Is Web Scraping Legal? A Step-by-Step Compliance Guide

Is Web Scraping Legal? A Step-by-Step Compliance Guide
Overview
Web scraping can be legal; however, its legality is contingent upon jurisdiction and the nature of the information collected, particularly concerning personal data and copyrighted materials. Understanding relevant laws, such as the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), is crucial for anyone involved in data extraction activities. By adhering to best practices, including checking a website's robots.txt file and reviewing terms of service, individuals can mitigate legal risks associated with web scraping.
Why is it important to grasp these legal frameworks? The implications of non-compliance can be severe, leading to potential legal action and financial penalties. Therefore, a thorough understanding of these regulations not only protects individuals but also enhances the credibility of their data practices. Ultimately, being informed about the legal landscape surrounding web scraping empowers users to navigate this complex environment responsibly and effectively.
Introduction
The rise of web scraping has opened up vast opportunities for data collection, presenting organizations with significant advantages in gathering insights and enhancing decision-making processes. However, this technique also raises pressing legal questions that can vary dramatically across different jurisdictions. As organizations increasingly rely on web scraping, understanding the legal landscape becomes essential to avoid potential pitfalls.
What specific legal implications and best practices must data collectors navigate to ensure compliance and protect themselves from costly repercussions? This article delves into the complexities of web scraping legality, offering a comprehensive guide to help individuals and businesses stay informed and responsible in their data extraction efforts.
Understand the Legal Landscape of Web Scraping
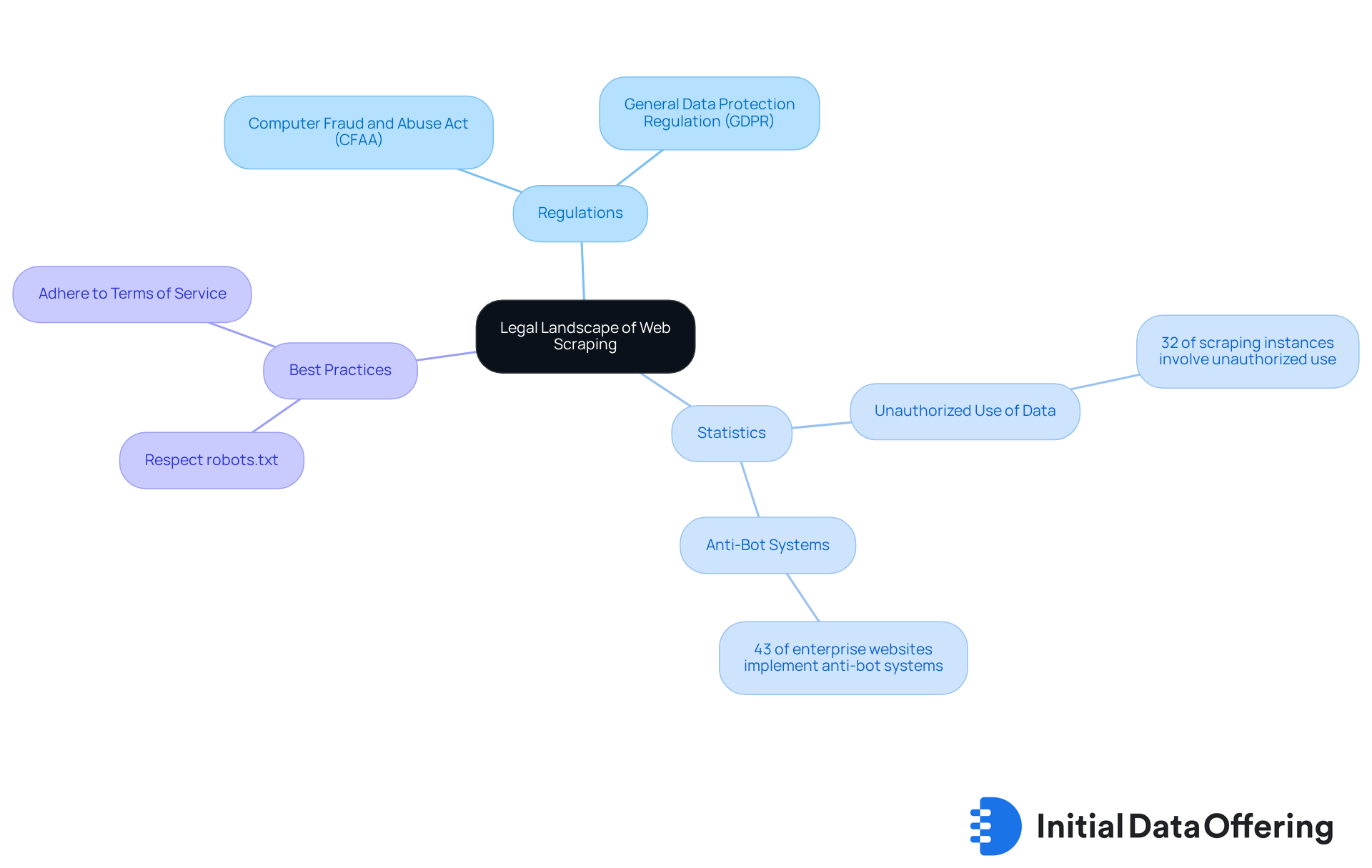
Web harvesting is a technique employed to gather information from websites, but the question of whether is web scraping legal can vary significantly based on jurisdiction and the type of content being collected. Collecting publicly accessible information is generally permissible; however, there are notable exceptions. For instance, gathering personal information or material protected by copyright can lead to significant complications. Understanding the regulatory landscape, including whether is web scraping legal, requires familiarity with pertinent laws, such as the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the U.S. and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. These regulations delineate what information can be gathered and under what circumstances, making it crucial for web scrapers to understand if is web scraping legal in their respective areas.
Significantly, around 32% of web scraping instances involve unauthorized use of personal or copyrighted information. This statistic underscores the essential requirement for adherence to these regulations. Moreover, approximately 43% of enterprise websites implement anti-bot systems, creating additional challenges for web scrapers and highlighting the importance of compliance with regulatory frameworks. It is essential to recognize that public information may still be protected by privacy or copyright regulations.
When considering best practices for legal web data extraction, one must ask, is web scraping legal, and ensure to check robots.txt files and respect Terms of Service. Ignoring these can lead to substantial legal consequences. Clarity and responsibility in information gathering are paramount for ethical online extraction practices. By following these guidelines, web scrapers can navigate the complexities of data collection while minimizing legal risks and fostering a more responsible online environment.
Identify Data Types That Are Illegal to Scrape
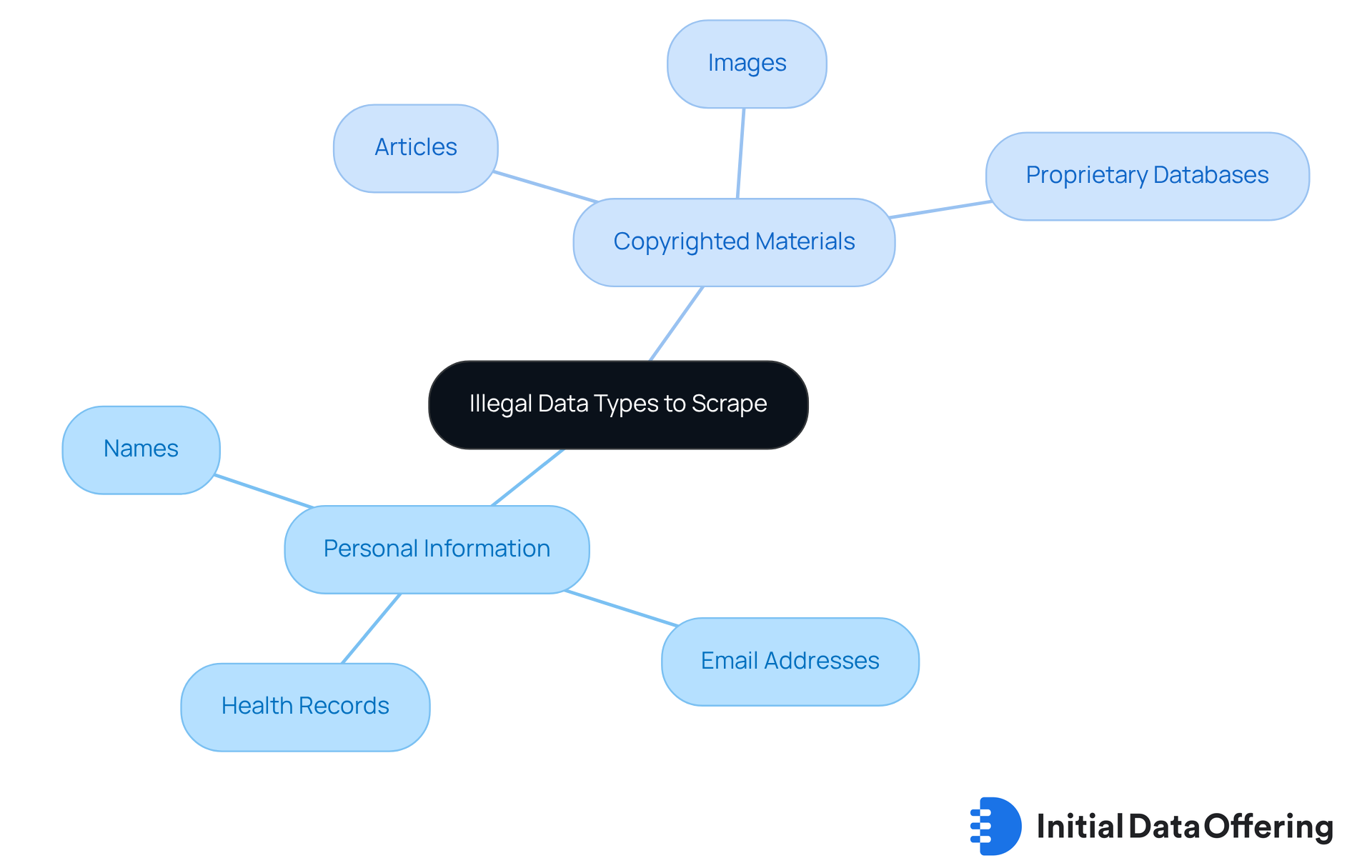
Understanding whether web scraping is legal is crucial for anyone involved in data collection. It is essential to recognize the types of information that cannot be scraped. Personal information, such as names, email addresses, and health records, is safeguarded by regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The consequences of gathering this information without explicit permission can be severe. Legal expert Omer Tene emphasizes that "collecting personal data without consent can expose organizations to severe penalties under GDPR."
Moreover, copyrighted materials—including images, articles, and proprietary databases—are off-limits for extraction unless permission is granted by the copyright holder. A significant statistic reveals that approximately 60% of websites include terms of service that explicitly prohibit data extraction activities. Violating these terms may lead to legal actions against the scraper, as evidenced by the Canadian Legal Information Institute's claim against Caseway AI Legal Ltd. for unauthorized data extraction.
Therefore, before commencing any data extraction activities, it is vital to thoroughly review a website's terms and conditions to understand if web scraping is legal. This diligence ensures compliance and helps avoid potential legal challenges, safeguarding your organization from unnecessary risks.
Review Relevant Laws and Regulations
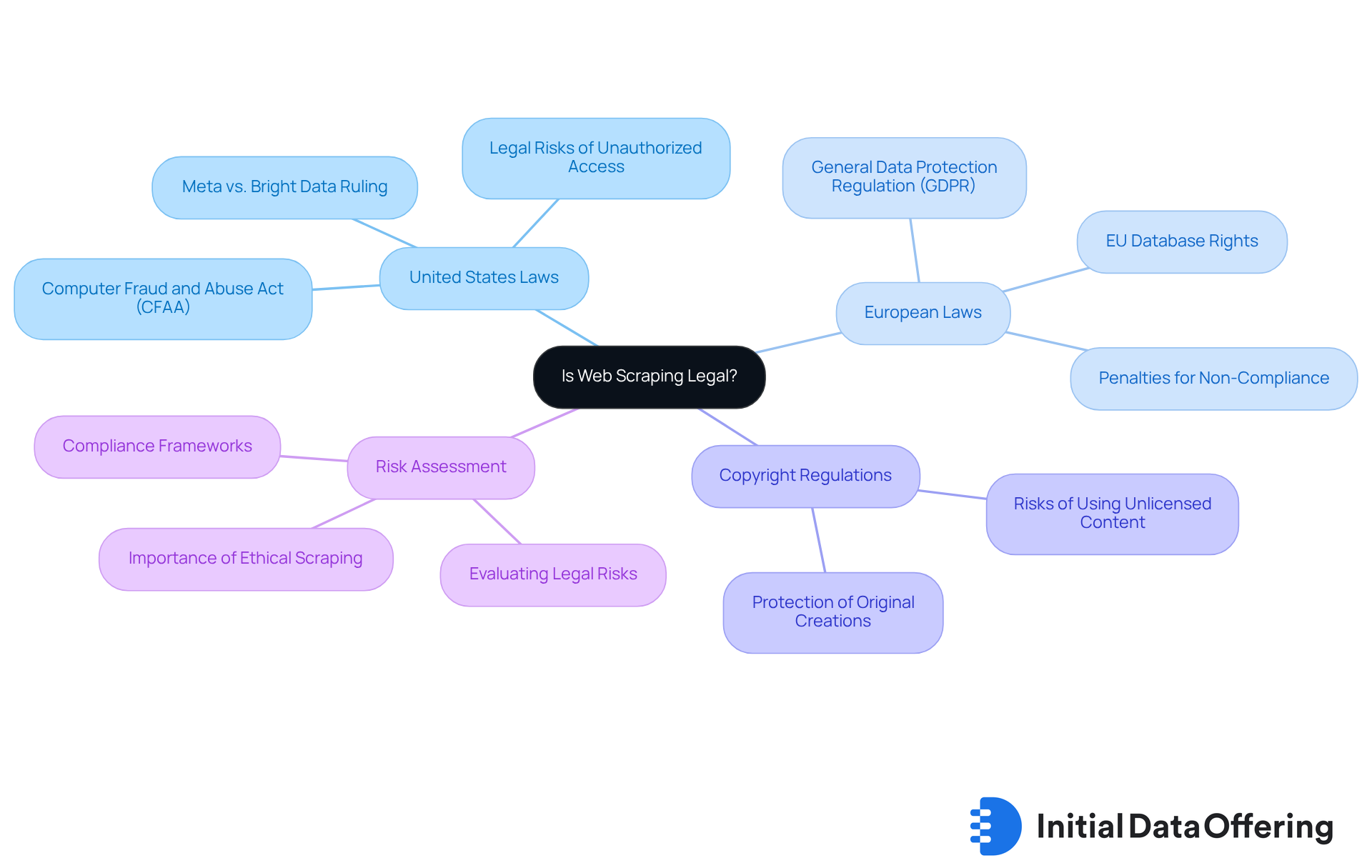
A complex array of laws and regulations that vary significantly by jurisdiction raises the question of whether is web scraping legal. In the United States, the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) plays a pivotal role in addressing unauthorized access to computer systems, leading many to question if is web scraping legal. Legal precedents indicate that extracting content behind contractual restrictions may constitute a breach, as confirmed in the 2024 Meta vs. Bright Data ruling. Additionally, the CFAA has been cited in many legal cases, which brings up the question of whether is web scraping legal and highlights the significance of adherence in data collection practices. As one unnamed executive noted, 'The question of is web scraping legal is crucial, as illegal scraping exposes enterprises to direct fines, injunctions, and business bans,' underscoring the serious consequences of non-compliance.
In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) raises concerns about whether web scraping is legal due to its stringent requirements on the collection and processing of personal information. As of 2025, even public web pages may contain personal data that necessitates GDPR safeguards, leading to the important question of whether is web scraping legal without explicit consent when handling such information. Failure to comply can result in substantial penalties, often stemming from insufficient protections rather than the question of whether is web scraping legal. Significantly, user feedback with identifiable information presents a high risk level due to GDPR exposure, which raises concerns about whether is web scraping legal.
Furthermore, copyright regulations safeguard original creations, raising the issue of whether is web scraping legal when extracting copyrighted material without consent, which can result in serious consequences. The ongoing lawsuits against AI firms highlight the risks associated with using unlicensed content for training models and raise the question of whether web scraping is legal, emphasizing the need for evidence of licensed datasets prior to deployment.
Entities involved in web data extraction should assess whether is web scraping legal and establish a formal risk evaluation framework to measure potential hazards prior to initiating projects. This involves assessing the likelihood and consequences of regulatory violations to evaluate if web scraping is legal, which can assist in making informed choices regarding vendor collaborations and project feasibility. Respecting robots.txt is also crucial to understand if web scraping is legal and to avoid disputes over data collection policies. By comprehending and following these regulatory structures, companies can navigate the intricacies of web data collection and consider whether is web scraping legal, thus reducing exposure to potential liabilities.
Implement Best Practices for Legal Web Scraping
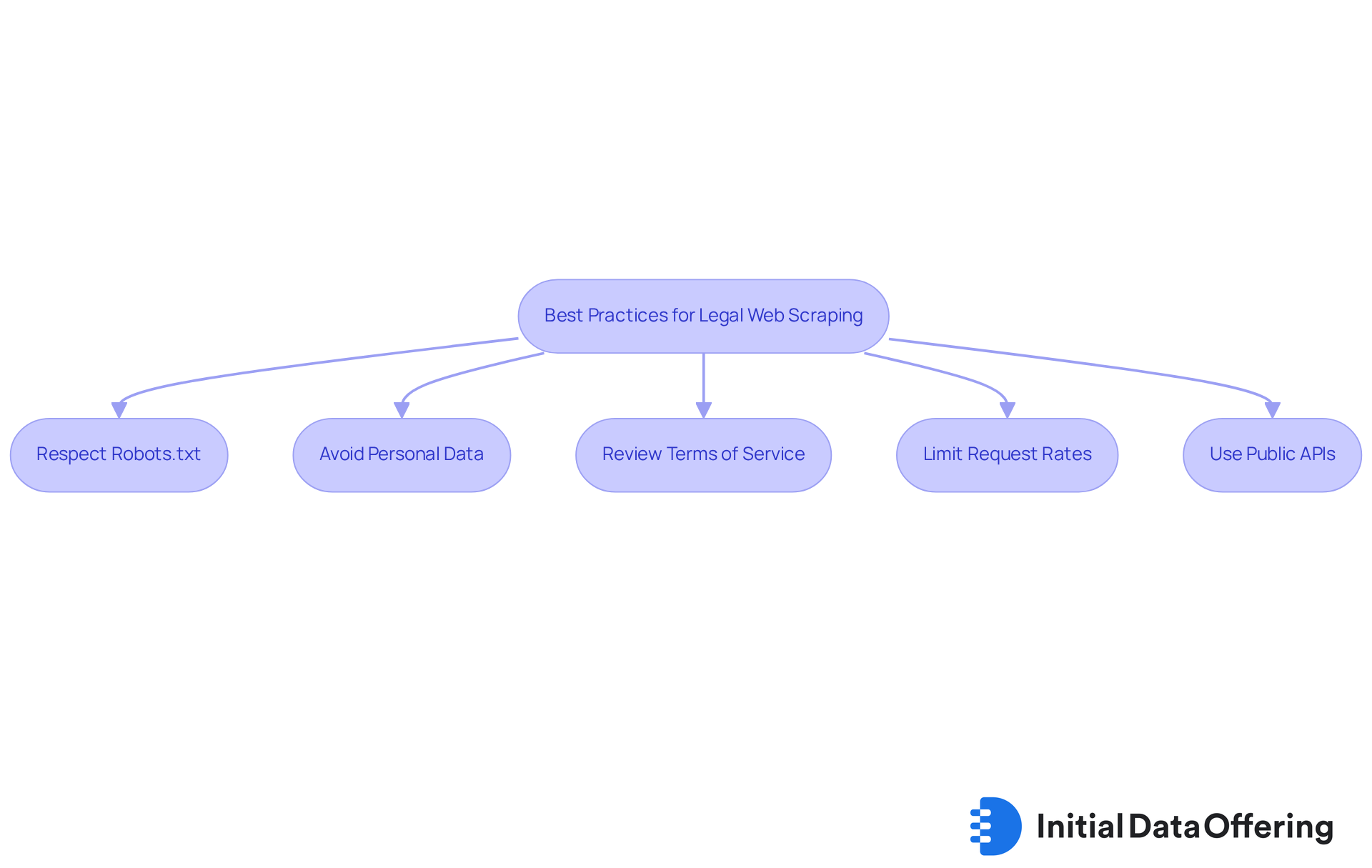
To ensure legal web extraction, it is essential to follow these best practices:
-
Respect Robots.txt: Always check the website's robots.txt file, which indicates which parts of the site can be scraped. This practice not only respects the website's preferences but also brings up the concern of whether web scraping is legal to help avoid potential legal issues.
-
Avoid Personal Data: Do not scrape personal information unless you have explicit consent from the individual. This approach safeguards privacy and adheres to legal standards, which leads to the important question of whether web scraping is legal, fostering trust in your data practices.
-
Review Terms of Service: Familiarize yourself with the website's terms of service to ensure that data extraction is permitted. Understanding these terms can help you effectively navigate the legal landscape regarding whether web scraping is legal.
-
Limit Request Rates: Avoid overwhelming the server by limiting the rate of requests. This strategy not only helps prevent potential bans but also reduces the risk of causing server issues, ensuring a smoother scraping experience.
-
Use Public APIs: Whenever possible, utilize public APIs provided by websites for data access. These APIs are designed for data extraction and often come with clear usage guidelines, making them a reliable resource.
By adhering to these practices, you can minimize legal risks and maintain ethical standards, thus ensuring that web scraping is legal in your activities. How might these strategies enhance your own data extraction efforts?
Conclusion
Understanding the legality of web scraping is essential for anyone involved in data collection. The core message emphasizes that while gathering publicly available information can be permissible, significant legal complexities arise when dealing with personal data or copyrighted material. Compliance with relevant laws, such as the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the U.S. and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, is crucial for avoiding legal repercussions.
Key insights from the article highlight the importance of recognizing what types of data are illegal to scrape, including:
- Personal information
- Copyrighted materials
With a considerable percentage of websites explicitly prohibiting data extraction in their terms of service, it is vital to conduct thorough due diligence before scraping. Additionally, implementing best practices—such as:
- Respecting robots.txt files
- Avoiding personal data collection without consent
- Utilizing public APIs
can significantly reduce legal risks associated with web scraping.
In a landscape where legal challenges are increasingly prevalent, it is imperative to approach web scraping with caution and responsibility. By adhering to established guidelines and staying informed about the evolving legal framework, individuals and organizations can engage in ethical web scraping practices. This not only fosters a more responsible online environment but also ensures compliance with the law, paving the way for sustainable data collection strategies in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is web scraping?
Web scraping is a technique used to gather information from websites.
Is web scraping legal?
The legality of web scraping varies based on jurisdiction and the type of content being collected. Generally, collecting publicly accessible information is permissible, but there are exceptions, especially concerning personal information and copyrighted material.
What laws should web scrapers be aware of?
Web scrapers should be familiar with laws such as the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the U.S. and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, as these regulations define what information can be collected and under what circumstances.
What percentage of web scraping instances involve unauthorized use of personal or copyrighted information?
Approximately 32% of web scraping instances involve unauthorized use of personal or copyrighted information.
What challenges do web scrapers face from enterprise websites?
Around 43% of enterprise websites implement anti-bot systems, which creates additional challenges for web scrapers and emphasizes the need for compliance with regulatory frameworks.
What best practices should be followed for legal web data extraction?
Web scrapers should check robots.txt files and respect Terms of Service to avoid potential legal consequences. Clarity and responsibility in information gathering are essential for ethical online extraction practices.
Can public information be protected by regulations?
Yes, public information may still be subject to privacy or copyright regulations, which web scrapers need to consider.