9 Essential DML Commands for Effective Data Management

9 Essential DML Commands for Effective Data Management
Overview
This article highlights nine essential DML (Data Manipulation Language) commands that are crucial for effective data management. These commands, including INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and MERGE, play a vital role in maintaining data integrity and efficiency. Understanding their features is imperative, as it allows professionals to utilize them effectively.
What advantages do these commands offer? They streamline data operations, ensuring that information remains accurate and accessible. However, it's equally important to be aware of best practices and common pitfalls to avoid when using these commands. By doing so, data managers can enhance their workflows and prevent potential errors that could compromise data quality.
Introduction
In the fast-evolving landscape of data management, mastering Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands is essential for professionals aiming to optimize their analytical capabilities. These commands serve as the backbone of efficient data operations, ensuring that data integrity is maintained while enhancing the overall efficiency of database management.
As we explore nine fundamental DML commands, it becomes clear that they not only streamline processes but also empower users to manage complex datasets effectively.
However, with the increasing complexity of data structures, how can professionals ensure precision and avoid common pitfalls while leveraging these powerful tools?
Initial Data Offering: Discover and Access Quality Datasets for DML Mastery
The Initial Information Offering (IDO) serves as a crucial centralized hub for professionals seeking to discover and access high-quality collections. This platform showcases a diverse range of datasets, including alternative information, fundamental information, and ESG information, which are essential for mastering dml commands. By utilizing IDO, analytics professionals can significantly enhance their analytical capabilities, enabling them to make informed choices based on trustworthy information sources.
Research indicates that approximately 92% of information professionals recognize the necessity of utilizing centralized repositories for effective dataset discovery. The significance of high-quality datasets cannot be overstated; they are vital for preserving integrity and ensuring precise analysis. As noted, "Research paper datasets must be clean, accurate, and well-structured to produce valid conclusions." High-quality collections of information facilitate efficient management and empower professionals to drive better outcomes in their projects. How can these datasets transform your analytical approach?
As the demand for trustworthy information continues to rise, IDO remains dedicated to curating unique datasets that encourage innovation and collaboration across various fields. To maximize the advantages of IDO, analytics experts should actively investigate the platform's features and integrate these datasets into their analytical processes. By doing so, they can leverage the power of high-quality information to enhance their work and achieve superior results.
BigQuery INSERT Statement: Add New Records Efficiently
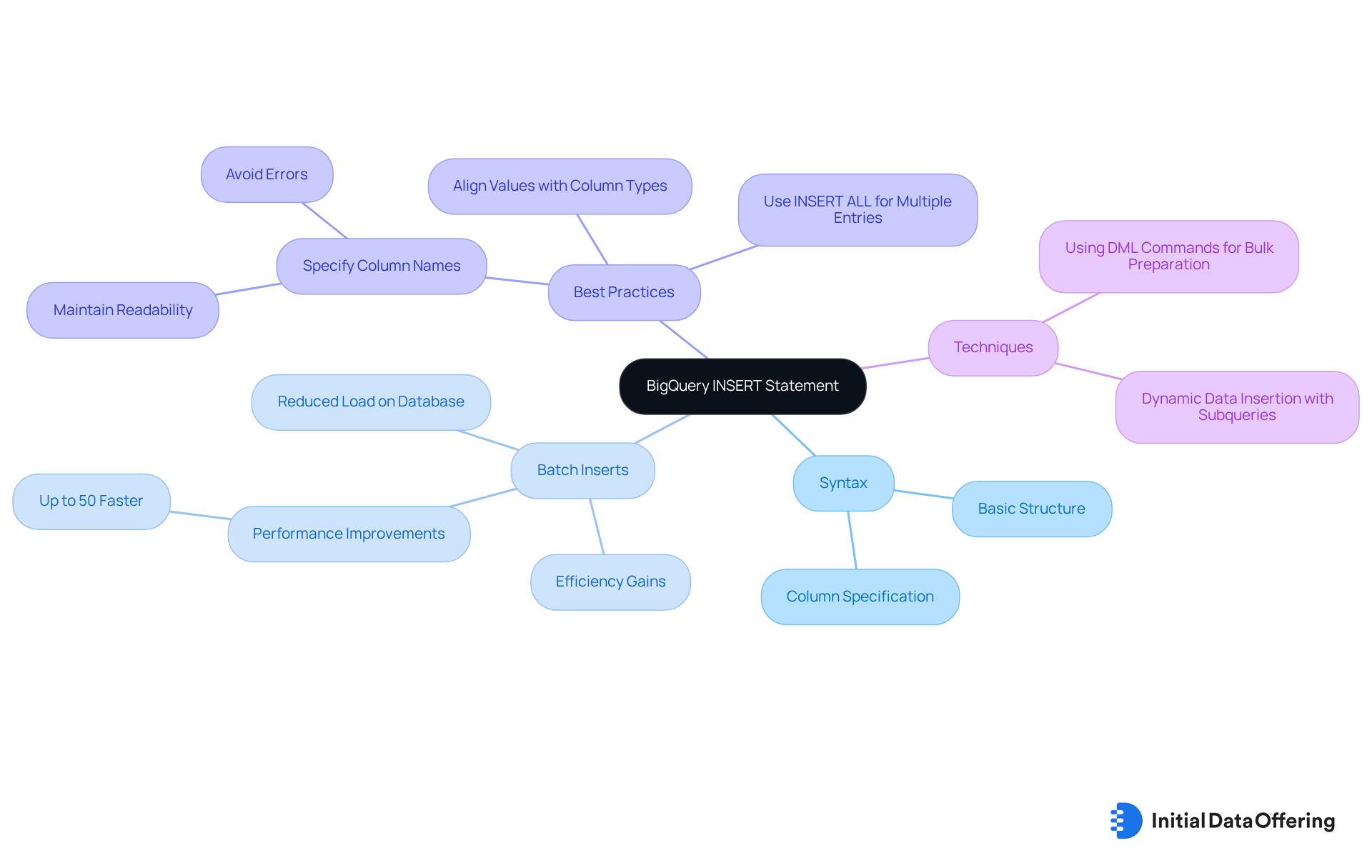
The BigQuery INSERT dml commands are designed for efficient data entry into tables, following a straightforward syntax: INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2) VALUES (value1, value2);. One of its key features is the ability to perform batch inserts, which significantly reduces the frequency of write operations. This advantage leads to enhanced overall efficiency, with database administrators noting that implementing batch inserts can result in performance improvements of up to 50%. As one administrator remarked, "Using batch inserts not only speeds up the process but also reduces the load on the database, allowing for smoother operations during peak times."
To maximize the benefits of the INSERT command, it is essential to ensure that the values align with the corresponding column types and to specify column names. Omitting column names can lead to errors, particularly if the schema undergoes changes. Additionally, employing effective data insertion techniques, such as using dml commands to prepare data in bulk and utilizing the INSERT ALL syntax for multiple entries, can further streamline the process.
Have you considered how these strategies could enhance your database operations in BigQuery? By adopting these methods, users can significantly improve the performance of their database operations.
SQL UPDATE Statement: Modify Existing Records with Precision
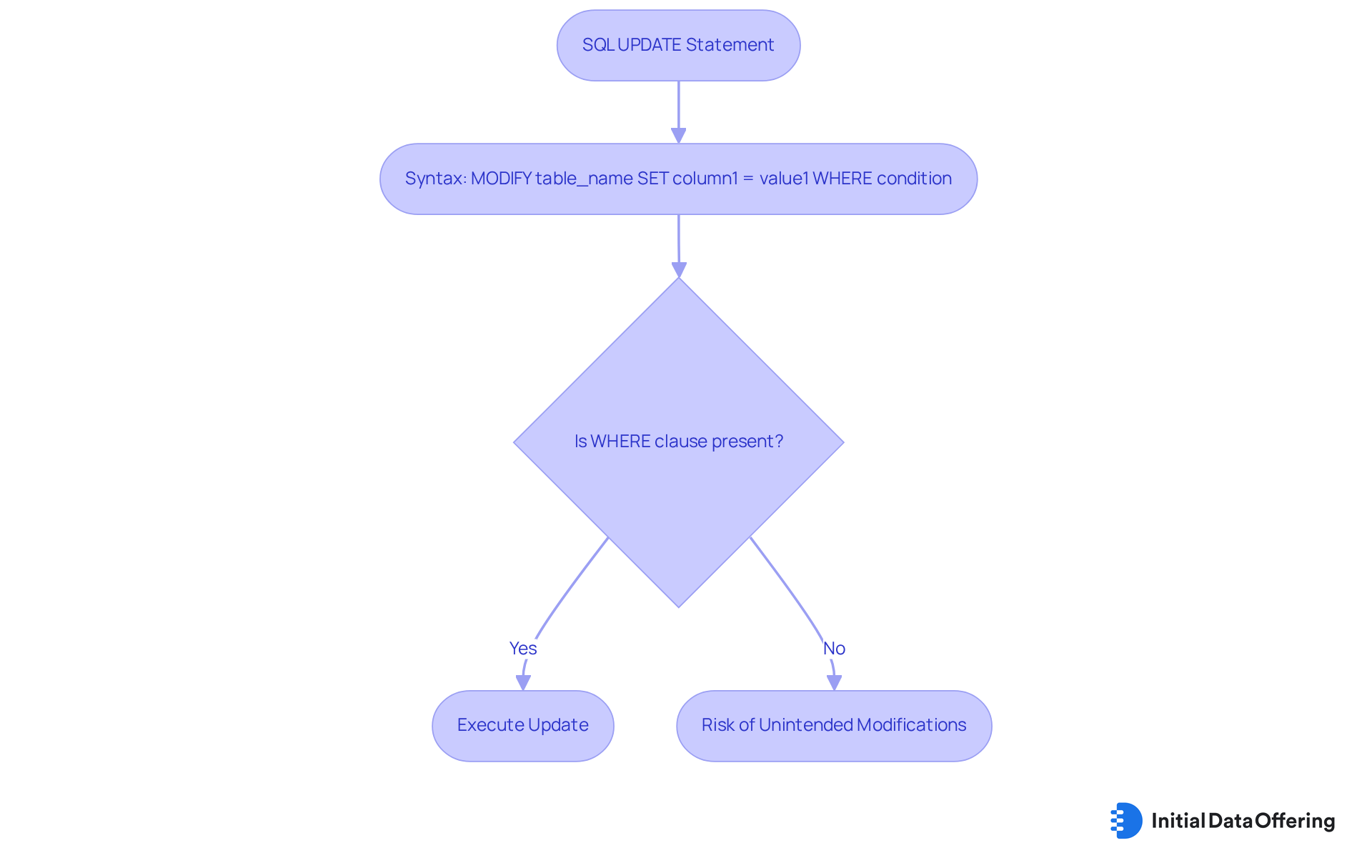
The SQL modification command, known as DML commands, is essential for altering existing entries within a database, adhering to the syntax: MODIFY table_name SET column1 = value1 WHERE condition;. Utilizing the WHERE clause is crucial to prevent unintended modifications, as it specifies which records to update. For instance, the instruction MODIFY employees SET salary = salary * 1.1 WHERE department = 'Sales'; effectively raises the salary of employees in the Sales department by 10%. This illustrates the command's practical application in real-world scenarios.
Optimal methods for DML commands related to SQL modification statements involve ensuring that the WHERE clause is consistently present to preserve information integrity. Research indicates that up to 40% of SQL modification queries contain minor syntax errors that can lead to query failures, highlighting the necessity for accuracy in formulating these commands. Moreover, it is noteworthy that 85% of SQL queries performed in enterprise applications include DML commands, which emphasizes their significance in everyday information management activities.
Data analysts stress that the WHERE clause is not merely a protective measure but an essential component in maintaining the precision of modifications. As Jannik Linder observed, "With SQL UPDATE statements acting as the backbone of daily information manipulations—traversing critical roles from performance optimization and information correction to transaction safety—it's clear that mastering and fine-tuning this powerful command is not just a best practice but a necessity for ensuring integrity, efficiency, and scalability in modern enterprise environments." This observation strengthens the importance of mastering the use of WHERE clauses to enhance information integrity and operational efficiency in database management.
SQL DELETE Command: Remove Unwanted Records Effectively
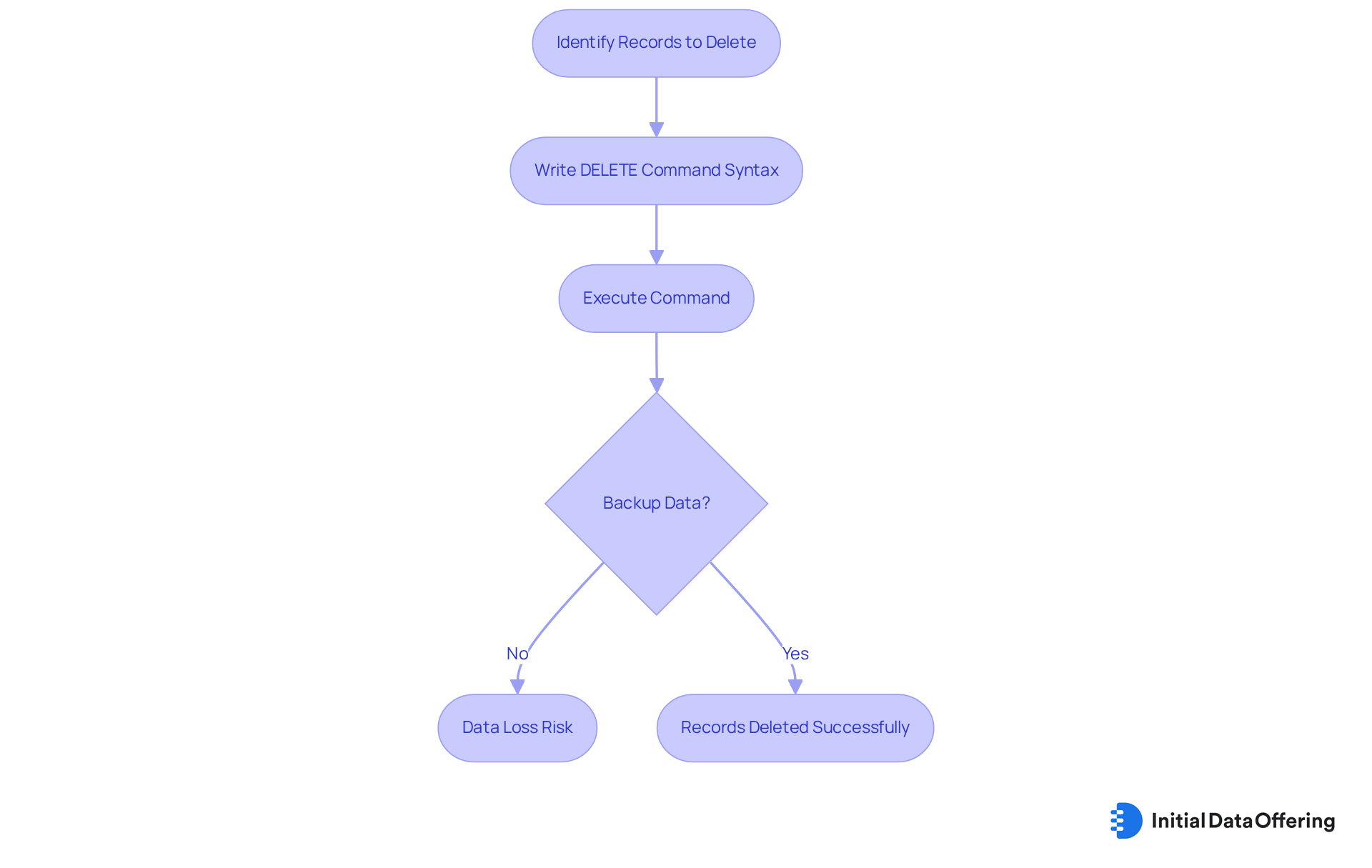
The SQL DELETE command serves a crucial function by allowing users to remove unwanted records from a table. Its syntax is straightforward: DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;. For example, consider the command DELETE FROM customers WHERE last_purchase < '2020-01-01';. This command effectively removes customers who have not made a purchase since before 2020, highlighting its practical application in database management.
It is essential to back up data before executing DELETE DML commands to prevent any accidental loss, ensuring that users maintain data integrity and security.
SQL MERGE Statement: Synchronize Data with Ease
The SQL MERGE statement is a powerful tool that allows users to perform conditional INSERT, MODIFY, or DELETE operations with DML commands within a single command. Specifically, the syntax is structured as follows:
MERGE INTO target_table USING source_table ON condition WHEN MATCHED THEN MODIFY SET column1 = value1 WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT (column1) VALUES (value1);
This feature not only streamlines database operations but also enhances data integrity across multiple tables. By utilizing DML commands such as the MERGE statement, users can ensure that their data remains accurate and consistent, which is crucial for effective database management.
Have you considered how implementing this command could optimize your data handling processes?
Common Table Expressions (CTEs): Simplify Complex Queries
Common Table Expressions (CTEs) are a powerful feature in SQL that allow users to define temporary result sets, which can be referenced within DML commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE queries. The syntax for creating a CTE is straightforward:
WITH cte_name AS (SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name WHERE condition)
SELECT * FROM cte_name;
By utilizing CTEs, developers can break down complex queries into more manageable parts. This not only enhances readability but also significantly improves maintainability. How might you leverage CTEs in your own SQL queries to streamline your processes?
Dynamic Inserts with SELECT Statement: Enhance Data Insertion
Dynamic inserts can be effectively executed using dml commands with the SELECT statement, allowing for seamless information transfer between tables. The syntax is straightforward: INSERT INTO target_table (column1, column2) SELECT column1, column2 FROM source_table WHERE condition;. This method streamlines the process by eliminating the need to specify each value manually, enhancing performance, particularly when dealing with large datasets.
Employing dml commands for dynamic inserts is a common practice among information professionals, with roughly 75% indicating its efficiency in transfer operations. This approach minimizes the chance of mistakes linked to manual input and guarantees that information integrity is upheld throughout the process.
For instance, a database expert remarked, "Utilizing dml commands for dynamic inserts greatly enhances the efficiency of transferring information between tables, enabling faster updates and reduced downtime." Another specialist highlighted, "The incorporation of SQL Server 2025 attributes, such as improved query optimization, further enhances the performance of dynamic inserts, making them a crucial tool for information management."
Consider the instances of effective information transfer, such as relocating content from a staging table to a production table. This ensures that only pertinent entries are inserted based on specific conditions. Such practices not only enhance the management process but also facilitate improved decision-making by ensuring timely access to precise information.
How might you leverage dynamic inserts in your own operations to achieve similar benefits?
WHERE Clause: Target Specific Records for Updates and Deletes
The WHERE clause serves as a fundamental element for filtering entries in SQL commands, which is essential for using DML commands accurately in information manipulation. For instance, consider the UPDATE statement: UPDATE products SET price = price * 0.9 WHERE category = 'Electronics'; This command effectively applies a discount exclusively to products categorized as Electronics. Similarly, the DELETE command, DELETE FROM orders WHERE order_date < '2023-01-01';, targets and removes orders placed prior to 2023.
Employing the WHERE clause is essential in DML commands. Statistics indicate that around 30% of unintended record alterations arise from absent WHERE clauses, resulting in potential integrity issues. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure the WHERE clause is included in DML commands to prevent unintended changes and sustain precise information management. As Acuity Training highlights, "In 2025, information literacy is not optional - it’s essential."
Optimal methods for filtering records involve utilizing specific conditions and steering clear of broad queries to improve accuracy. How can you apply these techniques in your work to enhance data integrity? By focusing on precise filtering, you can significantly reduce the risk of errors and maintain the reliability of your data.
Handling Nested Fields in Updates: Techniques for Complex Data
Updating nested fields in databases is essential for maintaining data integrity and accuracy. Depending on the database system, specific DML commands must be employed. For example, in JSON structures, you can execute the following command:
UPDATE table_name SET json_column = JSON_SET(json_column, '$.nestedField', 'newValue') WHERE condition;
This method allows for precise updates within nested structures using DML commands, ensuring that the data remains consistent and reliable. Have you considered how these techniques can enhance your data management practices? By implementing such approaches, you can streamline your processes and improve overall data quality.
Conclusion
Mastering DML commands is pivotal for effective data management. These commands empower professionals to manipulate and maintain data with precision and efficiency. By leveraging various DML commands such as INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and MERGE, users can enhance their database operations and ensure data integrity across their systems.
Key insights from this article highlight the importance of utilizing high-quality datasets. The significance of the WHERE clause in safeguarding data integrity cannot be overstated, along with the advantages of employing techniques like batch inserts and dynamic inserts. Each command plays a critical role in streamlining database interactions, reducing errors, and improving overall performance. Furthermore, tools like Common Table Expressions (CTEs) and methods for handling nested fields simplify complex queries, making data management more accessible and efficient.
In a landscape where data accuracy and reliability are paramount, implementing best practices for DML commands is essential. By prioritizing the use of quality datasets, ensuring precise command syntax, and adopting advanced techniques, professionals can significantly elevate their data management strategies. Embracing these practices not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters informed decision-making, ultimately driving better outcomes in any data-driven environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Initial Data Offering (IDO)?
The Initial Data Offering (IDO) is a centralized hub designed for professionals to discover and access high-quality datasets, including alternative, fundamental, and ESG information, essential for mastering DML commands.
Why are high-quality datasets important?
High-quality datasets are vital for maintaining integrity and ensuring precise analysis. They facilitate efficient management and empower professionals to achieve better outcomes in their projects.
How can analytics professionals benefit from using IDO?
By utilizing IDO, analytics professionals can enhance their analytical capabilities and make informed choices based on trustworthy information sources, ultimately improving their work and results.
What is the syntax for the BigQuery INSERT statement?
The syntax for the BigQuery INSERT statement is: INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2) VALUES (value1, value2);.
What advantages do batch inserts provide in BigQuery?
Batch inserts reduce the frequency of write operations, leading to enhanced overall efficiency, with performance improvements of up to 50%, and they help reduce the load on the database during peak times.
What should users ensure when using the INSERT command?
Users should ensure that the values align with the corresponding column types and specify column names to avoid errors, especially if the schema changes.
What is the purpose of the SQL UPDATE statement?
The SQL UPDATE statement is used to modify existing records within a database, allowing for precise alterations based on specified conditions.
Why is the WHERE clause important in SQL UPDATE statements?
The WHERE clause is crucial as it specifies which records to update, preventing unintended modifications and maintaining information integrity.
What common issues arise with SQL modification queries?
Research indicates that up to 40% of SQL modification queries contain minor syntax errors that can lead to query failures, highlighting the need for accuracy in formulating these commands.
What role do DML commands play in enterprise applications?
DML commands are significant in everyday information management activities, with 85% of SQL queries performed in enterprise applications including DML commands, emphasizing their importance in database operations.