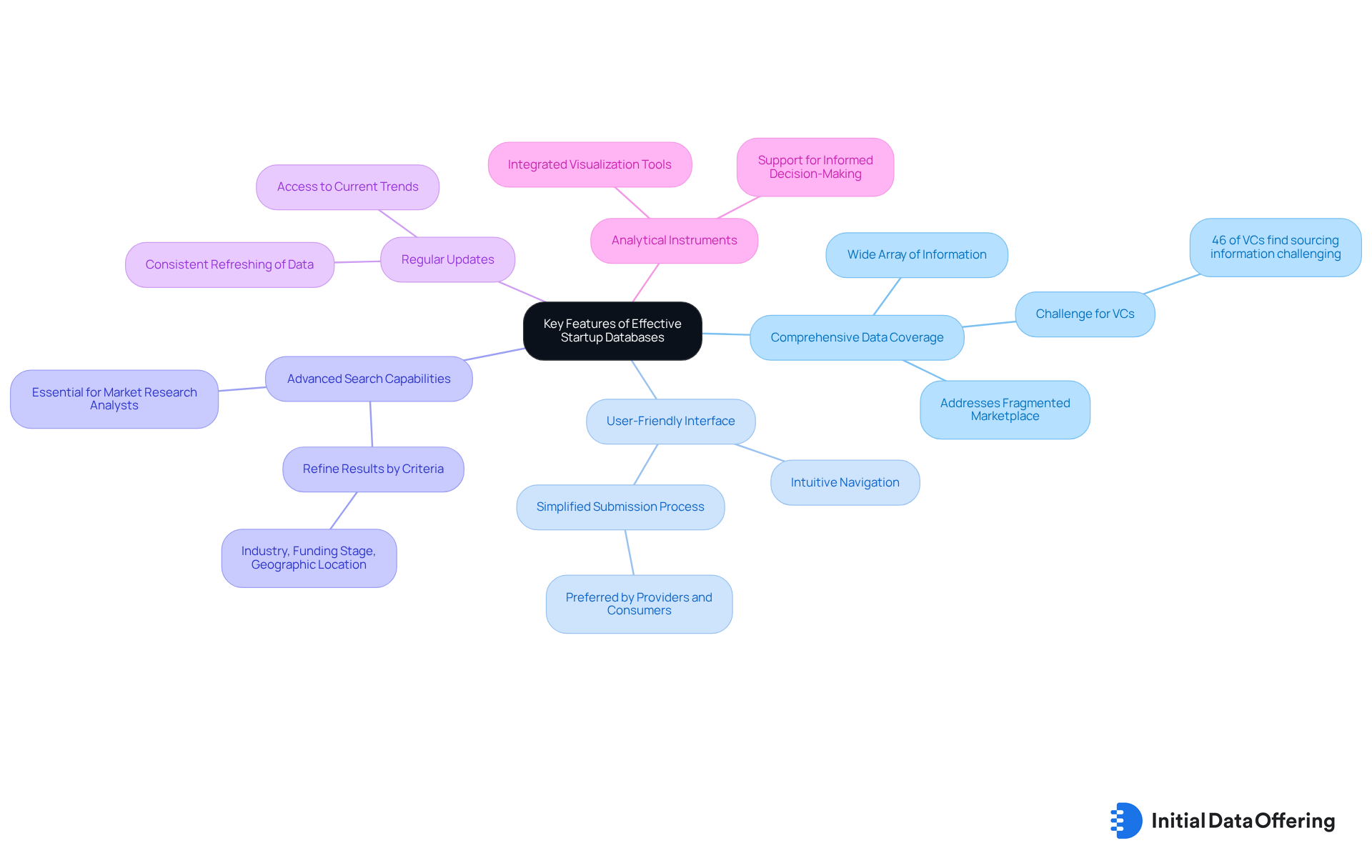
Effective startup databases possess several key features that significantly enhance their utility for users.
-
Comprehensive Data Coverage: A robust startup database should include a wide array of information, such as funding rounds, market segments, and performance metrics. This comprehensive coverage is essential, as 46% of analytics-driven VCs indicate that locating the appropriate information sources is a considerable challenge. The fragmented nature of the information marketplace further emphasizes the necessity for comprehensive coverage, ensuring that valuable datasets are easily accessible.
-
User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive interface is essential, allowing users to navigate the system effortlessly and access the information they need without unnecessary complexity. This ease of use is a primary factor that positions platforms like Initial Information Offering (IDO) as preferred choices for both providers and consumers, particularly due to IDO's user-friendly submission process that simplifies dataset listing.
-
Advanced Search Capabilities: Efficient information systems provide robust search functions that allow users to refine results according to specific criteria, such as industry, funding stage, or geographic location. This capability is essential for market research analysts who need to identify pertinent information swiftly from the startup database.
-
Regular Updates: To stay pertinent, startup information systems must be consistently refreshed with the latest details. With new collections listed daily, platforms like IDO ensure users have access to current trends and insights, which is essential for informed decision-making.
-
Analytical Instruments: Numerous efficient repositories offer integrated analytical instruments that enable users to visualize trends and produce insights. For example, IDO provides numerous analytical features that aid in informed decision-making, enabling users to utilize information effectively in their strategic planning.
These features collectively enhance the value of startup databases, making them indispensable resources for market research and strategic planning. As the landscape of startups evolves, the importance of comprehensive data coverage and user-friendly design cannot be overstated.
Conclusion
The startup database serves as a pivotal element in today’s business environment, functioning as a centralized repository that consolidates essential information about emerging companies. This extensive resource not only aids investors and entrepreneurs in making informed decisions but also enhances strategic planning by offering insights into market trends, competitive dynamics, and potential investment opportunities.
Key aspects of startup databases have been underscored throughout this discussion. They play a critical role in facilitating market research, evolving from fragmented information sources into indispensable tools for data-driven decision-making. Essential features such as comprehensive data coverage, user-friendly interfaces, advanced search capabilities, regular updates, and integrated analytical instruments significantly contribute to their effectiveness. These characteristics empower users to adeptly navigate the complexities of the entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Harnessing the power of startup databases can yield substantial competitive advantages in a rapidly changing market. Organizations are encouraged to utilize these insights for strategic growth and to remain agile in their approaches. As the significance of data within startup ecosystems continues to escalate, embracing these resources will be essential for overcoming challenges and seizing opportunities in the business landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a startup database?
A startup database is an organized collection that compiles comprehensive details about new businesses, including information on their founding teams, funding history, product offerings, and industry segments.
Who benefits from using a startup database?
Investors, entrepreneurs, and researchers benefit from using a startup database as it provides access to valuable information that can guide decision-making and strategic planning.
What are the primary functions of a startup database?
The primary functions of a startup database include information storage, retrieval, and analysis, which help users recognize trends, evaluate market opportunities, and assess competitive environments.
How do startup databases consolidate information?
Startup databases consolidate information from multiple sources to offer an extensive perspective of the entrepreneurial ecosystem, facilitating connections between new ventures and potential investors or collaborators.
What is the scale of data available in startup databases?
The size of startup databases can vary significantly, with some encompassing thousands of records. For example, there are over 82,000 new businesses in the U.S., highlighting the vast amount of data available for analysis.
Can you name examples of efficient business information systems?
Examples of efficient business information systems include Crunchbase and PitchBook, which provide organized data that empowers investors and entrepreneurs to make informed choices.
What insights do platforms like Crunchbase and PitchBook provide?
These platforms provide insights into funding rounds, valuations, industry trends, and emerging technologies.
Why is the startup database significant for investors and entrepreneurs?
The startup database is significant as it serves as an essential tool for investors seeking promising opportunities and for entrepreneurs striving to understand industry dynamics.
What challenges do new businesses face according to industry leaders?
Industry leaders note that approximately 90% of new businesses fail before reaching the venture capital phase, underscoring the necessity for thorough market research and data analysis.
What is the average cost of launching a business in the initial year?
The average cost of launching a business stands at $40,000 in the initial year, highlighting the financial considerations for new ventures.