Master Geospatial Data Management for Market Insights

Master Geospatial Data Management for Market Insights
Overview
Geospatial data management is vital for organizations seeking to gain market insights. It enables the visualization and analysis of trends, patterns, and relationships linked to specific locations. This capability ultimately enhances decision-making and operational efficiency.
Effective geospatial data collection techniques and robust management strategies significantly improve an organization's ability to identify opportunities and optimize strategies. By integrating these data sources, organizations can achieve a competitive edge in the market.
How can your organization leverage geospatial data to enhance its decision-making processes? Consider the potential advantages of adopting these practices.
Introduction
Geospatial data has emerged as a powerful tool that enables organizations to unlock valuable insights tied to specific locations on Earth. This data is characterized by its ability to provide detailed geographic context, which enhances decision-making processes and operational optimization. By harnessing geospatial information, businesses can gain a competitive edge in the market, allowing for more informed strategies and targeted actions.
However, as the landscape of data management evolves, organizations face the challenge of effectively integrating and managing geospatial data alongside traditional datasets. How can businesses navigate these complexities to fully leverage the potential of geospatial data for strategic advantage? This question invites exploration into the methods and practices that can facilitate this integration, ultimately maximizing the benefits of geospatial insights.
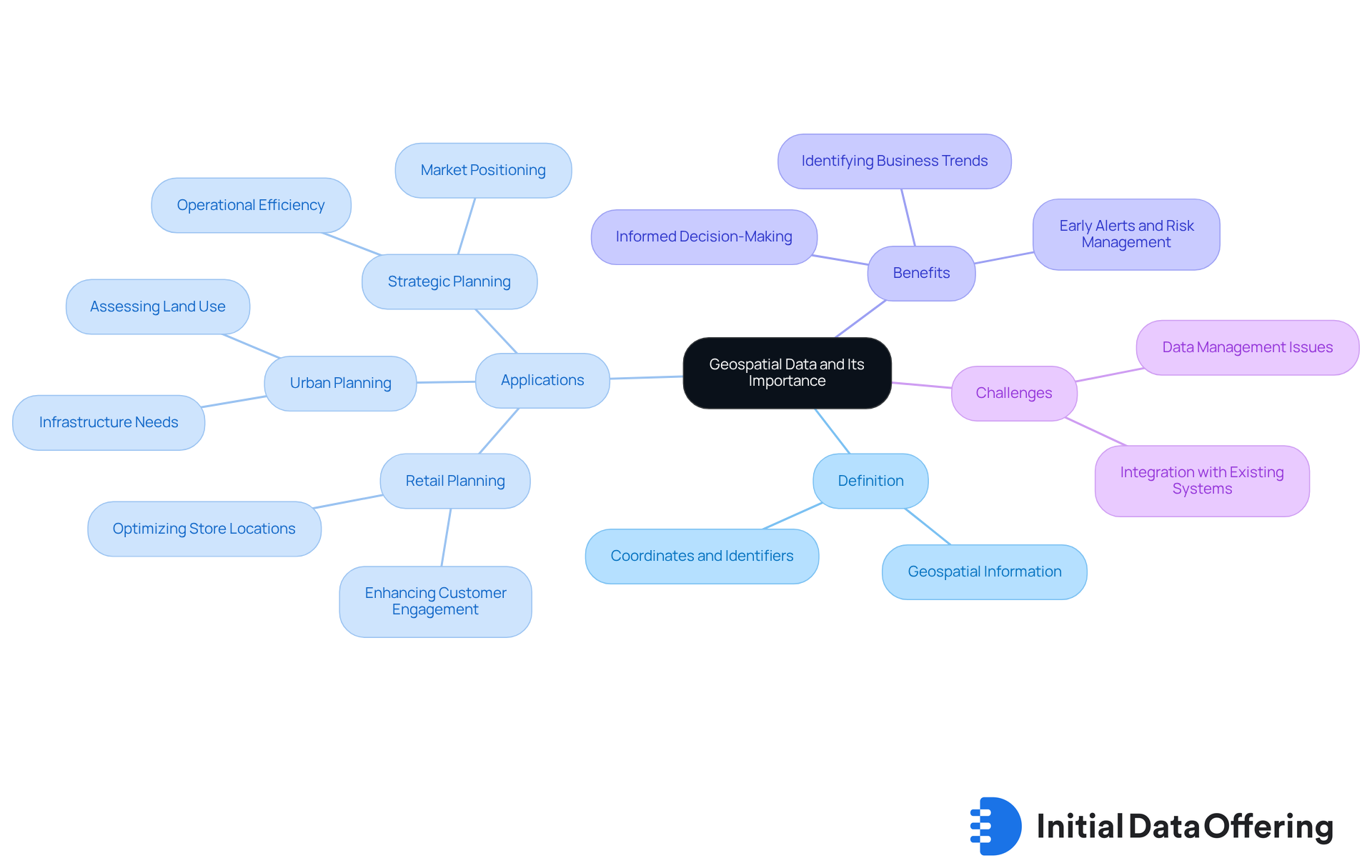
Define Geospatial Data and Its Importance
Geospatial information refers to details associated with specific locations on the Earth's surface, such as coordinates, addresses, and other identifiers. Its relevance is underscored by the context it provides to various datasets, which enables businesses to visualize trends, patterns, and relationships that are geographically significant. For example, retailers analyze foot traffic patterns to optimize store locations, thereby enhancing customer engagement and boosting sales. Similarly, urban planners leverage this information to assess land use and infrastructure needs, ensuring that development aligns with community requirements.
The integration of geospatial data management into strategic planning processes can greatly enhance operational efficiency. Organizations that effectively utilize this data can make informed decisions that enhance market positioning and provide a competitive edge. For instance, employing spatial analysis in retail planning allows companies to tailor their offerings to local demographics, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and potentially driving sales. Furthermore, expert insights indicate that spatial intelligence is crucial for identifying business trends that may otherwise remain hidden, revealing new opportunities and enhancing operational efficiency. As the demand for location-based insights continues to grow, the importance of geospatial data management in developing effective strategies becomes increasingly vital. Moreover, the use of spatial information can offer measurable benefits, such as facilitating early alerts and optimizing business processes, further highlighting its significance in strategic planning.
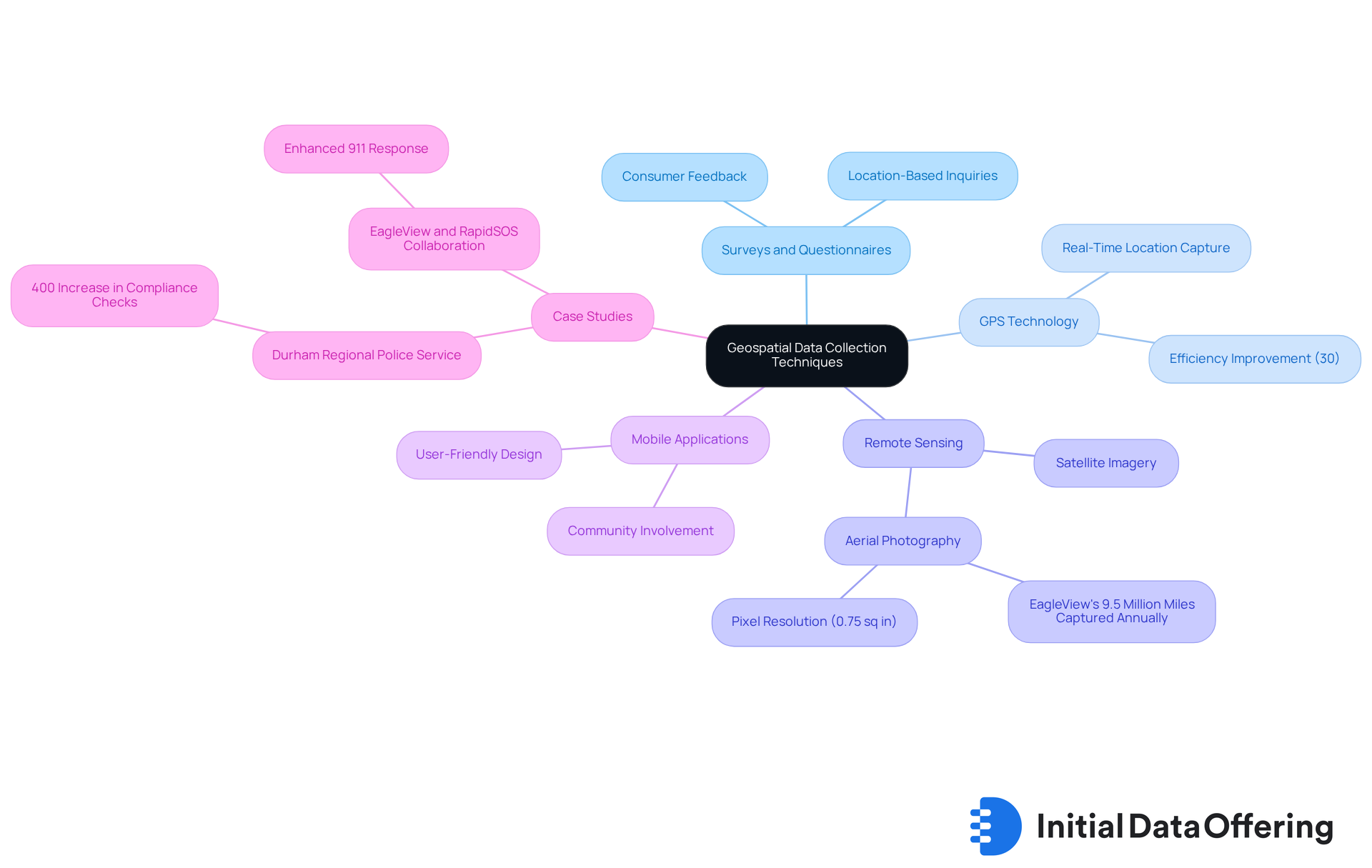
Implement Effective Geospatial Data Collection Techniques
To effectively gather information, organizations should adopt a multifaceted approach to geospatial data management that is tailored to their specific requirements. Key techniques include:
-
Surveys and Questionnaires: These tools implement location-based inquiries to gather direct feedback from consumers. This ensures the relevance of the information collected in geospatial data management, fostering a deeper understanding of audience needs.
-
GPS Technology: By utilizing GPS-enabled devices, organizations can capture precise location information in real-time. This significantly enhances accuracy, with research indicating that GPS technology can improve information gathering efficiency by as much as 30%. Such efficiency renders geospatial data management an essential resource for organizations aiming to make informed decisions.
-
Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photography are invaluable for gathering extensive spatial information. This enables thorough geospatial data management and analysis across vast regions. For instance, EagleView captures over 9.5 million miles of aerial imagery annually, with each pixel representing 0.75 square inches on the ground. Such detailed insights are beneficial for various applications in geospatial data management.
-
Mobile Applications: Developing user-friendly apps allows individuals to voluntarily share their location information. This not only enhances the dataset but also promotes community involvement, thus enriching the overall data collection process.
-
Case Studies and Real-World Applications: A notable example is the Durham Regional Police Service, which increased compliance checks by over 400% with the GIS-powered Bail Compliance Dashboard. This demonstrates the effectiveness of GIS technology in practical applications.
By utilizing these methods and being aware of common mistakes in geospatial data management, businesses can ensure the collection of high-quality spatial insights that accurately represent their target markets. This ultimately promotes informed decision-making and strategic planning. As Joe Oddi from EagleView stated, "By integrating EagleView imagery with RapidSOS Premium, we help public safety professionals respond in the most accurate and efficient way to citizens in distress.
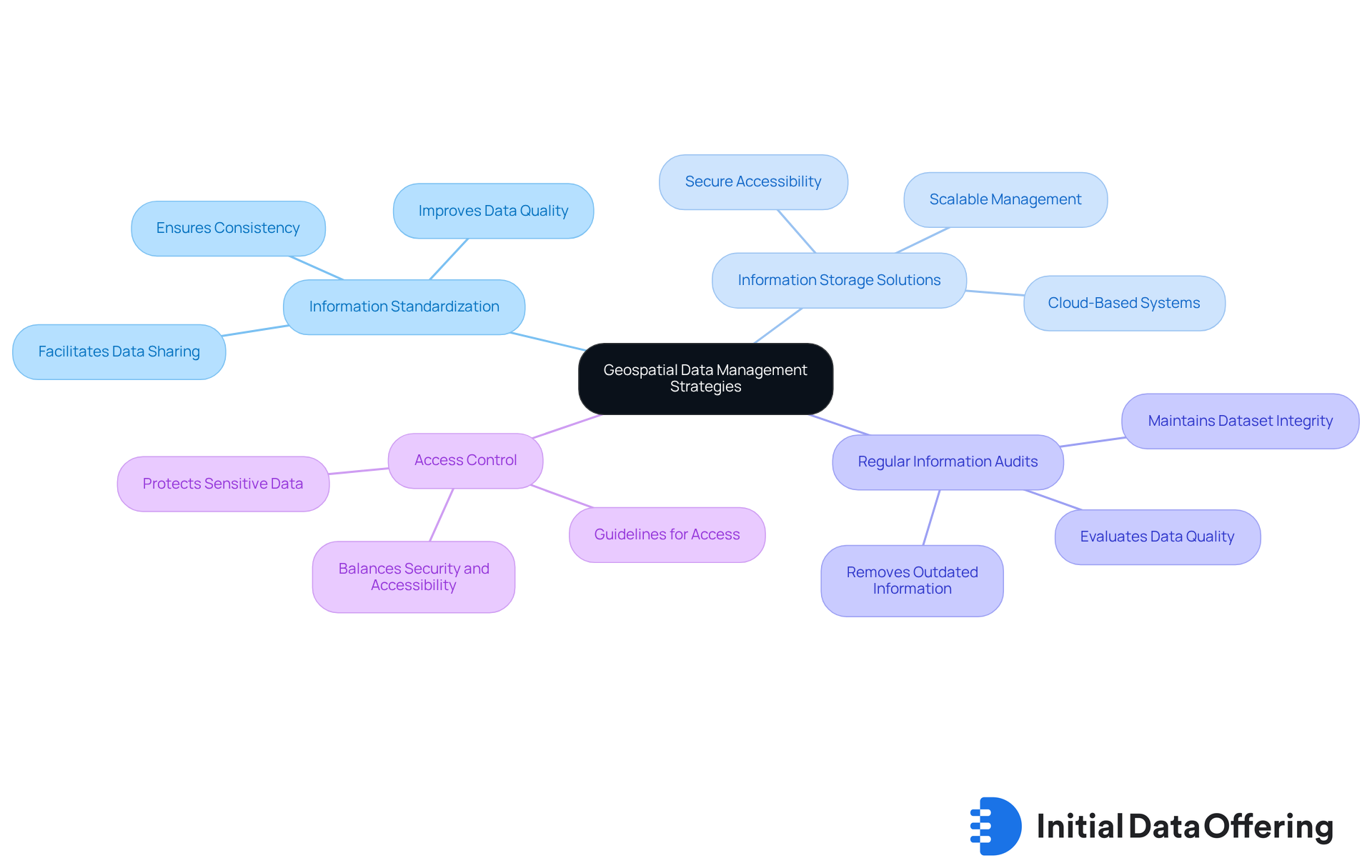
Establish Robust Geospatial Data Management Strategies
Establishing robust strategies for geospatial data management involves several key practices that can significantly enhance organizational efficiency and decision-making.
-
Information Standardization is essential; implementing standardized formats for information entry ensures consistency across datasets. This consistency not only improves data quality but also facilitates easier data sharing and collaboration among teams.
-
Information Storage Solutions play a critical role as well. Utilizing cloud-based storage systems allows for scalable and secure information management, enabling organizations to adapt to growing data needs while maintaining accessibility and security.
-
Conducting Regular Information Audits is another vital practice. Periodic assessments evaluate the quality and relevance of data, ensuring that outdated or flawed information is promptly removed. This proactive approach helps maintain the integrity of datasets, ultimately leading to better analysis outcomes.
-
Lastly, establishing Access Control protocols is crucial. Clear guidelines for information access protect sensitive details while allowing authorized personnel to retrieve necessary information efficiently. This balance of security and accessibility is key to effective data management.
By adhering to these strategies, organizations can uphold a high level of information integrity and usability in geospatial data management, enabling improved analysis and decision-making. How might these practices be integrated into your current data management strategies?
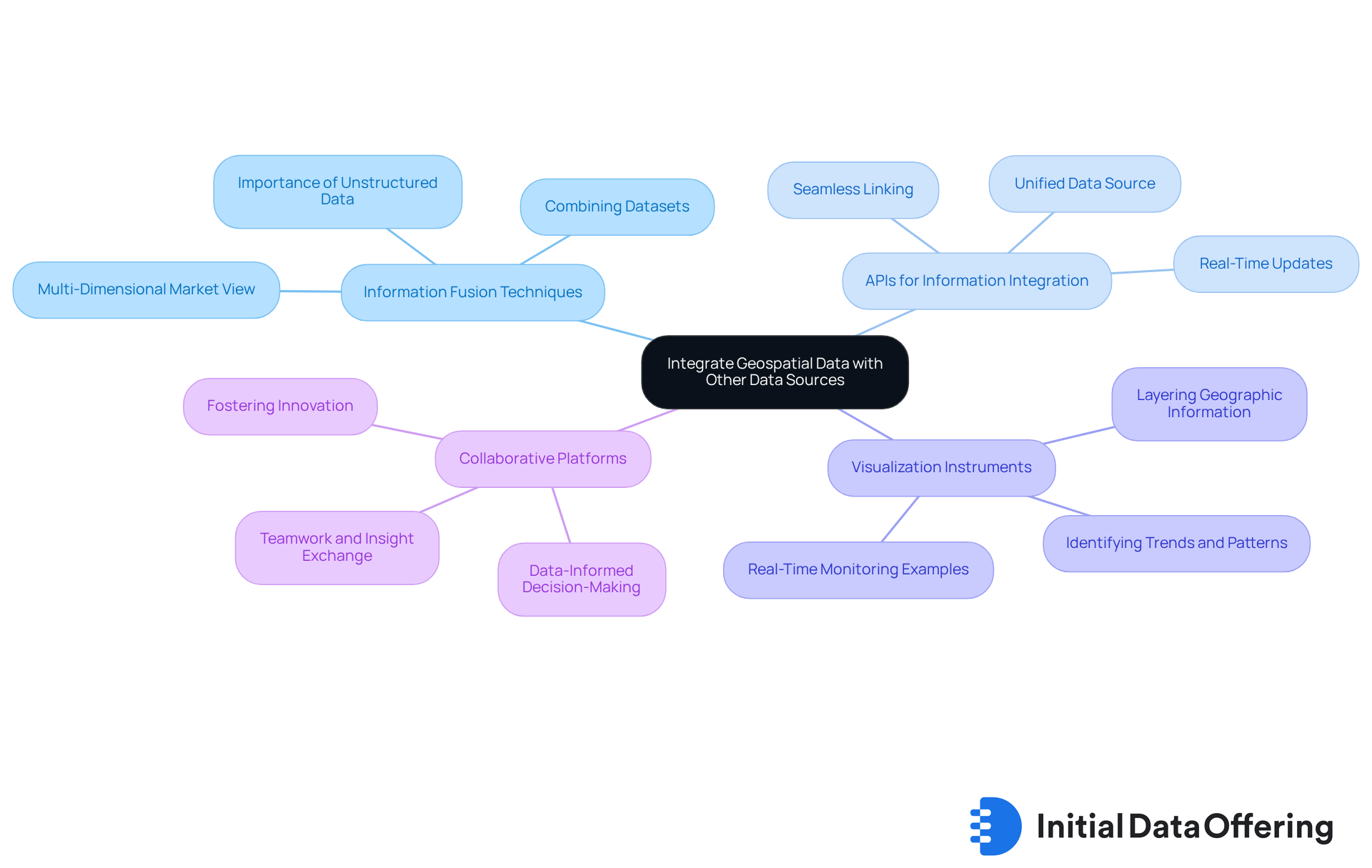
Integrate Geospatial Data with Other Data Sources
Incorporating spatial information with additional sources significantly enhances analytical capabilities, enabling organizations to derive deeper insights. To achieve effective integration, consider the following best practices:
-
Information Fusion Techniques: Implementing information fusion methods allows for the combination of demographic, economic, and behavioral datasets with geospatial data management. This approach creates a multi-dimensional view of the market, facilitating more nuanced analysis and informed decision-making. Current trends indicate that the integration of unstructured information into GIS is increasingly important, as it fosters intelligent decision-making and strengthens the overall analytical framework.
-
APIs for Information Integration: Utilizing Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) can seamlessly link spatial information with various databases. This ensures real-time updates and accessibility, which are crucial for timely insights that drive strategic initiatives. As Stephen Griffin, a senior account executive at LightBox, noted, "It is essential that project managers, field representatives, and various departments operate from a unified, reliable source of information instead of depending on disjointed, project-specific datasets."
-
Visualization Instruments: Employing sophisticated visualization instruments allows for the layering of geographic information with other datasets. This enhances the interpretation of complex information, making it easier to identify trends and patterns that may not be immediately apparent. For instance, the Nebraska Department of Transportation has successfully used real-time information to monitor wildlife locations, demonstrating the practical applications of integrated geospatial information.
-
Collaborative Platforms: Promoting teamwork among departments to exchange insights derived from integrated information fosters a culture of data-informed decision-making and innovation.
By effectively combining other sources with geospatial data management, organizations can uncover hidden patterns and correlations, ultimately guiding strategic decisions and enhancing analysis. Statistics indicate that the market value for intelligent transportation systems is projected to grow significantly, underscoring the importance of leveraging integrated data for competitive advantage.
Conclusion
Geospatial data management stands as a pivotal element in enhancing market insights and strategic decision-making. By effectively harnessing location-based information, organizations can unlock valuable trends and patterns that inform their operational strategies. This understanding not only aids in optimizing resources but also fosters a competitive advantage in an increasingly data-driven marketplace.
The article highlights several key aspects of geospatial data management, including:
- Its definition and significance
- Effective collection techniques
- Robust management strategies
- The integration of geospatial data with other sources
Techniques such as surveys, GPS technology, and remote sensing are crucial for gathering accurate data. Meanwhile, strategies like information standardization and regular audits ensure data integrity. Moreover, the integration of geospatial information with other datasets enhances analytical capabilities, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of market dynamics.
In light of these insights, organizations are encouraged to embrace geospatial data management as an essential part of their strategic framework. By investing in effective collection techniques, robust management practices, and integration with other data sources, businesses can improve their decision-making processes while uncovering new opportunities for growth and innovation. The future of market analysis is undeniably intertwined with the effective use of geospatial data, making it imperative for organizations to adapt and evolve in this direction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is geospatial data?
Geospatial data refers to information associated with specific locations on the Earth's surface, including coordinates, addresses, and other identifiers.
Why is geospatial data important?
Geospatial data is important because it provides context to various datasets, allowing businesses to visualize trends, patterns, and relationships that are geographically significant, which enhances decision-making and operational efficiency.
How do retailers use geospatial data?
Retailers use geospatial data to analyze foot traffic patterns, optimize store locations, enhance customer engagement, and boost sales.
In what ways do urban planners utilize geospatial data?
Urban planners leverage geospatial data to assess land use and infrastructure needs, ensuring that development aligns with community requirements.
How can geospatial data management improve strategic planning?
Effective geospatial data management can enhance operational efficiency, inform decision-making, improve market positioning, and provide a competitive edge for organizations.
What benefits does spatial analysis offer in retail planning?
Spatial analysis in retail planning allows companies to tailor their offerings to local demographics, increasing customer satisfaction and potentially driving sales.
Why is spatial intelligence crucial for businesses?
Spatial intelligence is crucial for identifying hidden business trends, revealing new opportunities, and enhancing operational efficiency.
What measurable benefits can geospatial data provide?
Geospatial data can facilitate early alerts and optimize business processes, highlighting its significance in strategic planning.