5 Best Practices for Effective Data Warehousing Solutions

5 Best Practices for Effective Data Warehousing Solutions
Overview
The article outlines five best practices for effective data warehousing solutions, underscoring the significance of centralized data storage in enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency. Key practices include:
- The utilization of ETL and ELT processes for seamless data integration
- The careful selection of the appropriate deployment model
- A comprehensive understanding of data warehouse architecture
By leveraging these practices, organizations can improve their analytics and insights, ultimately leading to enhanced data quality and more informed strategic initiatives. How can these practices be integrated into your current operations to drive better outcomes?
Introduction
Data warehousing has emerged as a cornerstone of modern business intelligence, serving as a centralized repository for data that enhances decision-making and operational efficiency. As organizations navigate the complexities of data management, it becomes crucial to understand best practices for effective data warehousing.
What strategies can organizations adopt to optimize their data warehousing solutions and ensure they harness the full potential of their information assets? This article explores five essential practices that can transform data warehousing from a mere storage solution into a powerful tool for insight and innovation.
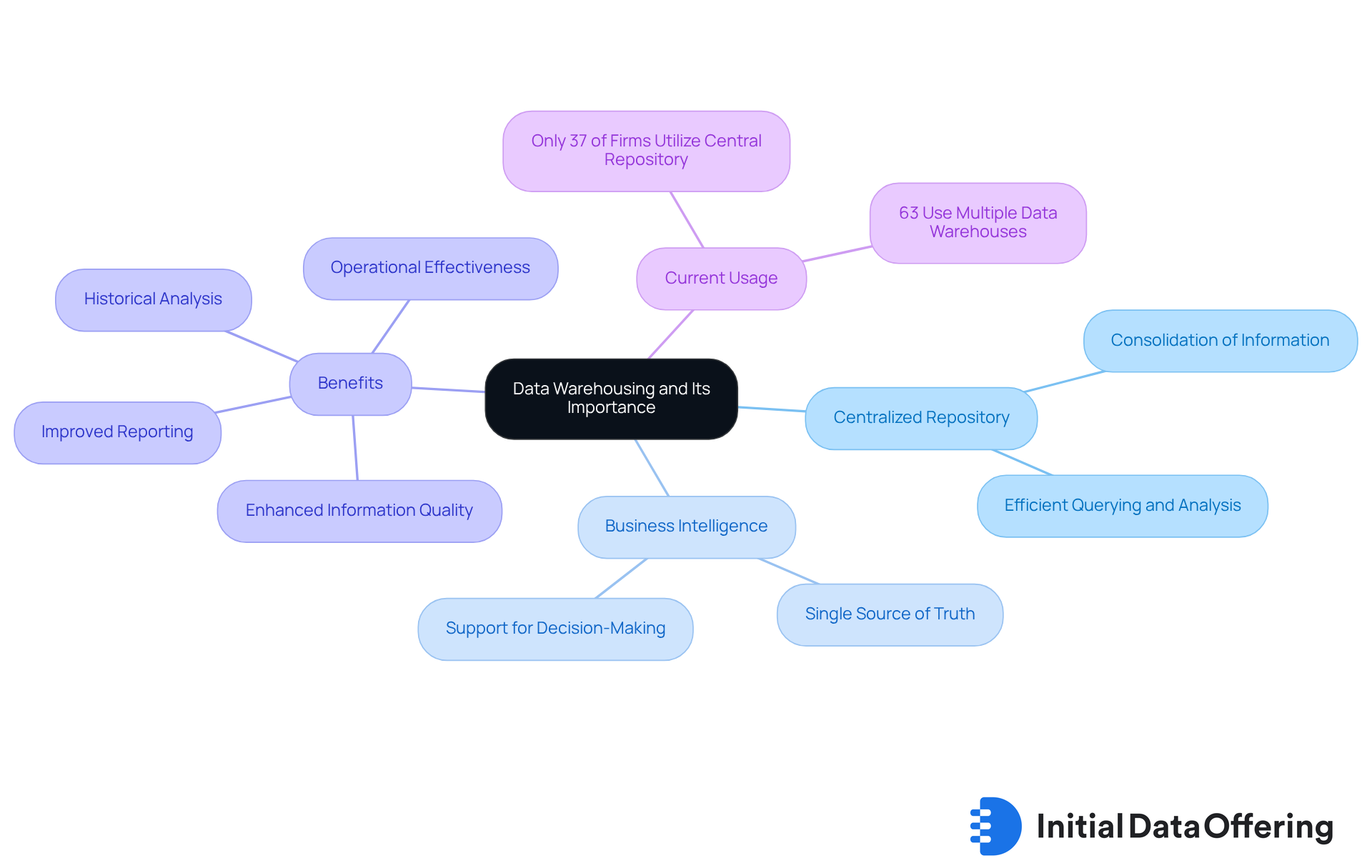
Define Data Warehousing and Its Importance
Data warehousing solutions serve as a centralized repository that consolidates information from diverse sources, facilitating efficient querying and analysis. This system is crucial in business intelligence (BI) by serving as one of the key data warehousing solutions, providing a single source of truth for decision-makers. Its significance is underscored by its ability to enhance information quality, improve reporting capabilities, and support historical analysis. By merging data, organizations can derive practical insights that drive strategic initiatives and operational effectiveness. For example, a retail firm that employs information warehousing can analyze sales patterns over time, which enhances inventory management and ultimately boosts profitability.
Despite its advantages, only 37% of firms utilize a central information repository, leaving many organizations struggling to manage their data effectively. This highlights the urgent need for robust storage solutions. As businesses increasingly recognize the importance of clean data, the role of data warehousing solutions in ensuring data integrity becomes even more critical. This shift paves the way for informed decision-making and improved business outcomes.
How might your organization leverage information warehousing to enhance its operations?
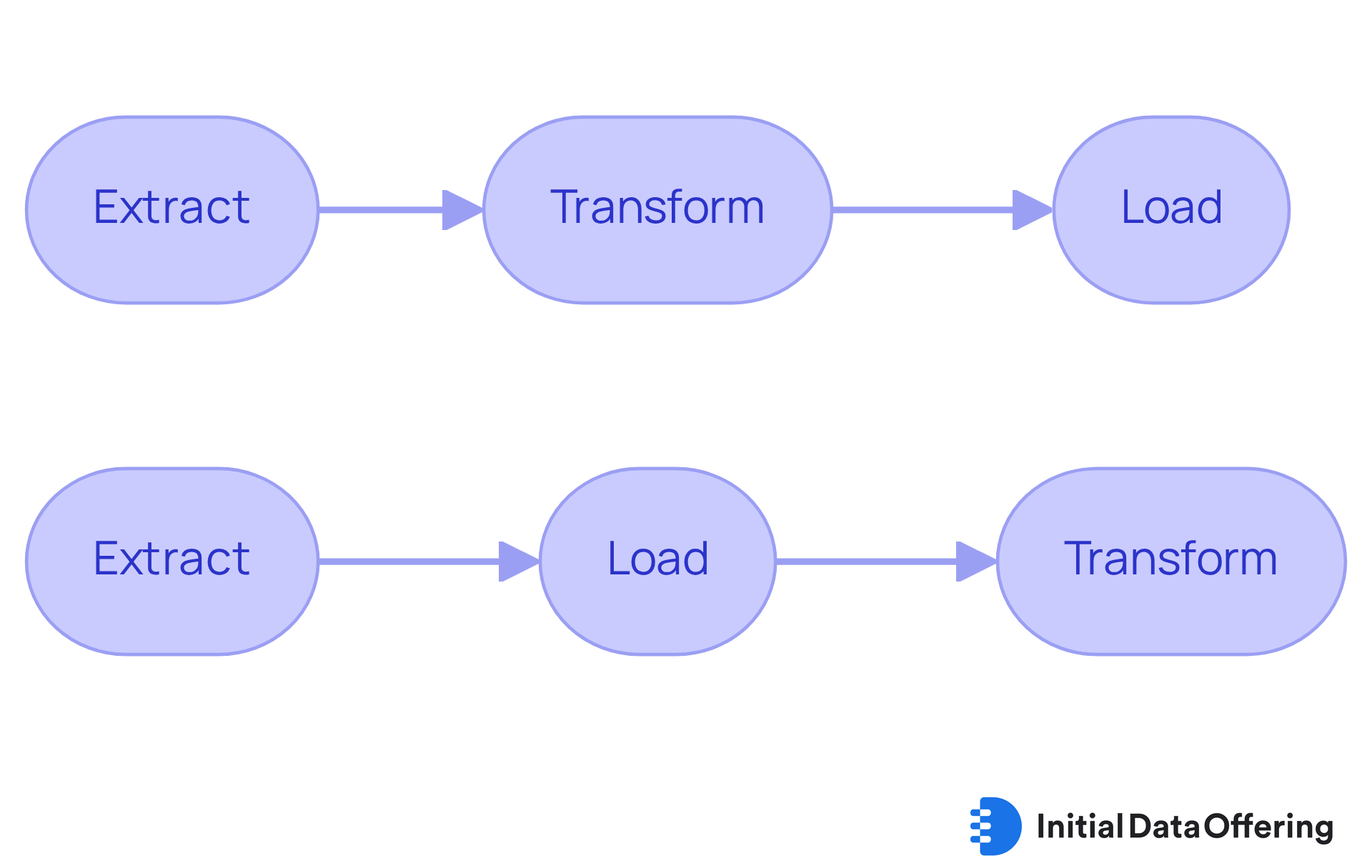
Utilize ETL and ELT Processes for Data Integration
Organizations can effectively incorporate information into a storage facility by employing ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) or ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) processes. ETL is particularly advantageous when information requires extensive cleaning or restructuring prior to analysis. This approach involves retrieving information from source systems, converting it into an appropriate format, and then loading it into the information repository. For instance, a financial organization may employ ETL to carefully refine transaction information, ensuring accuracy and reliability before conducting any analysis. According to industry projections, the ETL market is expected to grow from $7.63 billion in 2024 to $29.04 billion by 2029, underscoring the increasing importance of these processes in the current market landscape.
In contrast, ELT enables unprocessed information to be loaded straight into the storage facility, where it is modified as needed. This approach is often faster and more efficient, especially in cloud environments, as it leverages the processing power of the warehouse itself. A tech firm, for example, might adopt ELT to swiftly load user interaction information, facilitating real-time analytics and quicker insights. How might your organization benefit from adopting ELT in its data strategy?
Current trends suggest a rising inclination for ELT in cloud-based data warehousing solutions, as companies seek to capitalize on the scalability and flexibility these platforms provide. Optimal approaches indicate that regardless of the technique selected, ensuring information quality through thorough cleaning and validation procedures is crucial for effective decision-making and analysis. As Donal Tobin highlights, information quality continues to be a major challenge; organizations must guarantee reliability, lineage, and validation at every phase of the pipeline to prevent expensive mistakes. Furthermore, the introduction of a cloud-based information storage system at Tarleton University demonstrates the practical advantages of ETL processes, leading to cost savings and improved reporting capabilities. Addressing common pitfalls, such as the significance of information quality checks, is essential for successful integration.
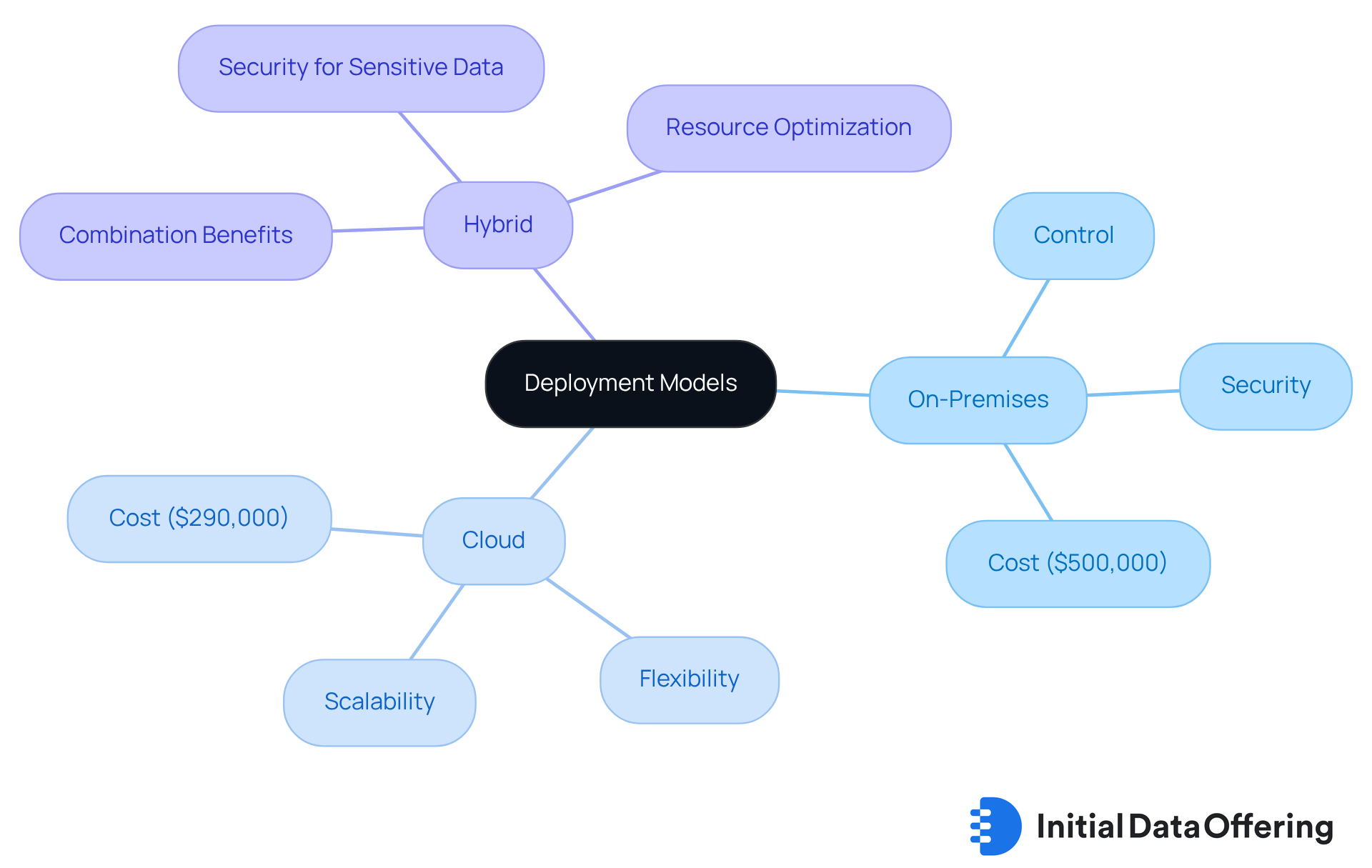
Choose the Right Deployment Model: On-Premises, Cloud, or Hybrid
When selecting a deployment framework for an information repository, organizations must consider their specific needs and limitations.
-
On-premises solutions provide complete control and security, yet they necessitate significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. The projected annual expense for an on-site information repository is approximately $500,000, considerably higher than the typical cost of a cloud-hosted information storage solution, which is around $290,000.
-
Cloud-based storage warehouses are considered effective data warehousing solutions that offer scalability, flexibility, and reduced initial expenses, making them ideal for companies looking to lower infrastructure overhead.
-
Hybrid models for data warehousing solutions combine both approaches, allowing organizations to benefit from the strengths of both on-premises and cloud solutions. For instance, a healthcare entity might opt for a hybrid model to keep sensitive patient information on-premises while utilizing the cloud for less sensitive analytics tasks.
This strategy not only enhances information security but also optimizes resource distribution, enabling organizations to adapt effectively to evolving information needs.
How might these frameworks align with your organization’s objectives?
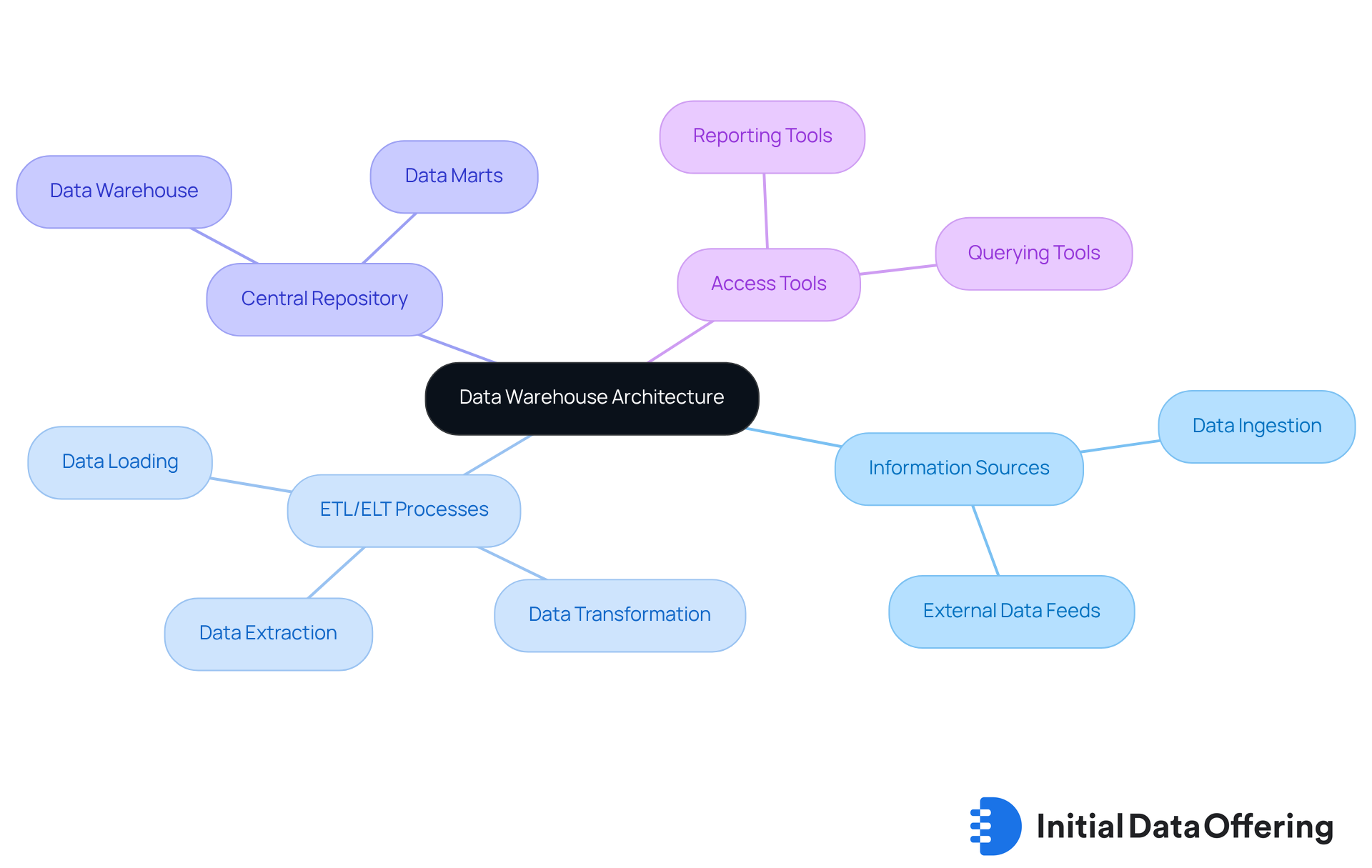
Understand Data Warehouse Architecture and Components
Information storage architecture encompasses several critical components:
- Information sources
- ETL/ELT processes
- A central repository
- Access tools for querying and reporting
This architecture can be visualized in layers, starting from information ingestion, progressing to information storage, and culminating in information presentation. Understanding these elements is vital for organizations aiming to construct data warehousing solutions that fulfill their analytical needs.
How might a well-designed information storage architecture impact your organization’s efficiency? For example, a manufacturing firm may implement a star schema architecture to optimize query performance for sales and production data, leading to quicker insights into operational efficiency.
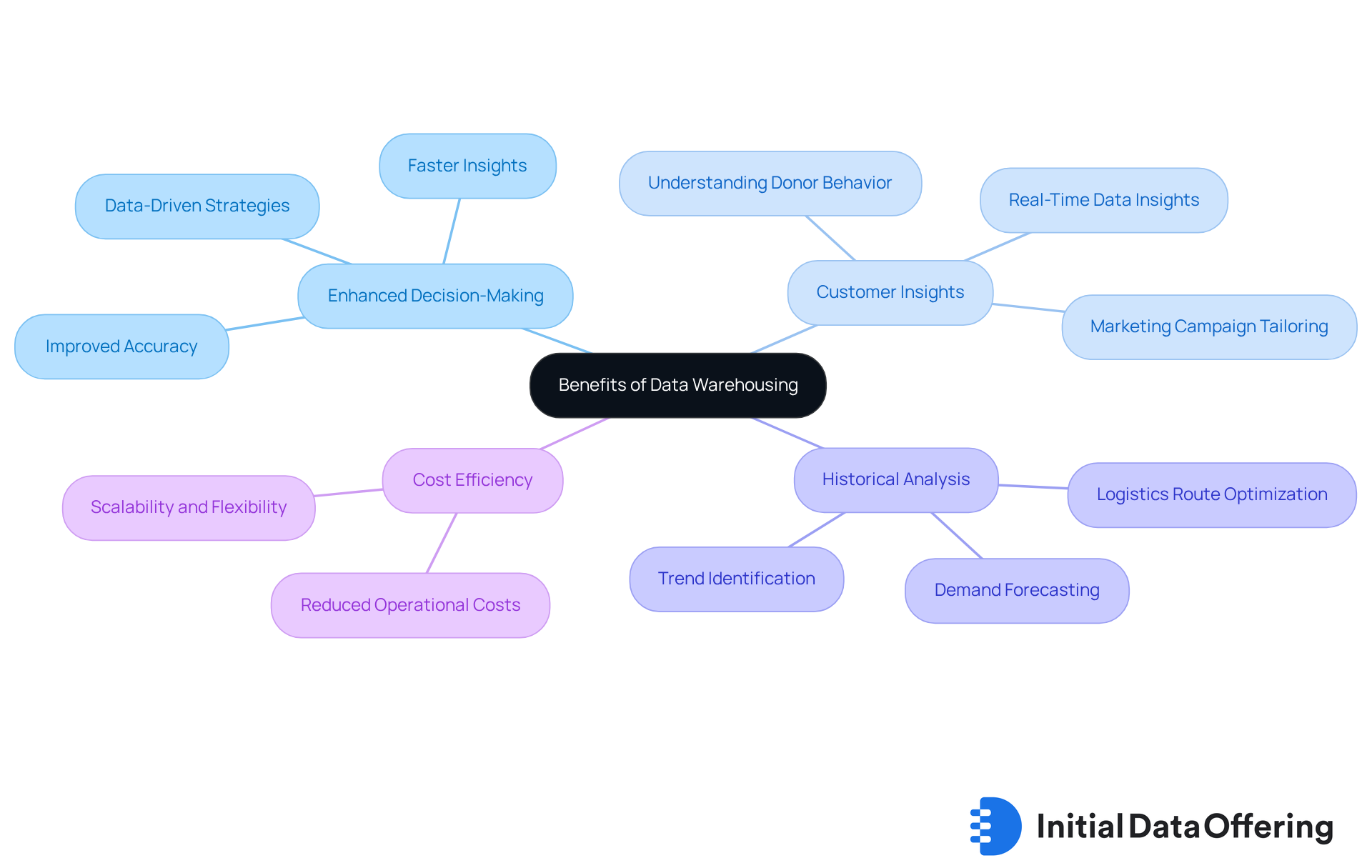
Leverage the Benefits of Data Warehousing for Enhanced Decision-Making
Information storage serves as a centralized repository for high-quality information, significantly enhancing decision-making abilities. This feature allows entities to conduct thorough analyses, leading to practical insights. For example, marketing teams can leverage information storage to analyze customer behavior across various channels, enabling them to tailor campaigns effectively and achieve higher engagement rates. Notably, companies employing data-driven strategies are three times more likely to experience substantial improvements in decision-making compared to their peers, according to PwC.
Moreover, data warehousing solutions facilitate historical analysis, empowering organizations to identify trends over time and make proactive decisions. A pertinent example is a logistics firm that utilized historical shipping data to optimize routes, resulting in reduced costs and improved service delivery. This capability is crucial, as 60% of users cite process enhancement and cost-effectiveness as primary reasons for adopting analytics, highlighting the importance of information quality in decision-making.
By harnessing the power of information storage, organizations can enhance their analytical capabilities, leading to improved customer insights and more effective marketing strategies. Additionally, companies that utilize real-time data insights are significantly more likely to attract new customers and achieve profitability, underscoring the transformative potential of data warehousing solutions.
Conclusion
Data warehousing solutions serve as a cornerstone for organizations aiming to consolidate and analyze their data effectively. These systems provide a centralized repository that enhances information quality and supports informed decision-making. The increasing acknowledgment of the significance of clean and reliable data emphasizes the necessity for businesses to adopt robust data warehousing practices.
Key practices include:
- The utilization of ETL and ELT processes for effective data integration
- The careful selection of deployment models—whether on-premises, cloud, or hybrid
- A solid understanding of data warehouse architecture
Each of these components is crucial for enabling organizations to leverage their data, enhancing operational efficiency and strategic insights. Companies that harness quality data are better positioned to identify trends and optimize their strategies, thereby improving decision-making capabilities.
Ultimately, embracing these best practices fosters a culture of data-driven decision-making and enables organizations to maintain competitiveness in an increasingly data-centric landscape. By investing in effective data warehousing solutions, companies can unlock the full potential of their data, driving innovation and achieving sustained growth. How might your organization benefit from implementing these practices?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is data warehousing and why is it important?
Data warehousing is a centralized repository that consolidates information from various sources, allowing for efficient querying and analysis. It is important in business intelligence as it provides a single source of truth, enhances information quality, improves reporting capabilities, and supports historical analysis, which helps organizations derive insights for strategic initiatives and operational effectiveness.
How can data warehousing benefit organizations?
Data warehousing can help organizations analyze trends, such as sales patterns over time, which improves inventory management and boosts profitability. It also supports informed decision-making and improved business outcomes through enhanced data integrity.
What are ETL and ELT processes in data integration?
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) involves extracting data from source systems, transforming it into an appropriate format, and then loading it into a data repository. ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) allows unprocessed data to be loaded directly into the storage facility, where it is transformed as needed, often leading to faster and more efficient data processing.
When is ETL preferred over ELT?
ETL is preferred when data requires extensive cleaning or restructuring before analysis, as it ensures accuracy and reliability. For example, financial organizations may use ETL to refine transaction data prior to analysis.
What advantages does ELT provide, particularly in cloud environments?
ELT enables faster and more efficient data processing by loading unprocessed data directly into the storage facility, leveraging the processing power of the warehouse itself. This is particularly beneficial in cloud environments, allowing for real-time analytics and quicker insights.
What trends are emerging regarding ETL and ELT in the market?
There is a rising inclination for ELT in cloud-based data warehousing solutions as companies seek scalability and flexibility. The ETL market is also expected to grow significantly, indicating the increasing importance of these processes in data management.
What challenges do organizations face with information quality in data processes?
Organizations must ensure reliability, lineage, and validation of data at every phase of the pipeline to prevent costly mistakes. Information quality checks are essential for successful data integration and analysis.
Can you provide an example of successful ETL implementation?
The introduction of a cloud-based information storage system at Tarleton University demonstrated the practical advantages of ETL processes, leading to cost savings and improved reporting capabilities.