Understanding Boston Hedge Funds: Key Features and Trends

Understanding Boston Hedge Funds: Key Features and Trends
Overview
Boston hedge funds are distinguished by their diverse investment strategies, limited partnership structure, and a commitment to innovation and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors. These features collectively enhance their resilience and performance in the financial market. By focusing on these aspects, Boston hedge funds not only achieve strong returns but also integrate technology effectively. This positions them as significant players in the evolving investment landscape. Consequently, they present attractive options for investors who seek robust returns while adhering to responsible investment practices.
How can these characteristics influence your investment decisions?
Introduction
The hedge fund landscape in Boston presents a dynamic and multifaceted arena, featuring innovative strategies and evolving trends that shape investment opportunities. Investors seeking to navigate this complex market will find valuable insights into the unique characteristics of Boston hedge funds. These funds are distinguished by their diverse investment approaches, as well as the growing influence of technology and sustainability.
As the industry adapts to regulatory changes and market fluctuations, one must consider:
- Which strategies will truly stand the test of time?
- Which strategies will deliver robust returns?
This question invites further exploration into the resilience and adaptability of investment methodologies in this vibrant market.
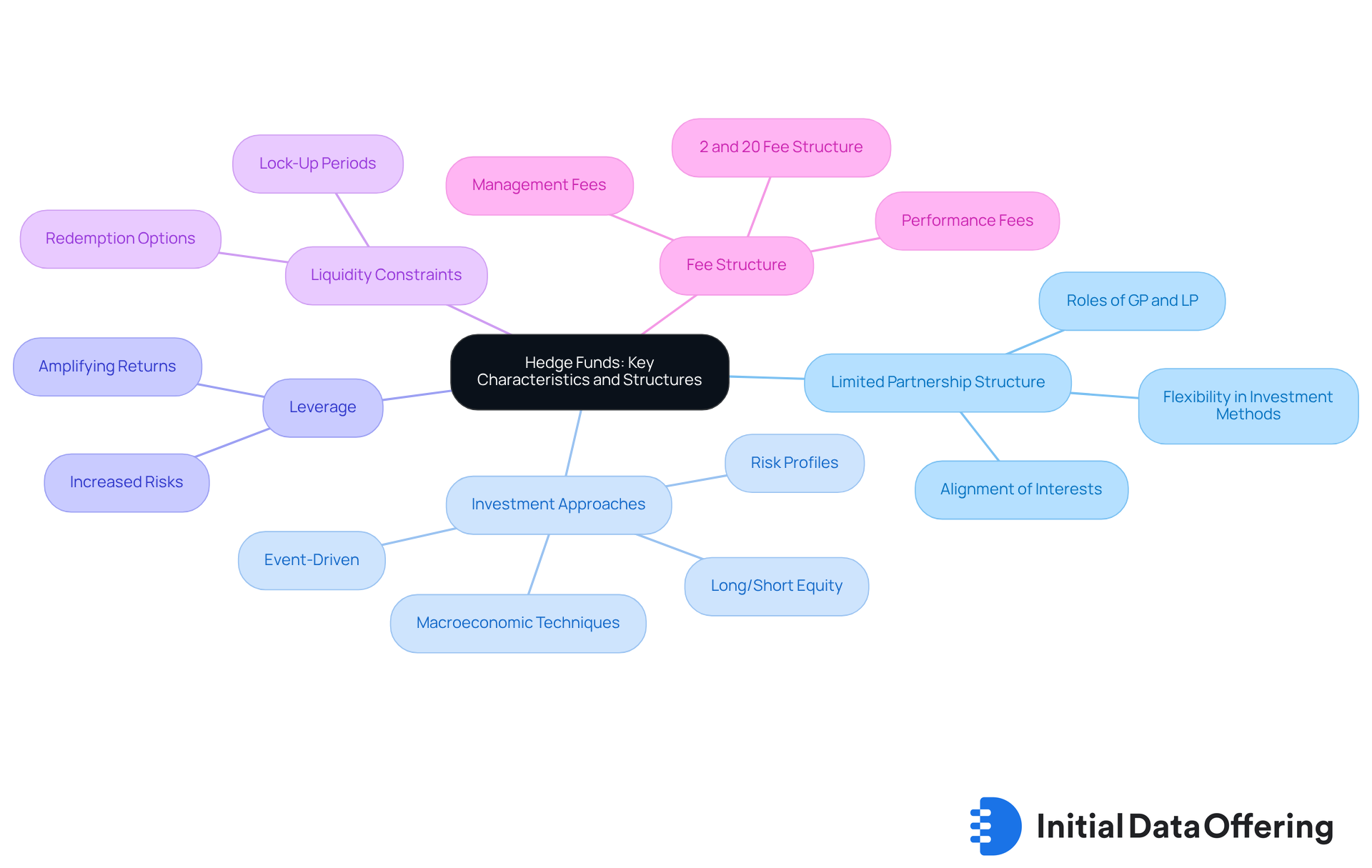
Define Hedge Funds: Key Characteristics and Structures
Hedge vehicles are combined resources that utilize various approaches to attain exceptional returns. The essential characteristics and structures that define them include:
- Limited Partnership Structure: The majority of hedge funds operate as limited partnerships, where the fund manager serves as the general partner (GP) and the investors are limited partners (LPs). This structure offers flexibility in investment methods and fee arrangements, enabling customized approaches to fulfill investor needs. Hedge fund managers often emphasize the benefits of this model, pointing out its capacity to promote a strong alignment of interests between GPs and LPs, ultimately boosting overall performance.
- Investment Approaches: Hedge pools utilize various methods, including long/short equity, event-driven, and macroeconomic techniques. Each approach has its own risk profile and potential for gains, allowing investors to choose options that align with their risk tolerance and financial objectives. Effective strategies for financial management often highlight a blend of stringent risk control and market understanding, as illustrated in case studies like 'The Role of Emotional Intelligence in Trading.'
- Leverage: Numerous hedge groups utilize leverage to enhance their financial positions, significantly amplifying returns. However, this also increases the associated risks, making it crucial for investors to understand the implications of leverage in their investment decisions.
- Liquidity Constraints: Hedge vehicles often impose lock-up periods during which investors cannot withdraw their capital, resulting in lower liquidity compared to traditional mutual investment schemes. Typically, investors can on a monthly or quarterly basis after an initial lock-up period, usually lasting one year. This structure is designed to stabilize the capital base, allowing managers to execute long-term strategies without the pressure of sudden withdrawals.
- Fee Structure: The traditional fee arrangement for hedge vehicles is frequently called '2 and 20', which comprises a 2% management charge and a 20% performance fee on gains. Performance fees typically account for 10% to 20% of any total profits produced by the investment vehicle in a specific year. This encourages asset managers to maximize returns, aligning their interests with those of the investors.
Grasping these traits is essential for investors considering alternative investment options as part of their portfolio. In 2025, around 80% of investment partnerships continue to employ the limited partnership structure, indicating its efficiency in overseeing investor relationships and operations.
Explore Boston's Hedge Fund Landscape: Trends and Unique Features
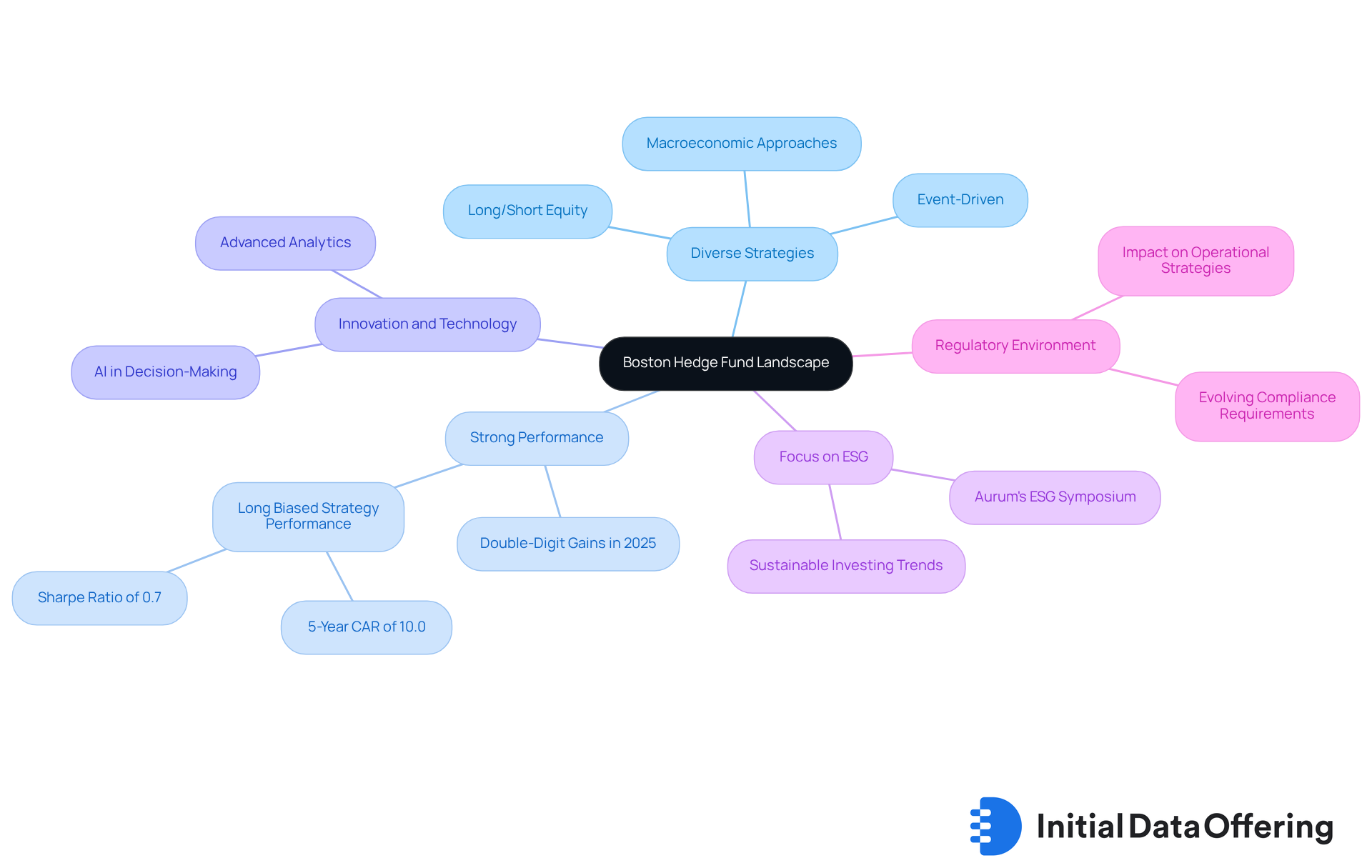
Boston hedge funds contribute to a vibrant industry, characterized by several key trends and unique features that are essential for understanding its dynamics.
Boston hedge funds utilize diverse strategies, such as long/short equity, event-driven, and macroeconomic approaches. This diversity allows firms to adapt to changing market conditions effectively, enhancing their resilience in various economic climates.
- Strong performance: Recent reports indicate that Boston hedge funds have demonstrated resilience and strong results. Many portfolios, particularly those concentrated on equity strategies, posted double-digit gains in 2025. This performance underscores the potential for robust returns offered by Boston hedge funds.
- Innovation and Technology: The incorporation of technology in financial processes is becoming increasingly common. Numerous Boston asset management firms utilize advanced analytics and AI to improve decision-making, providing a competitive edge in the fast-evolving financial landscape.
- Focus on ESG: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are gaining traction among Boston hedge funds. This shift reflects a broader trend in the investment community towards , highlighting the importance of ethical considerations in investment strategies.
- Regulatory Environment: The regulatory landscape for investment vehicles in Boston is evolving. Increased scrutiny and compliance requirements can impact operational strategies, making it crucial for firms to stay informed and adaptable.
These trends demonstrate the dynamic character of Boston hedge funds' investment sector, emphasizing both the opportunities and challenges investors might encounter. How can these insights inform your investment strategies moving forward?
Key Players in Boston's Hedge Fund Market
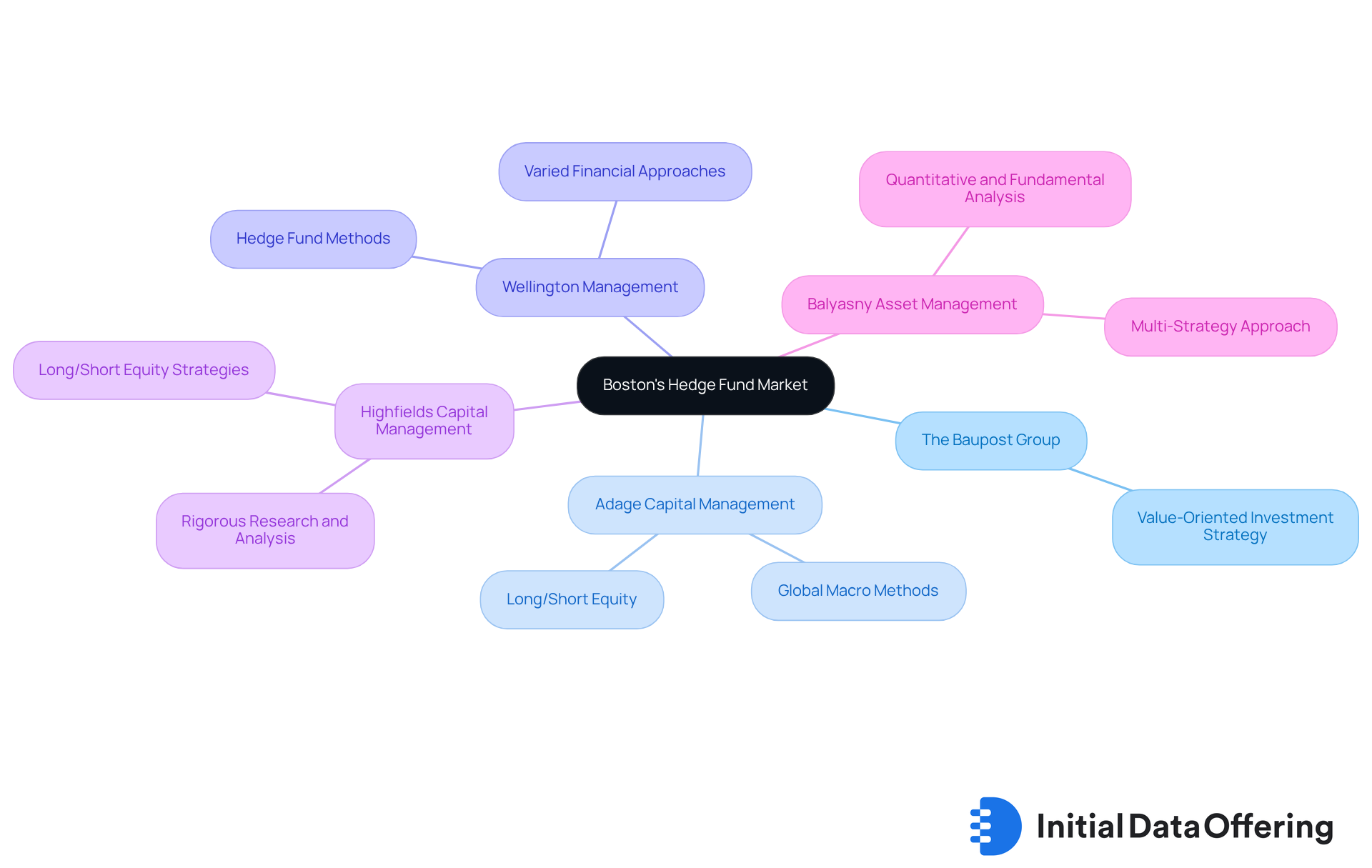
Boston's investment management market features several prominent firms that have established themselves as industry leaders. Understanding these key players can provide insights into the market's dynamics and investment strategies.
- The Baupost Group stands out with its value-oriented investment strategy, consistently delivering strong returns. As one of the largest Boston hedge funds, it exemplifies how a focused approach can yield significant advantages in capital growth.
- Adage Capital Management employs a multi-faceted strategy, concentrating on long/short equity and global macro methods. This versatility not only enhances its market presence but also offers investors a robust framework for diverse investment opportunities.
- Wellington Management is recognized for its varied financial approaches, serving as a prominent asset manager that also implements hedge fund methods. Its commitment to institutional investors highlights the importance of tailored investment solutions in achieving financial goals.
- Highfields Capital Management focuses on long/short equity strategies, backed by rigorous research and analysis. This dedication to thorough investigation ensures that investment decisions are well-informed, providing a competitive edge in the market.
- Balyasny Asset Management is noted for its multi-strategy approach, merging quantitative and fundamental analysis. This integration allows for informed financial decisions, illustrating the benefits of combining different analytical perspectives.
Boston hedge funds not only shape the local financial landscape but also influence broader market trends and capital allocation strategies. How might these insights inform your investment decisions or strategies in the current market?
Investment Strategies Employed by Boston Hedge Funds
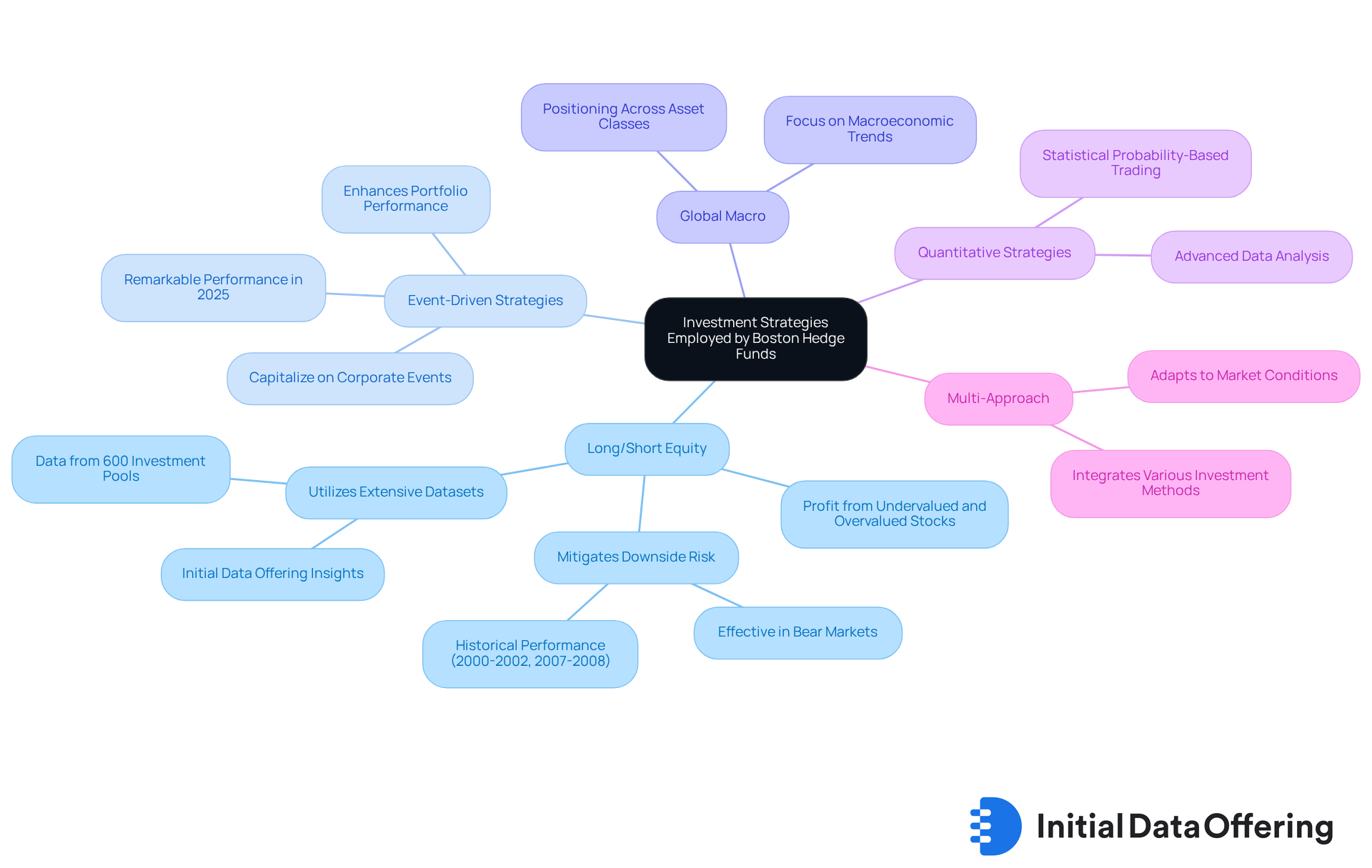
Boston hedge funds utilize a diverse array of investment strategies tailored to navigate the complexities of the market. Each approach is designed to fulfill specific financial goals, and understanding these methods can greatly inform investment decisions. Key strategies include:
- Long/Short Equity: This strategy entails buying undervalued stocks while simultaneously shorting overvalued ones, allowing funds to profit regardless of market trends. Historically, long-short equity strategies have proven effective in mitigating downside risk during bear markets, with notable performance during downturns such as those in 2000-2002 and 2007-2008. Hedge vehicles leverage extensive datasets, including those from Initial Data Offering, which provide long and short position information across global equities and swaps. This proprietary dataset, derived from over 600 investment pools representing $700 billion in GMV, offers insights into 15,000 equities and includes historical data dating back to February 2017. Such comprehensive data enables nuanced market trend analysis and positioning.
- Event-Driven Strategies: These investment vehicles seek to capitalize on specific corporate events, such as mergers, acquisitions, or restructurings, aiming to profit from the resulting price changes. In 2025, the performance of event-driven hedge funds has been particularly remarkable, with analysts noting their ability to generate consistent returns amidst market volatility. For instance, the AIP Hedge Fund team emphasizes that incorporating event-driven strategies into a diversified portfolio can enhance overall performance by seizing unique market opportunities. Notably, alternative asset classes are projected to reach $5 trillion by 2029, indicating a growing interest in these strategies.
- Global Macro: This strategy focuses on macroeconomic trends and geopolitical events, allowing capital to be positioned across various asset classes. By analyzing global economic indicators, investment firms can make informed decisions that align with broader market movements.
- Quantitative Strategies: Many Boston hedge organizations utilize advanced quantitative models to identify trading opportunities. These approaches rely on rigorous data analysis and algorithms, enabling firms to execute trades based on statistical probabilities rather than subjective judgments.
- Multi-Approach: Certain portfolios adopt a multi-approach model, integrating various investment methods to diversify risk and enhance returns. This adaptability allows managers to modify their strategies in response to evolving market conditions, optimizing overall portfolio performance.
Understanding these strategies equips investors with the knowledge necessary to of investing in Boston hedge funds, particularly in a rapidly changing financial landscape.
Conclusion
Boston hedge funds constitute a dynamic sector within the investment landscape, marked by their distinctive structures and diverse strategies. Understanding the intricacies of hedge funds—such as their limited partnership model, various investment approaches, and fee structures—is essential for investors aiming to navigate this complex market. The capacity to leverage different strategies, including long/short equity and event-driven methods, enables these funds to adapt to shifting market conditions, thereby presenting opportunities for substantial returns.
Key trends within Boston's hedge fund market further illustrate its vibrancy. The integration of technology and an increasing focus on ESG factors signify a shift towards more innovative and responsible investing practices. Moreover, the performance of leading firms like The Baupost Group and Wellington Management highlights the potential for strong returns in this competitive environment. By staying informed about these trends and the strategies employed by key players, investors can make more informed decisions that align with their financial objectives.
As the hedge fund landscape continues to evolve, it becomes increasingly important for investors to contemplate how these insights can shape their investment strategies. Embracing the unique features and trends of Boston hedge funds not only enhances understanding but also empowers investors to capitalize on emerging opportunities. Thoughtful engagement with this sector can lead to more strategic investment choices, ultimately contributing to long-term financial success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are hedge funds?
Hedge funds are pooled investment vehicles that utilize various strategies to achieve exceptional returns, often employing a combination of investment approaches and financial techniques.
What is the typical structure of a hedge fund?
Most hedge funds operate as limited partnerships, with the fund manager acting as the general partner (GP) and the investors as limited partners (LPs). This structure allows for flexibility in investment methods and fee arrangements.
How do hedge funds align the interests of managers and investors?
The limited partnership structure promotes a strong alignment of interests between general partners and limited partners, which can enhance overall performance.
What types of investment approaches do hedge funds use?
Hedge funds utilize various methods, including long/short equity, event-driven strategies, and macroeconomic techniques, each with distinct risk profiles and potential for gains.
What is leverage in the context of hedge funds?
Leverage refers to the use of borrowed capital to amplify financial positions, which can enhance returns but also increases associated risks for investors.
What are the liquidity constraints associated with hedge funds?
Hedge funds often have lock-up periods during which investors cannot withdraw their capital, resulting in lower liquidity compared to traditional mutual funds. Investors typically can redeem shares on a monthly or quarterly basis after an initial lock-up period, which usually lasts one year.
How is the fee structure typically organized for hedge funds?
The traditional fee arrangement for hedge funds is often referred to as "2 and 20," consisting of a 2% management fee and a 20% performance fee on gains, which incentivizes managers to maximize returns.
Why is it important to understand the characteristics of hedge funds?
Understanding the characteristics of hedge funds is crucial for investors considering alternative investment options, as these traits can significantly impact investment decisions and portfolio management.