Mastering Array Contains in Snowflake: A Step-by-Step Guide

Mastering Array Contains in Snowflake: A Step-by-Step Guide
Overview
This article serves as a comprehensive guide to mastering the ARRAY_CONTAINS function in Snowflake. It details the function's syntax, application, and real-world scenarios pertinent to data analysis. By emphasizing its utility in efficiently filtering datasets based on specific criteria, the article illustrates how this function can significantly enhance data retrieval and analytical capabilities.
The ARRAY_CONTAINS function offers various features that allow users to filter datasets effectively. One of its primary advantages is the ability to quickly identify customer preferences, which can lead to more targeted marketing strategies. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in inventory management, ensuring that businesses maintain optimal stock levels based on real-time data analysis.
Consider how the ARRAY_CONTAINS function could transform your data analysis processes. By implementing this function, you can streamline your workflows and improve decision-making efficiency. Practical examples, such as analyzing customer behavior or managing inventory, highlight its significance in the realm of data analytics.
In conclusion, mastering the ARRAY_CONTAINS function not only enhances your analytical capabilities but also empowers you to make more informed decisions based on accurate data insights. Embracing this tool can lead to substantial benefits for your organization, ultimately driving success in a data-driven landscape.
Introduction
Mastering data management in Snowflake requires a solid grasp of its powerful capabilities, particularly the 'Array Contains' function. This function serves as a feature that enhances data analysis by allowing users to efficiently query and manipulate array data. The advantages of utilizing this function are significant; it enables users to streamline their data processes and uncover insights that may otherwise remain hidden. As a result, the benefits extend beyond mere functionality, empowering users to make informed decisions based on comprehensive data analysis.
However, with great power comes the challenge of effective usage—what best practices can users adopt to avoid common pitfalls while maximizing the utility of arrays in Snowflake?
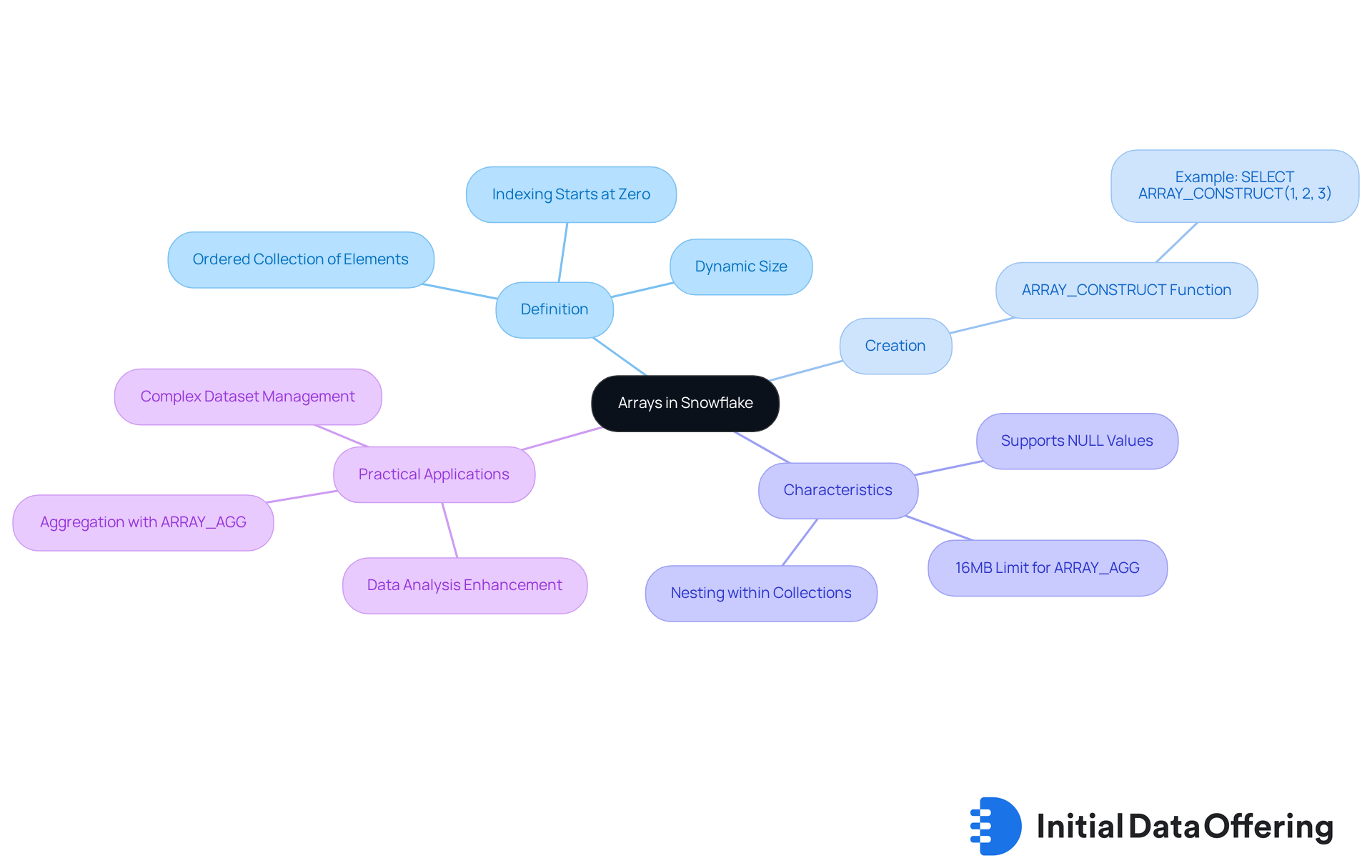
Understand Arrays in Snowflake
In Snowflake, a list serves as an ordered collection of elements, capable of holding multiple values of the same data type. These collections are dynamic, allowing them to expand or contract in size as necessary. Each component within a collection is accessible via its index, which starts at zero. For instance, creating a collection with the values [1, 2, 3] allows access to the first element using collection[0], which returns 1. Mastering the creation and handling of collections is essential for effectively employing the method where the array contains snowflake.
To generate a collection in Snowflake, the ARRAY_CONSTRUCT function is utilized. For example:
SELECT ARRAY_CONSTRUCT(1, 2, 3) AS my_array;
This SQL command generates an array containing the values 1, 2, and 3. Notably, collections can also include NULL values and can be nested within other collections or structures, offering considerable flexibility in information representation. This versatility is particularly advantageous in analysis, where organizations increasingly rely on collections to manage complex datasets and enhance their analytical capabilities.
According to industry insights, a significant number of organizations incorporate structures into their information analysis processes, underscoring their importance in contemporary information management. Moreover, the ARRAY_AGG method in Snowflake facilitates the aggregation of information into lists. However, it is crucial to recognize the 16MB limit for a single invocation, which can impact performance and information management. Practical applications of the ARRAY_CONSTRUCT capability demonstrate that the array contains snowflake, which illustrates its effectiveness in various analytical scenarios and how organizations leverage collections to optimize their data operations.
Explore the 'Array Contains' Function: Syntax and Parameters
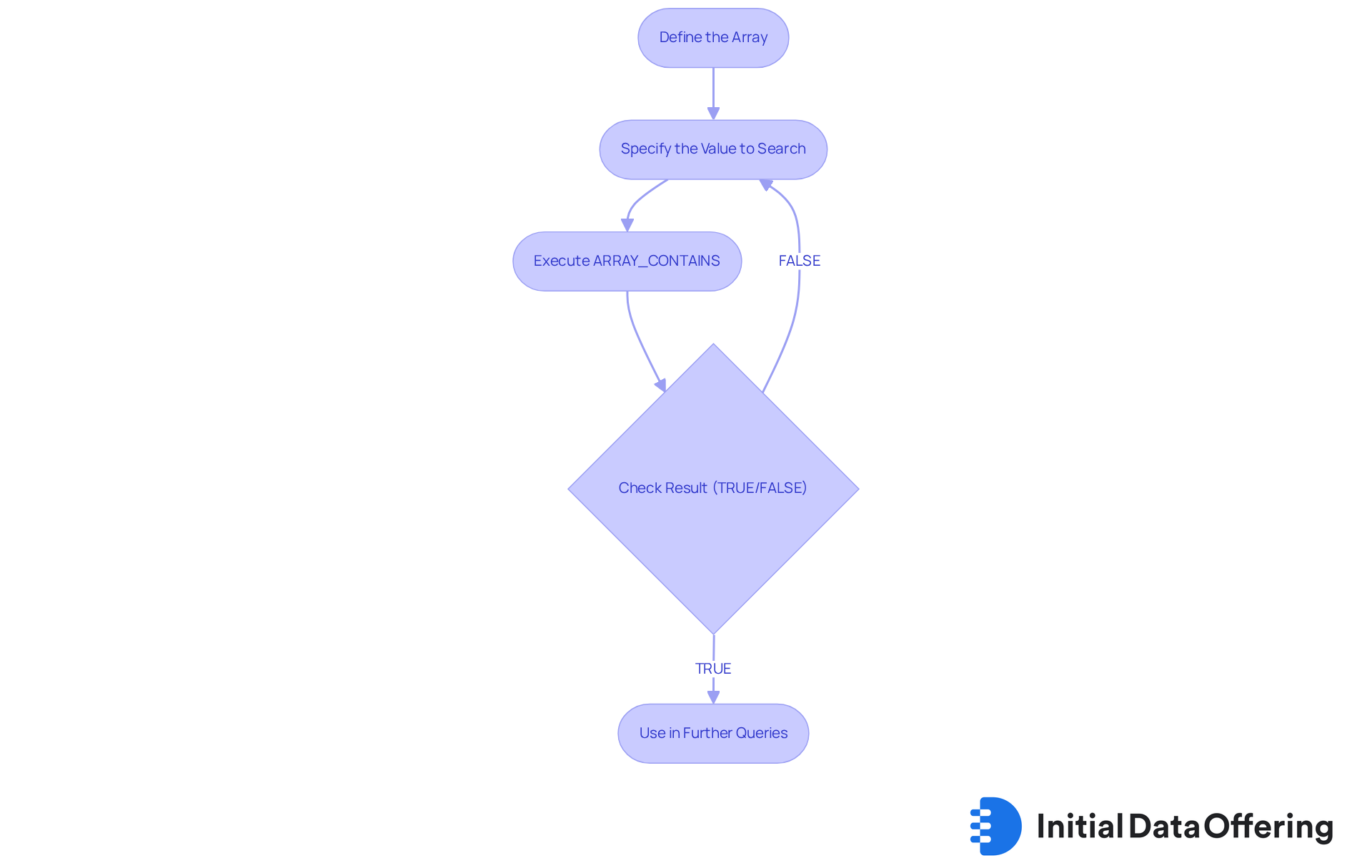
The ARRAY_CONTAINS method in Snowflake is crucial for determining whether the array contains snowflake. Its syntax is straightforward:
ARRAY_CONTAINS(array, value_expr)
- array: This parameter signifies the array you wish to search through.
- value_expr: This is the value you are seeking within the list, which can be of any comparable data type, including strings, numbers, and complex data structures.
When executed, this procedure returns TRUE if the specified value exists in the collection and FALSE if it does not. Notably, if either the value or the list is NULL, the method will return NULL.
For example, consider the following array:
SET my_array = ARRAY_CONSTRUCT('apple', 'banana', 'cherry');
To check for the presence of 'banana', you would execute:
SELECT ARRAY_CONTAINS(my_array, 'banana') AS contains_banana;
This query will yield TRUE, confirming that 'banana' is indeed part of the array.
The ARRAY_CONTAINS method is frequently employed in queries, particularly to check if the array contains snowflake for refining datasets according to specific criteria. Data scientists recognize its significance in enhancing data analysis capabilities, allowing for efficient retrieval of relevant information. Have you considered how this utility could aid in recognizing trending products or sorting user profiles based on interests? Its versatility is evident across various analytical contexts.
Moreover, this function can be combined with other SQL operations, such as COUNT or JOIN, to perform more complex tasks. For instance, you can utilize it within a JOIN clause to filter results based on array values from multiple tables. Performance factors are also crucial; indexing columns that are frequently searched with this method can significantly enhance query efficiency. Understanding these aspects will empower users to maximize the potential of this feature in their data analysis endeavors.
Apply 'Array Contains' in Real-World Scenarios
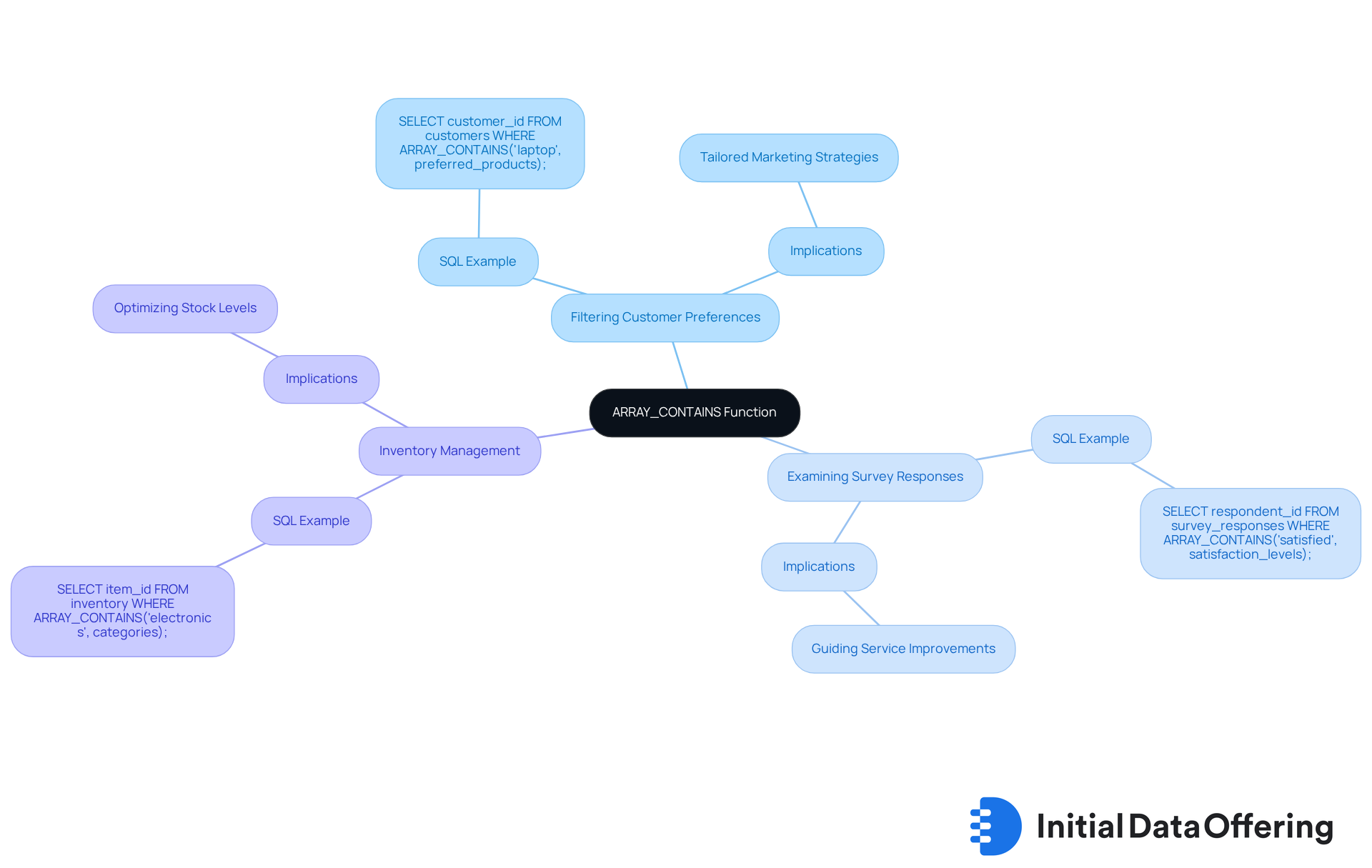
The function proves invaluable in various real-world scenarios, particularly for filtering datasets based on specific criteria. This capability offers numerous practical applications that enhance data analysis and retrieval.
Filtering Customer Preferences: In a customer database where favored products are stored as a list, a function can identify customers supporting a specific product. For instance:
SELECT customer_id
FROM customers
WHERE ARRAY_CONTAINS('laptop', preferred_products);
This query retrieves all customers who have 'laptop' listed among their preferred products. By targeting specific preferences, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies effectively.
Examining Survey Responses: When analyzing survey data where participants choose several options, their responses can be stored in a list. To find those who selected a particular option, you might use:
SELECT respondent_id
FROM survey_responses
WHERE ARRAY_CONTAINS('satisfied', satisfaction_levels);
This query returns all respondents who indicated they were 'satisfied'. Understanding customer satisfaction levels can guide improvements in services or products.
Inventory Management: In an inventory table where items belong to multiple categories stored as an array, you can filter items by category. For example:
SELECT item_id
FROM inventory
WHERE ARRAY_CONTAINS('electronics', categories);
This query lists all items categorized as 'electronics'. Efficient inventory management is crucial for businesses to optimize stock levels and meet customer demands.
These examples emphasize how the ARRAY_CONTAINS procedure simplifies information retrieval and analysis, especially when the array contains snowflake, rendering it a vital resource for information professionals. By utilizing this feature, users can improve their capability to derive meaningful insights from complex datasets. Furthermore, as highlighted by Snowflake Specialists, 'The function that array contains snowflake offers a robust tool for filtering and aggregating information based on the presence of specific values within an array.' It is also important to be aware of common pitfalls, such as the excessive use of ARRAY_CONTAINS in unnecessary queries, which can complicate SQL statements. Understanding these aspects can significantly enhance the effectiveness of data analysis.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of arrays in Snowflake, particularly the ARRAY_CONTAINS function, is essential for efficient data management and analysis. This guide has illuminated the significance of arrays as dynamic collections that enhance analytical capabilities across various applications. Understanding how to create, manipulate, and query arrays empowers users to extract valuable insights from complex datasets.
Key insights discussed include the syntax and parameters of the ARRAY_CONTAINS function, alongside its practical applications in:
- Filtering customer preferences
- Analyzing survey responses
- Managing inventory
Each of these scenarios showcases how this function can streamline data retrieval processes, making it a vital tool for data professionals seeking to optimize their operations.
Incorporating the ARRAY_CONTAINS function into data analysis strategies not only improves retrieval efficiency but also enhances decision-making processes. As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven insights, mastering this functionality becomes crucial. Embracing the versatility of arrays in Snowflake can lead to more nuanced analyses and tailored solutions, ultimately driving better business outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an array in Snowflake?
An array in Snowflake is an ordered collection of elements that can hold multiple values of the same data type. Arrays are dynamic, meaning they can expand or contract in size as needed.
How can I access elements within an array in Snowflake?
Each element in an array can be accessed using its index, which starts at zero. For example, in an array created with the values [1, 2, 3], the first element can be accessed with collection[0], which returns 1.
How do I create an array in Snowflake?
You can create an array in Snowflake using the ARRAY_CONSTRUCT function. For example, the SQL command SELECT ARRAY_CONSTRUCT(1, 2, 3) AS my_array; generates an array containing the values 1, 2, and 3.
Can arrays in Snowflake contain NULL values?
Yes, arrays in Snowflake can include NULL values and can be nested within other collections or structures.
Why are arrays important for data analysis in organizations?
Arrays provide considerable flexibility in representing information, which is particularly advantageous in analysis. Organizations increasingly rely on collections to manage complex datasets and enhance their analytical capabilities.
What is the ARRAY_AGG method in Snowflake?
The ARRAY_AGG method in Snowflake is used to aggregate information into lists. However, it is important to note that there is a 16MB limit for a single invocation, which can affect performance and information management.
How do organizations leverage arrays in their data operations?
Organizations use the ARRAY_CONSTRUCT capability to optimize their data operations and effectively handle complex analytical scenarios, illustrating the effectiveness of arrays in managing data.