Master Data Licensing: Essential Insights for Market Research Analysts

Master Data Licensing: Essential Insights for Market Research Analysts
Overview
The article "Master Data Licensing: Essential Insights for Market Research Analysts" highlights the pivotal role of data licensing in market research and its implications for analysts. Understanding the various types of data licenses is crucial, as it ensures compliance with legal and ethical standards. This knowledge empowers analysts to strategically acquire data, enabling them to navigate the complexities of data usage effectively.
Protecting intellectual property rights is essential, as is maintaining the credibility of their findings. How can market research analysts leverage data licensing to enhance their work? By grasping these essential insights, analysts can elevate their research practices and uphold the integrity of their results.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of data licensing is essential for market research analysts navigating today's data-driven landscape. As organizations increasingly depend on high-quality information for informed decision-making, the ability to legally access, utilize, and distribute datasets becomes crucial.
However, with various types of licenses available and the potential legal pitfalls associated with non-compliance, how can analysts ensure they are making the right choices? This article explores the essential insights of master data licensing, offering valuable guidance on its importance, types, and ethical considerations.
By empowering analysts with this knowledge, we aim to enhance their research practices while safeguarding their organizations.
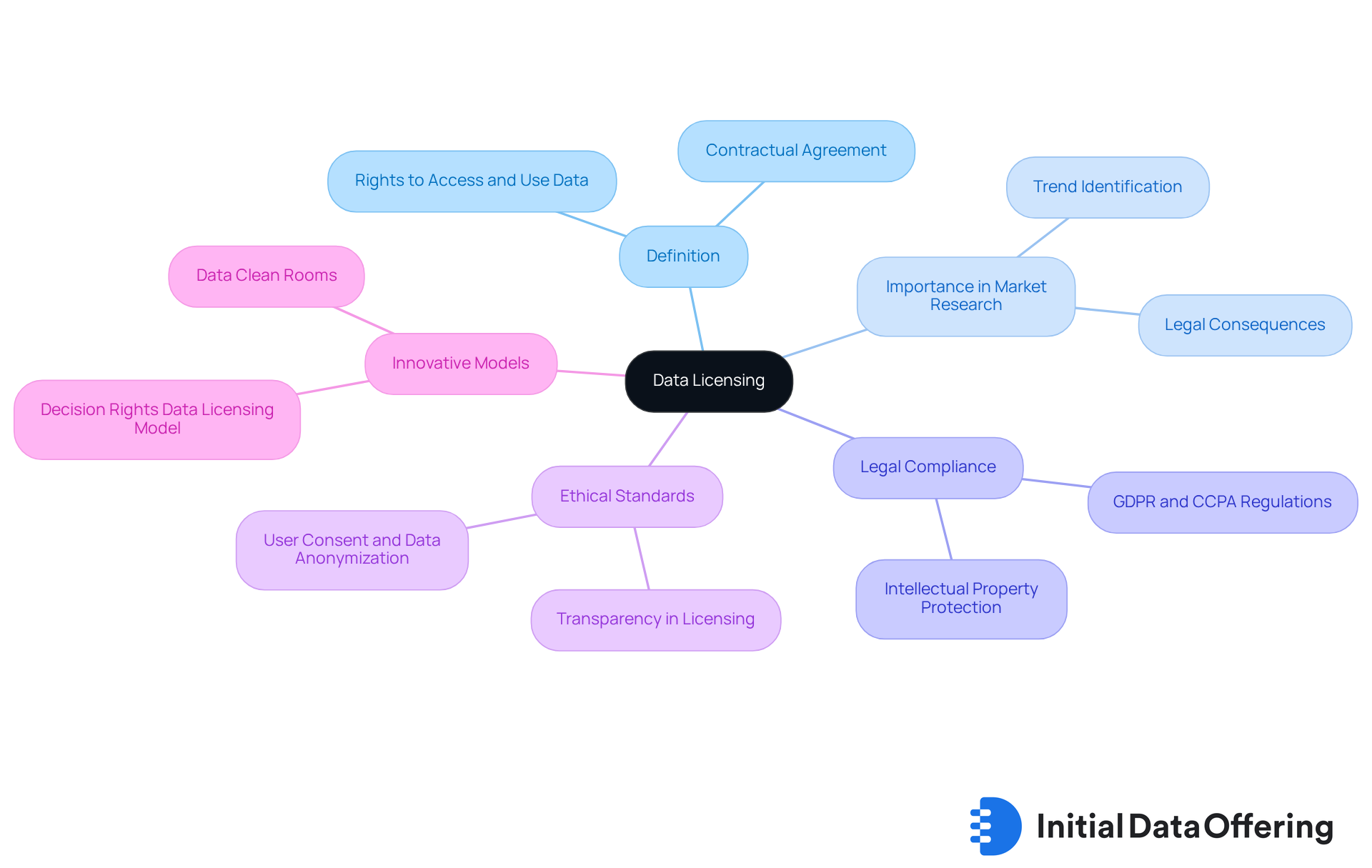
Define Data Licensing and Its Importance in Market Research
Data licensing is a contractual agreement that grants organizations the right to access, use, and distribute specific datasets from another entity. In the realm of commercial analysis, understanding data licensing is essential. It ensures that analysts can legally employ information to derive insights while honoring intellectual property rights. This legal structure protects the ownership of information providers and defines the extent of use for licensees, which is crucial for maintaining ethical standards in data licensing.
For example, a market research analyst may license consumer behavior information to identify trends. A thorough understanding of the permission terms associated with data licensing is vital; failure to comply with these agreements can result in legal consequences and damage the organization's reputation. As the demand for high-quality information escalates, especially in an AI-driven economy, the significance of robust data licensing practices becomes increasingly evident. By proactively engaging with data licensing, market research analysts can navigate the complexities of information acquisition, ensuring compliance with legal requirements and enhancing the credibility of their findings.
Moreover, specialist perspectives highlight the importance of information literacy in this evolving environment. As William A. Tanenbaum notes, innovative data licensing models, such as the 'Decision Rights Data Licensing Model,' establish clearer boundaries for information usage. This allows organizations to leverage resources effectively while minimizing risks. Such an approach fosters transparency and builds trust with stakeholders, which is essential in today's data-driven landscape.
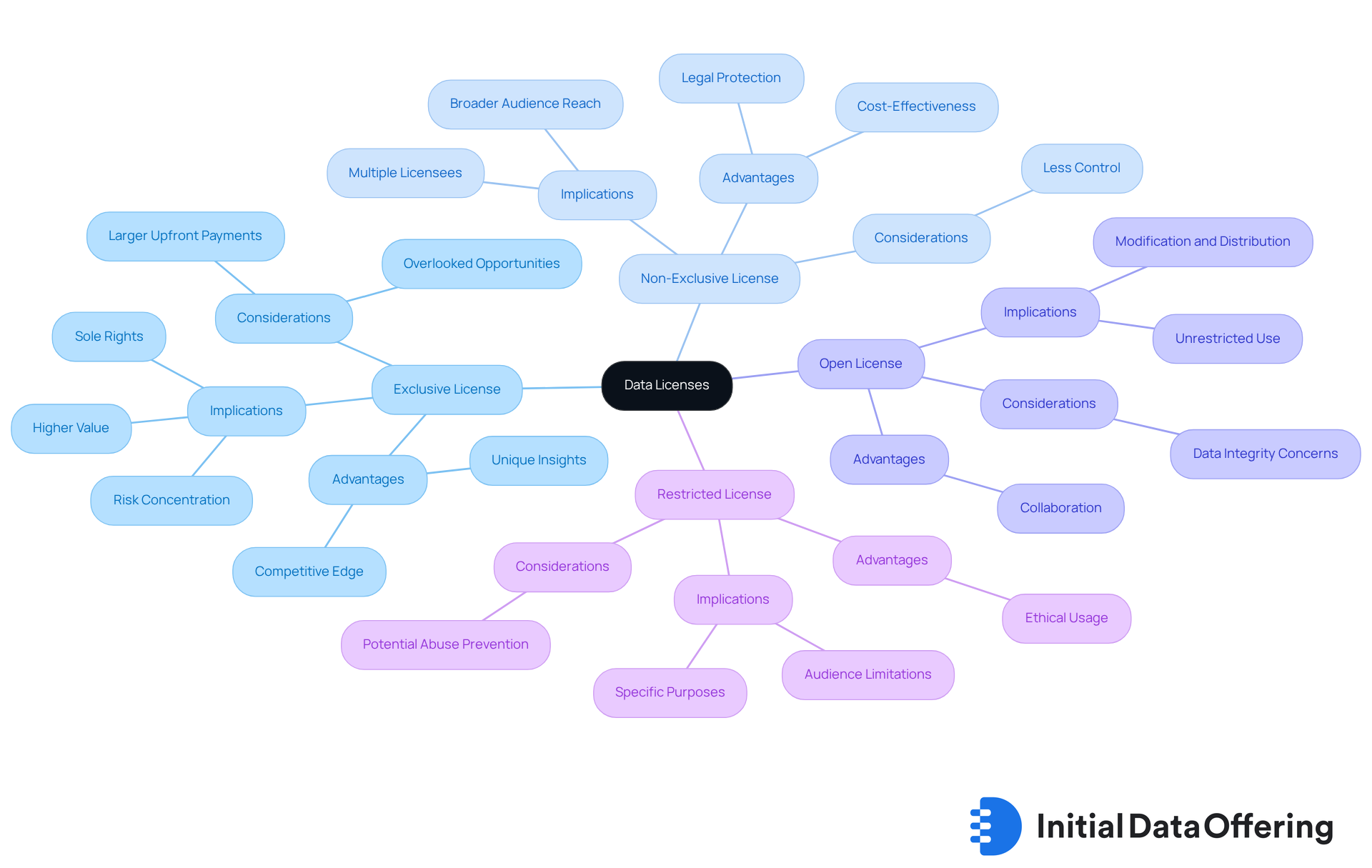
Explore Different Types of Data Licenses and Their Implications
Data licensing can be categorized into several types, each with distinct implications for usage.
-
Exclusive License: This type grants the licensee sole rights to utilize the information, preventing the licensor from offering the same material to others. Organizations seeking a competitive edge often benefit from this license, as it allows for unique insights and strategic advantages. The advantage of an exclusive license lies in its potential for higher value per license compared to non-exclusive options, although it typically requires larger upfront payments. However, this concentration of rights can also lead to overlooked business opportunities, as it places significant risk in one licensee.
-
Non-Exclusive License: This license permits several licensees to utilize the same information, making it a popular option in market analysis. By broadening audience reach, non-exclusive licenses offer additional legal protection, enabling various analysts and organizations to access valuable datasets without the constraints of exclusivity. The cost-effectiveness of non-exclusive licenses is particularly beneficial for wider investigative initiatives, providing essential legal protections for compliance.
-
Open License: This license allows for unrestricted use, modification, and distribution of the information. While ideal for collaborative research initiatives, open licenses may raise concerns about the integrity and quality of the data. Thus, careful consideration of the reliability of the information is necessary.
-
Restricted License: This type limits the use of information to specific purposes or audiences, which is crucial for handling sensitive content. Restricted licenses promote ethical and responsible usage, safeguarding both the information provider and the user from potential abuse.
Understanding these categories of licenses is crucial for analysts in selecting suitable data sources while adhering to legal and ethical standards of data licensing. For example, while an exclusive license may be advantageous for a company seeking unique insights, a non-exclusive license may enable broader investigative initiatives at a lower expense. As industry analysis trends evolve in 2025, the choice of authorization model will significantly impact income, sector control, and competition management. Additionally, traditional contract terms such as geographical restrictions and liability limitations should be considered to fully grasp the implications of each licensing type.
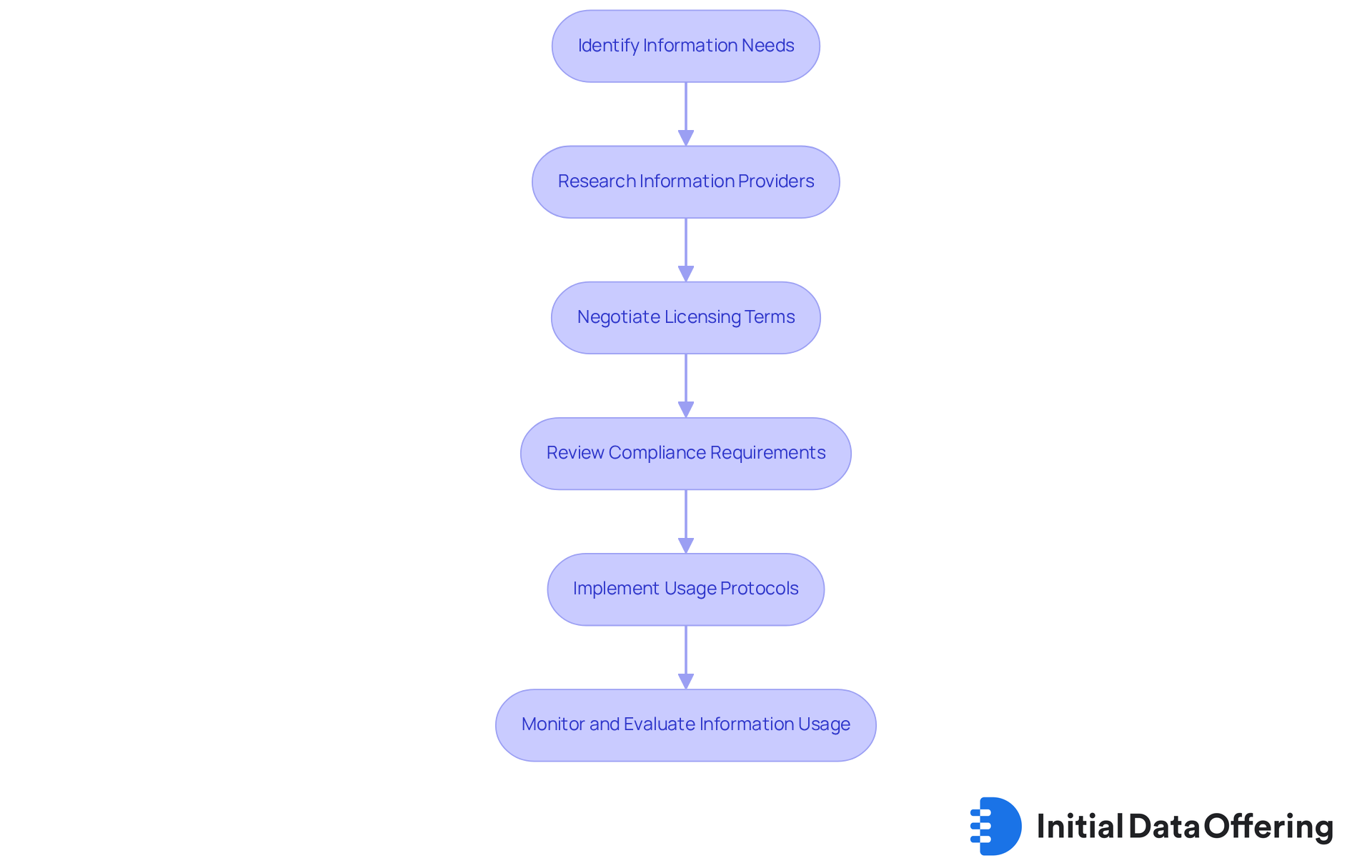
Guide to Acquiring and Utilizing Licensed Data for Market Research
Acquiring and utilizing data licensing for market research involves several essential steps that can significantly enhance the quality of your analysis.
-
Identify Information Needs: Clearly define the specific type of information required for your research objectives. Understanding the metrics and insights you seek is essential for efficient information selection, ensuring that you focus on what truly matters.
-
Research Information Providers: Look for trustworthy providers that offer the datasets you require. Assess their terms of use, information quality, and customer feedback to guarantee dependability and consistency with your objectives. This diligence helps ensure that the data you acquire is both relevant and reliable.
-
Negotiate Licensing Terms: Engage in discussions with the information provider to negotiate favorable licensing terms. Aim for agreements that align with your research objectives and budget constraints, ensuring clarity on data licensing, usage rights, and limitations. Richard Huffine, FDIC chief of library and public information, highlights the significance of evaluating the usefulness and worth of licensed datasets, stating, "Even in that worst case scenario, you have a chance to address someone's needs to combine these resources to make better decisions."
-
Review Compliance Requirements: Familiarize yourself with compliance obligations associated with the license, including protection regulations and ethical considerations. This step is essential to avoid legal pitfalls and ensure responsible usage through data licensing. As emphasized in conversations at Data Summit 2023, organizations must evaluate if their information resources fulfill client requirements to prevent unnecessary expenses.
-
Implement Usage Protocols: After acquiring the information, establish clear protocols for its use, sharing, and storage. This guarantees that all team members comply with the licensing agreement and uphold information integrity, fostering a culture of responsibility within your organization.
-
Monitor and Evaluate Information Usage: Regularly assess how the licensed information is being utilized in your studies. This ongoing evaluation aids in recognizing potential compliance issues and ensures that the information remains pertinent to your objectives. The worldwide industry for analysis is projected to produce $140 billion in revenue in 2024, highlighting the significance of efficient data licensing practices.
By adhering to these steps, market analysis professionals can effectively obtain and utilize information through data licensing, maximizing the value of their analysis while reducing legal risks. Successful negotiations and adherence to best practices can significantly enhance the quality and relevance of the information, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making.
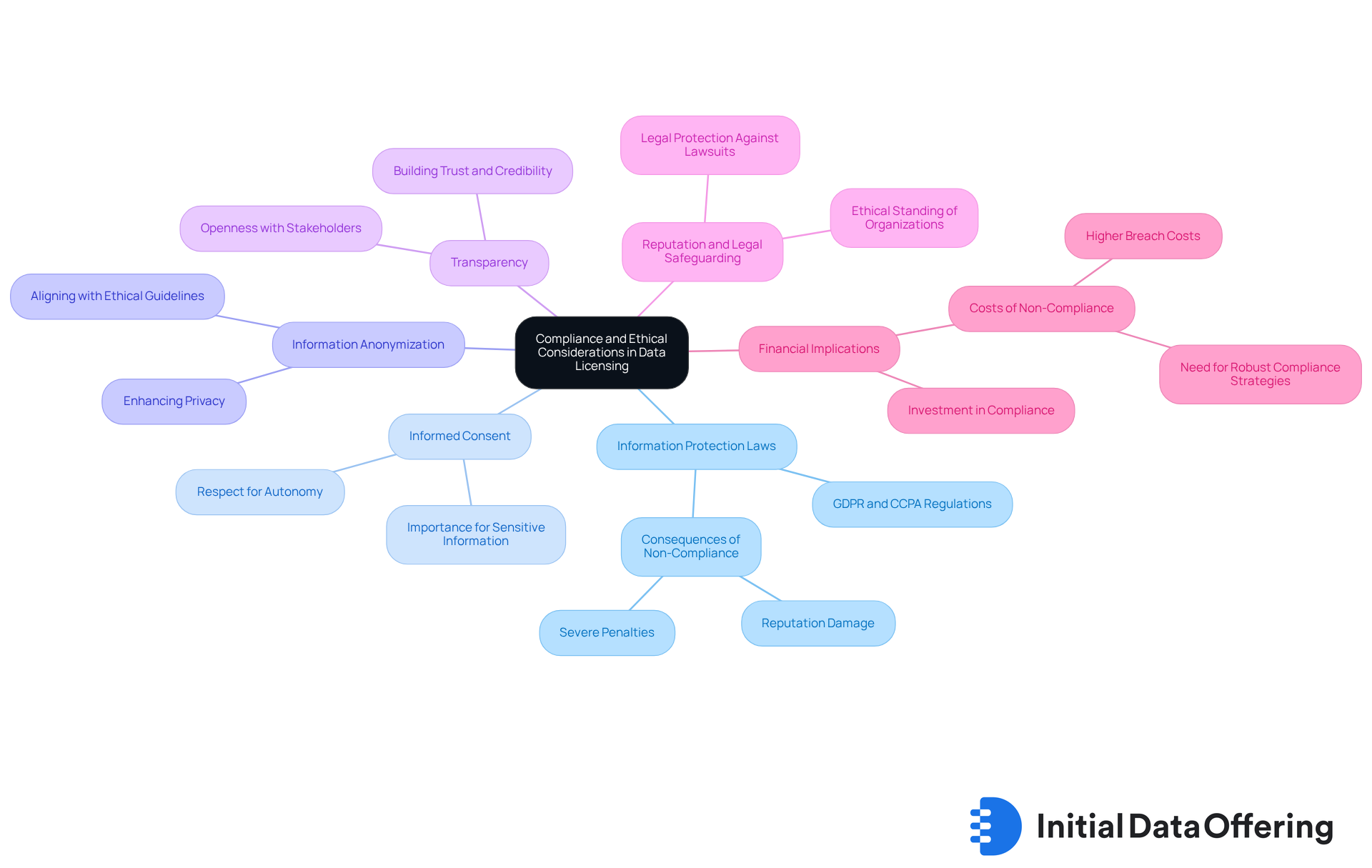
Understand Compliance and Ethical Considerations in Data Licensing
Adherence to ethical considerations in data licensing is essential for guaranteeing responsible research practices. Analysts must be aware of several key factors that significantly impact their work.
-
Information Protection Laws: Familiarize yourself with pertinent information protection regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, which govern how personal details can be collected, utilized, and shared. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties and damage to an organization's reputation. Understanding these laws is a fundamental step in ensuring ethical practices.
-
Informed Consent: It is crucial to ensure that any information gathered from individuals has been obtained with their informed consent. This is particularly important for sensitive information that could identify individuals, as it respects their autonomy and privacy.
-
Information Anonymization: When utilizing personal information, consider anonymizing it to safeguard individual identities. This practice not only enhances privacy but also aligns with ethical guidelines, reinforcing the importance of protecting personal data.
-
Transparency: Maintaining openness with stakeholders regarding how information is sourced, utilized, and shared fosters trust and credibility in your findings. Transparency is vital for establishing a responsible data ecosystem.
Regular audits should involve conducting evaluations of your usage practices to ensure compliance with data licensing agreements and legal requirements. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring that ethical standards are upheld.
-
Reputation and Legal Safeguarding: Adhering to industry study regulations offers legal safeguards against expensive lawsuits and penalties, while also assisting in upholding an organization's ethical standing. According to a survey, 83% of compliance professionals emphasize the importance of adhering to relevant laws in decision-making, highlighting the critical nature of compliance.
-
Financial Implications: Understanding the financial risks associated with non-compliance is essential. For instance, breaches linked to non-compliance can incur significantly higher costs, emphasizing the need for robust compliance strategies to mitigate financial exposure.
By prioritizing compliance and ethical considerations, market research analysts can uphold the integrity of their work and contribute to a responsible data ecosystem. What steps can you take today to enhance your adherence to these ethical standards?
Conclusion
Understanding data licensing is crucial for market research analysts. It provides the legal framework for utilizing various datasets and ensures compliance with ethical standards. By grasping the nuances of data licensing, analysts can effectively navigate the complexities of information acquisition, safeguarding both their organization and the integrity of their research.
The article delves into the importance of different types of data licenses—exclusive, non-exclusive, open, and restricted. Each type presents unique implications for data usage. Acquiring licensed data through a structured process is significant, which includes:
- Identifying information needs
- Negotiating terms
- Ensuring compliance with legal and ethical standards
These insights underscore the necessity of maintaining a responsible approach to data usage, particularly in an increasingly data-driven environment.
Ultimately, prioritizing data licensing enhances the quality and relevance of market research while cultivating trust and credibility with stakeholders. Analysts are encouraged to adopt best practices in data licensing and compliance, ensuring that their research contributes to a responsible data ecosystem. As the landscape of market research evolves, embracing robust data licensing practices will be pivotal in navigating future challenges and opportunities in the field.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is data licensing?
Data licensing is a contractual agreement that grants organizations the right to access, use, and distribute specific datasets from another entity.
Why is data licensing important in market research?
Data licensing is essential in market research because it ensures that analysts can legally use information to derive insights while respecting intellectual property rights, thus maintaining ethical standards.
What are the consequences of failing to comply with data licensing agreements?
Failure to comply with data licensing agreements can result in legal consequences and damage the organization's reputation.
How does data licensing relate to the demand for high-quality information?
As the demand for high-quality information increases, especially in an AI-driven economy, the significance of robust data licensing practices becomes more evident, helping organizations navigate the complexities of information acquisition.
What is the 'Decision Rights Data Licensing Model'?
The 'Decision Rights Data Licensing Model' is an innovative data licensing approach that establishes clearer boundaries for information usage, allowing organizations to leverage resources effectively while minimizing risks.
How does effective data licensing contribute to transparency and trust?
Effective data licensing fosters transparency and builds trust with stakeholders, which is essential in today's data-driven landscape.