10 Essential Data Manipulation Language Commands for Analysts

10 Essential Data Manipulation Language Commands for Analysts
Overview
This article presents ten essential Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands that analysts must master to enhance their data management capabilities. The commands discussed include:
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
- MERGE
- SELECT
Each command serves a crucial role in efficient data manipulation. These commands not only facilitate the handling of data but also maintain data integrity, which is vital for informed decision-making across various analytical contexts.
Understanding the features of these commands is paramount. For instance, the INSERT command allows for the addition of new records, while UPDATE modifies existing data. DELETE provides the means to remove unnecessary information, and MERGE combines data from different sources effectively. SELECT is fundamental for querying and retrieving specific data, making it indispensable for analysis.
The advantages of mastering these commands extend beyond mere functionality. By leveraging these DML commands, analysts can ensure that their data remains accurate and relevant, ultimately leading to better insights and decisions. How might the effective use of these commands improve your analytical processes?
In conclusion, the mastery of these ten DML commands empowers analysts to manipulate data efficiently and maintain its integrity. This not only enhances their analytical capabilities but also supports informed decision-making in their respective fields. As you consider the implications of these commands, think about how they can be integrated into your data management practices for optimal results.
Introduction
In a world increasingly driven by data, the ability to manipulate and analyze information effectively is paramount for analysts across various sectors. This article explores ten essential Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands that empower data professionals to streamline their workflows and enhance decision-making capabilities. These commands not only improve operational efficiency but also ensure the integrity and accuracy of data.
As organizations grapple with the complexities of managing vast datasets, how can analysts leverage these commands to achieve their goals? This exploration will provide actionable insights into the effective use of DML commands, highlighting their significance in today’s data-centric landscape.
Initial Data Offering: Access Diverse Datasets for Effective Data Manipulation
The Initial Information Offering (IDO) serves as a crucial centralized hub for information exchange, providing a diverse array of datasets tailored for various sectors. Analysts can access alternative information, fundamental metrics, and ESG insights, among others, which significantly enhance their capabilities with data manipulation language commands. Notably, research indicates that 41% of companies depend on the Highest Paid Person's Opinion (HiPPO) for business strategies rather than data-driven insights. This statistic underscores the increasing importance of alternative datasets in today's decision-making landscape.
By leveraging these unique datasets, data professionals can extract actionable insights that inform decision-making and strategic planning across sectors. IDO's commitment to curating high-quality collections not only facilitates effective data manipulation language commands but also empowers analysts to drive innovation and improve outcomes in their respective fields. Successful implementations of information marketplaces, as discussed by industry leaders, have shown that access to diverse datasets significantly enhances the analytical process. This access enables organizations to fully harness their information assets.
As emphasized by Thomas Redman, the role of analytics professionals and tools in helping organizations manage their information efficiently cannot be overstated. This makes centralized information exchange platforms like IDO essential for contemporary practices. How can your organization leverage IDO's offerings to enhance its analytical capabilities and drive better business outcomes?
INSERT Command: Add New Records to Your Database Efficiently
The INSERT operation in SQL is one of the data manipulation language commands that serves as a fundamental tool for analysts, facilitating the addition of new records to a database table. The basic syntax is straightforward: INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2) VALUES (value1, value2);. This instruction can be applied for both single and multiple rows, enhancing its versatility for information entry tasks. For example, to add a new customer record, one might use: INSERT INTO Customers (Name, Age) VALUES ('John Doe', 30);.
Utilizing data manipulation language commands, such as the INSERT instruction, effectively can significantly streamline database management processes. Companies, particularly in e-commerce, leverage SQL Server Bulk Insert to manage millions of daily transactions, which decreases loading times and enhances operational efficiency. The instruction INSERT INTO Products(ProductName, SupplierID) VALUES ('ProductA', 1), ('ProductB', 2), ('ProductC', 3); illustrates how multiple entries can be added in a single operation, saving time and reducing the risk of errors. Research indicates that employing data manipulation language commands, particularly the INSERT function, can save an average of 30% in time compared to manual entry techniques, allowing analysts to focus on more strategic tasks.
Specialists in database administration emphasize the importance of mastering data manipulation language commands, especially the INSERT instruction, noting that it not only keeps databases current but also preserves the integrity of information through batch inserts and conflict resolution. For instance, the instruction INSERT INTO PremiumUsers SELECT * FROM Users WHERE UserType = 'Premium'; can transfer millions of records within seconds, demonstrating its efficiency in handling large datasets. This capability is crucial for maintaining performance as information volumes grow.
Recent advancements in SQL information entry techniques have further optimized the INSERT function, making it an essential skill for professionals seeking to enhance their productivity and information management capabilities. By adopting best practices and understanding the nuances of the INSERT function—including the significance of information integrity and conflict resolution—analysts can ensure their databases remain relevant and responsive to business needs.
UPDATE Command: Modify Existing Data to Ensure Accuracy
The UPDATE instruction, which is one of the data manipulation language commands, is a critical feature for modifying existing records in a database, ensuring data accuracy and relevance. Its syntax is straightforward: UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2 WHERE condition;. For example, to update a customer's age, one would use: UPDATE Customers SET Age = 31 WHERE Name = 'John Doe';. This function is vital for maintaining current information, which is essential for effective analysis.
The advantage of the UPDATE instruction lies in its ability to keep data up-to-date, with approximately 70% of analysts relying on it to maintain information integrity, according to industry insights. Organizations like Salesforce and Amazon exemplify the practical applications of advanced SQL UPDATE methods to manage customer data and optimize inventory. For instance, Amazon dynamically adjusts product prices based on market conditions and demand, illustrating the real-world benefits of this system.
Recent advancements in data modification techniques, such as indexing, batch updates, and transactions, further enhance the efficiency of the UPDATE operation. These innovations allow for more complex and targeted modifications, ultimately benefiting organizations by improving their data management capabilities. As noted by the Codecademy Team, "The UPDATE statement in SQL is one of the data manipulation language commands that is essential for modifying existing records, allowing users to update table attributes efficiently."
However, it is crucial to exercise caution when using the SQL UPDATE statement without a WHERE clause, as this can lead to unintended changes across all rows in a table. Mastering the UPDATE function is essential for maintaining precise and reliable datasets, which in turn enhances decision-making processes.
DELETE Command: Remove Unwanted Records from Your Database
The DELETE instruction serves as a fundamental tool for analysts, enabling the removal of specific records from a database. Its syntax is straightforward: DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;. For example, to delete a customer record, one might execute: DELETE FROM Customers WHERE Name = 'John Doe';. However, incorporating the WHERE clause is crucial to prevent the unintentional removal of all records, which can lead to significant integrity concerns.
Effective management of datasets relies heavily on the proper use of data manipulation language commands, especially the DELETE command. Over 70% of information management specialists emphasize the importance of effective deletion strategies in relational databases. As one professional stated, "Implementing sound deletion strategies is essential for maintaining relevant datasets." Businesses that adopt best practices, such as backing up data before deletion and testing queries, can safeguard against unintended data loss.
Recent discussions in the field highlight that frequent errors, such as neglecting the WHERE clause, mismanaging operations, and misunderstanding cascading deletes, can result in costly mistakes. By mastering data manipulation language commands such as the DELETE command and adhering to best practices, analysts can ensure their datasets remain streamlined and relevant. This ultimately enhances operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities. Furthermore, employing advanced techniques like transactions and batch processing can optimize performance during deletion operations. It is also vital to manage interconnected data effectively, as removing entries from multiple tables simultaneously is often necessary to maintain consistency within a database. In certain scenarios, truncation can be up to 100 times faster than deletion, making it a valuable option for professionals dealing with large datasets.

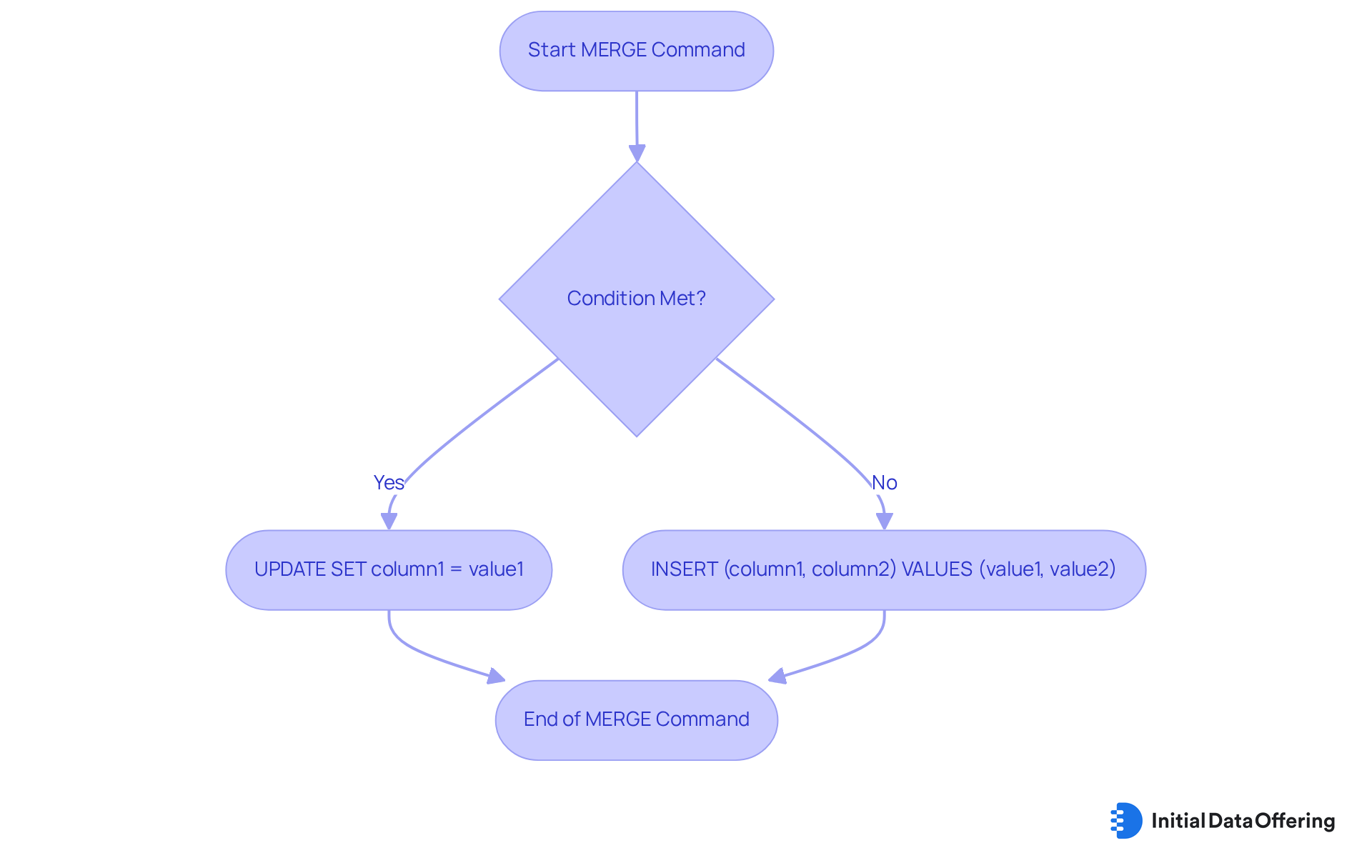
MERGE Command: Combine INSERT and UPDATE for Advanced Data Management
The MERGE instruction effectively combines the functionalities of INSERT and UPDATE through data manipulation language commands, enabling analysts to synchronize two tables based on a specified condition. This dual capability is crucial for data manipulation language commands in data management, as it allows for both updating existing records and inserting new ones when necessary. The syntax for this powerful instruction is:
MERGE INTO target_table
USING source_table
ON condition
WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET column1 = value1
WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT (column1, column2) VALUES (value1, value2);
What advantages does this bring? By preserving information integrity, the MERGE instruction ensures that records are either revised or included as needed through data manipulation language commands. This not only streamlines information management tasks but also enhances the overall accuracy of data manipulation language commands. For professionals dealing with large datasets, understanding and utilizing the MERGE instruction can significantly improve efficiency and reliability in data operations.
In summary, the MERGE instruction is a vital tool for analysts, offering a seamless way to manage data synchronization. Its ability to handle both updates and inserts makes it indispensable for maintaining data integrity and operational efficiency.
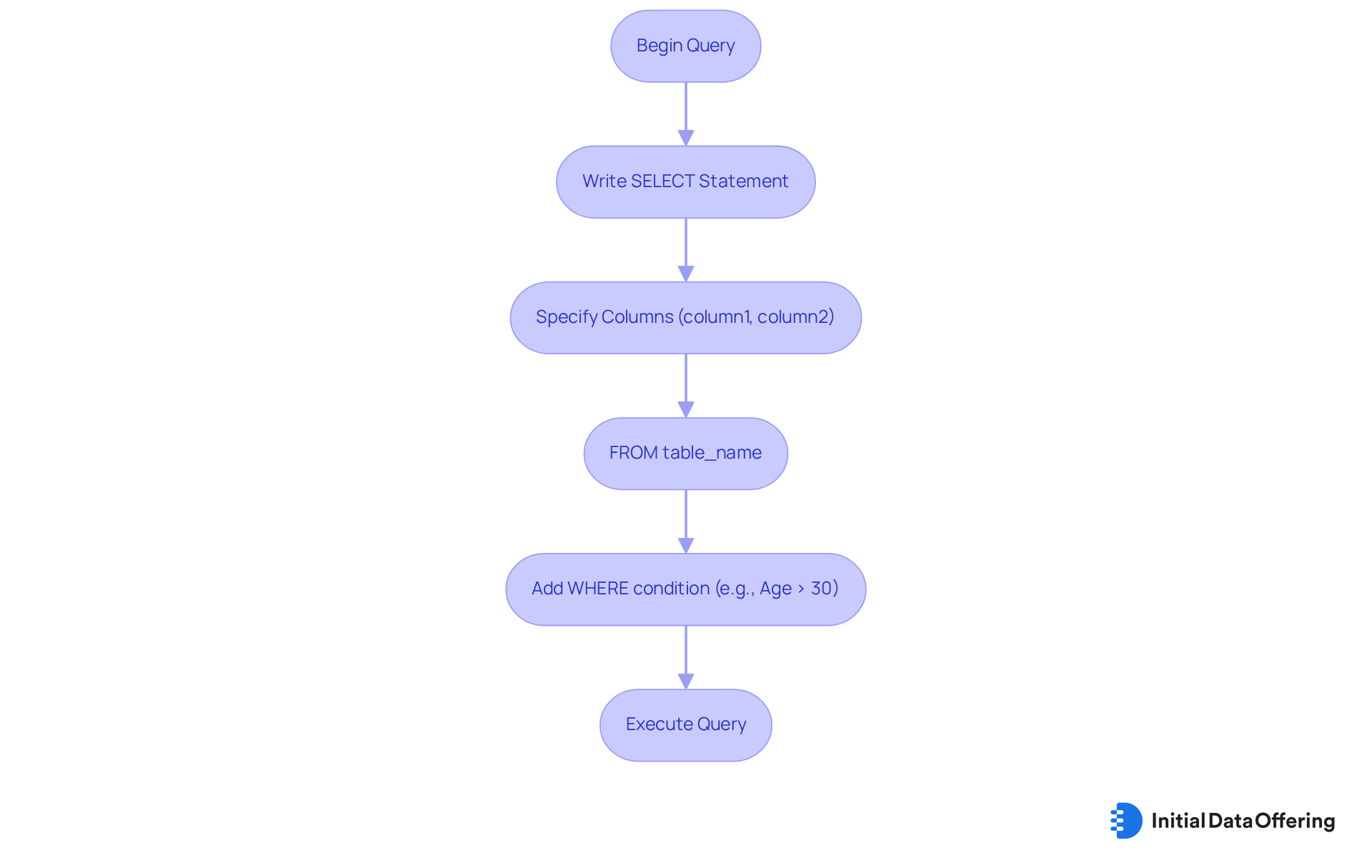
SELECT Command: Retrieve Data for Informed Decision-Making
The SELECT instruction is one of the essential data manipulation language commands used for obtaining information from a database. Its basic syntax is straightforward: SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name WHERE condition;. For instance, if you wish to retrieve all customers over the age of 30, you would write: SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Age > 30;. This instruction is essential for analysts, as it allows them to use data manipulation language commands to collect the necessary information for examination and decision-making. By utilizing data manipulation language commands, analysts can effectively extract valuable insights from the available resources using the SELECT instruction. How might this capability enhance your data analysis processes?
Transactions: Ensure Data Integrity During DML Operations
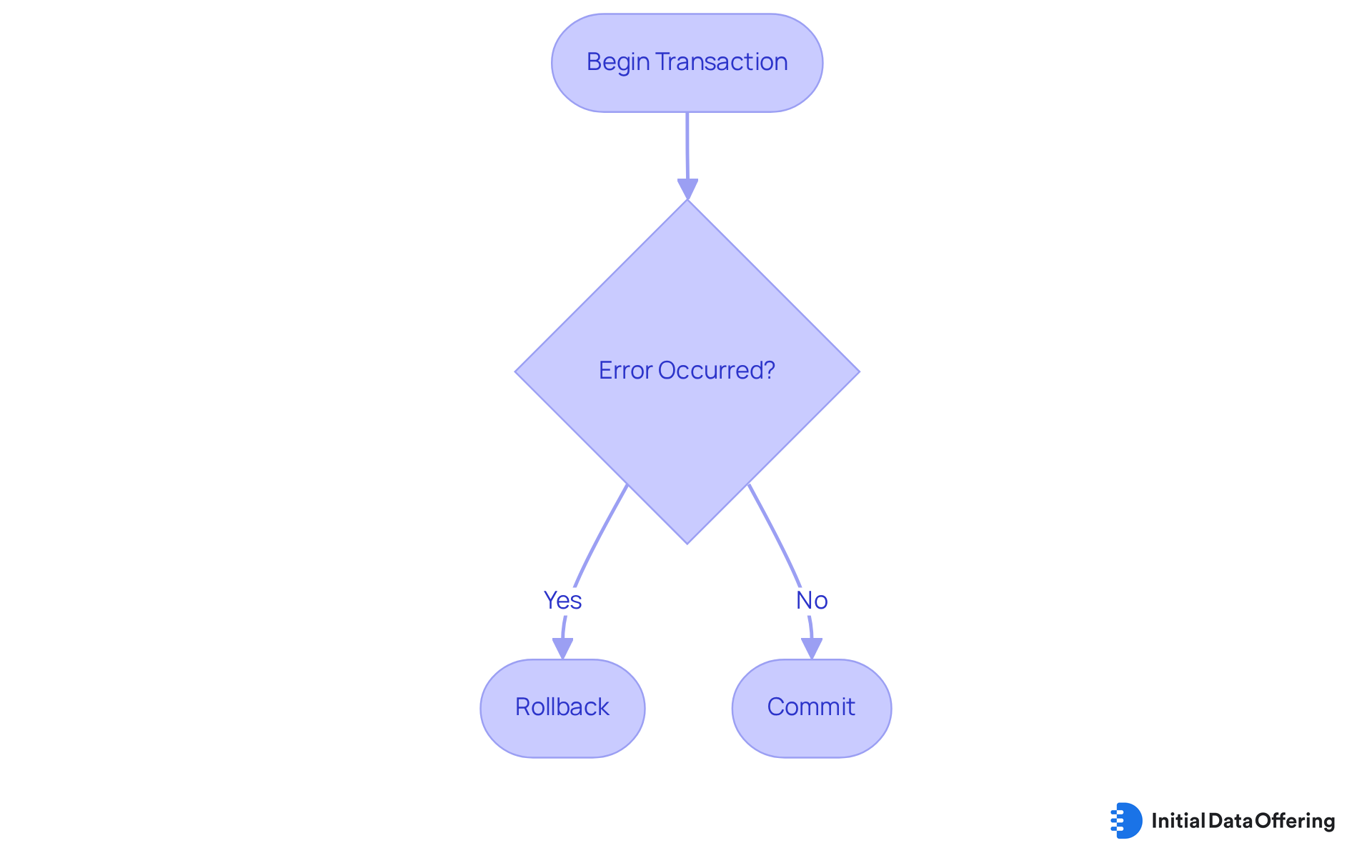
Transactions in SQL are a critical mechanism for grouping multiple data manipulation language commands into a cohesive unit of work. This ensures that either all operations are executed successfully or none at all, which is vital for maintaining data integrity across various applications. The basic instructions for handling operations consist of BEGIN TRANSACTION, COMMIT, and ROLLBACK. For instance, if an error occurs during a series of updates, issuing a ROLLBACK command restores all changes made during the operation, safeguarding the database's integrity.
Organizations across sectors, particularly in banking and finance, depend significantly on process management to ensure data integrity. Banking systems, for example, employ exchanges to handle fund transfers, ensuring that all steps—such as debiting one account and crediting another—are completed successfully or not at all. This adherence to atomic operations prevents inconsistencies and maintains accurate account balances, which is crucial for customer trust and operational reliability.
Insights from database specialists emphasize the importance of managing operations during data manipulation language commands activities. They stress that preserving information integrity is crucial, especially in high-concurrency situations. Recent advancements in SQL management have introduced sophisticated methods, such as savepoints, which enable partial rollbacks within processes, improving control and efficiency. As the TiDB Team observes, SQL processes offer a strong framework for handling intricate operations effectively.
Statistics reveal that a substantial percentage of analysts—over 70%—employ activities to maintain data integrity in their operations. This trend underscores the growing recognition of the importance of robust transaction management in today’s data-driven landscape, where the integrity of information is crucial for informed decision-making. How are you ensuring data integrity in your operations? Consider the implications of adopting advanced transaction management techniques.
Parameterized Queries: Enhance Security in Data Manipulation
Parameterized queries are a crucial feature in database management, allowing users to execute SQL statements with parameters. This approach offers significant advantages, particularly in enhancing security by preventing SQL injection attacks. For instance, the syntax typically includes placeholders for parameters, as seen in: SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Name = ?. By utilizing parameterized queries, researchers can treat user input as mere information rather than executable code. This not only safeguards their database operations but also fosters trust in the system.
How might incorporating parameterized queries into your own projects improve security? Understanding and implementing this feature can lead to more secure and robust database interactions.
Error Handling: Manage Exceptions in Data Manipulation Commands
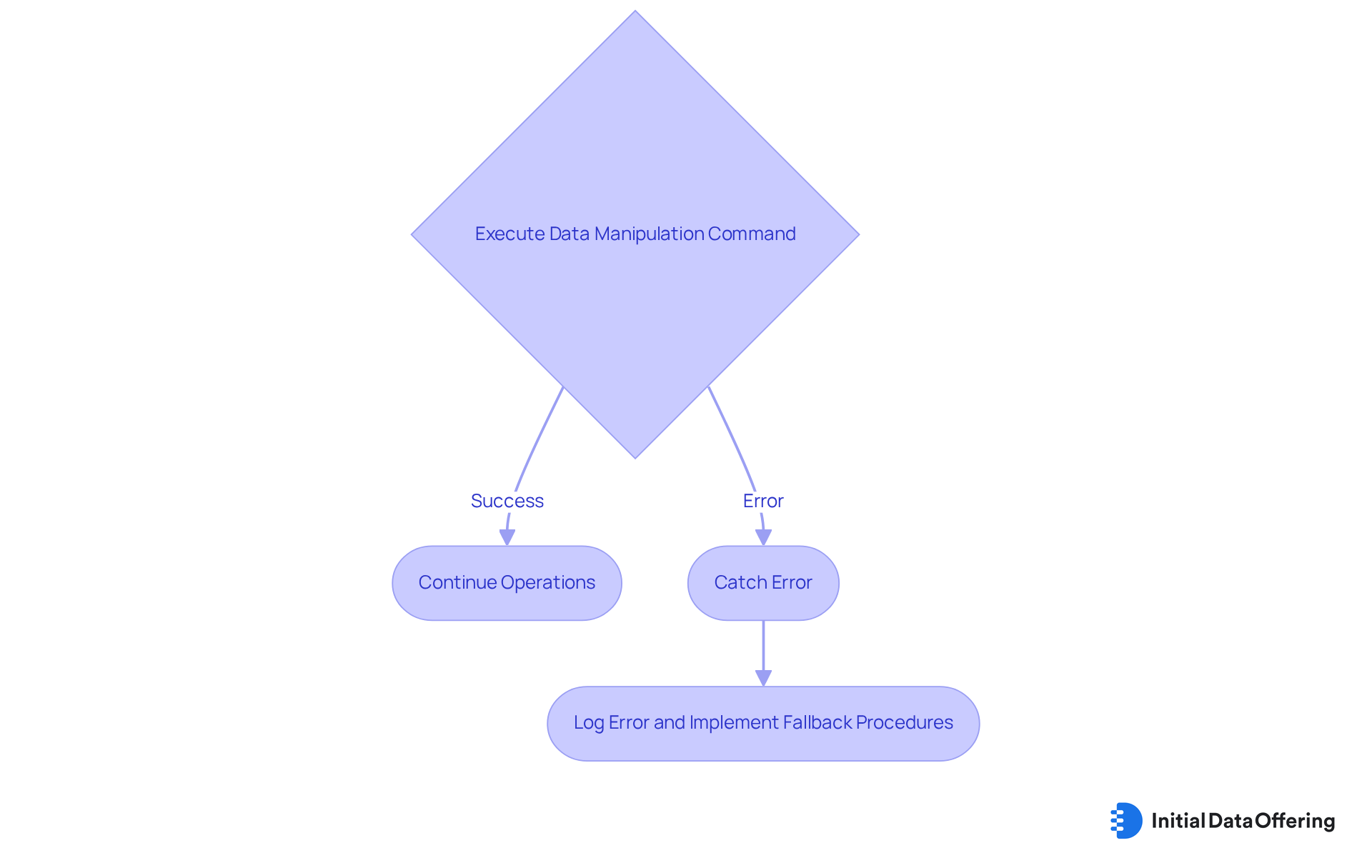
Error handling in SQL is effectively managed through the use of TRY...CATCH blocks. These blocks allow users to catch and respond to errors that may occur during data manipulation language commands operations. For instance, consider the following SQL code:
BEGIN TRY
UPDATE Customers SET Age = Age + 1;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
PRINT 'An error occurred';
END CATCH
This method not only helps analysts implement fallback procedures but also enables them to log errors for further investigation. As a result, data integrity is preserved even in the face of unforeseen issues. How might you leverage this approach in your own SQL operations to enhance reliability and maintain data quality?
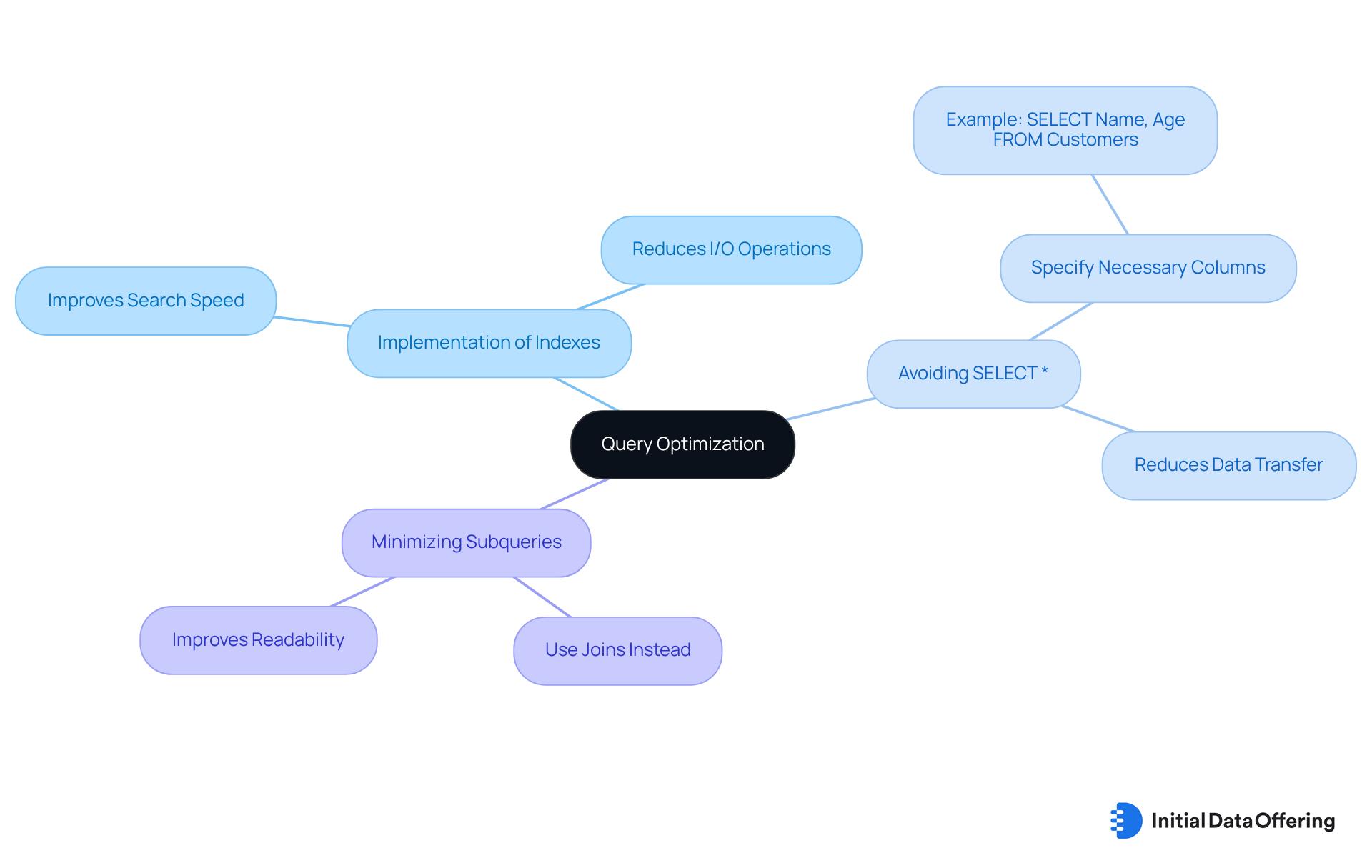
Query Optimization: Improve Performance of DML Operations
Query optimization encompasses various techniques designed to enhance the performance of SQL commands, particularly in data manipulation language commands. Key strategies include:
- The implementation of indexes
- The avoidance of using
SELECT * - The minimization of subqueries
For instance, rather than employing SELECT *, it is more efficient to specify only the necessary columns, such as in the query: SELECT Name, Age FROM Customers;. By optimizing queries in this manner, analysts can significantly reduce execution time, leading to improved overall efficiency in their data manipulation language commands tasks. This not only streamlines processes but also empowers analysts to derive insights more rapidly, ultimately enhancing decision-making capabilities.
Conclusion
Understanding and mastering data manipulation language (DML) commands is essential for analysts aiming to enhance their data management and analytical capabilities. This article highlights ten critical commands that not only facilitate effective data manipulation but also empower professionals to extract meaningful insights from diverse datasets. By leveraging these commands, analysts can ensure their databases remain accurate, relevant, and responsive to evolving business needs.
Key insights discussed include the importance of commands such as:
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
- MERGE
These commands streamline data management processes and enhance operational efficiency, providing analysts with the tools necessary to respond swiftly to changing data requirements. The article emphasizes the significance of using parameterized queries for security and highlights the necessity of robust error handling and transaction management to maintain data integrity. Furthermore, query optimization strategies are presented as vital techniques for improving the performance of DML operations, ultimately leading to faster and more reliable data analysis.
In a data-driven landscape, the ability to manipulate and manage data effectively is paramount. Analysts are encouraged to adopt best practices around these DML commands and continually seek ways to optimize their processes. By embracing the tools and techniques outlined, organizations can harness the full potential of their data, driving informed decision-making and fostering innovation across various sectors. How can you apply these DML commands in your organization to enhance data management and analysis? The opportunity to improve your data practices is at your fingertips.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Initial Data Offering (IDO)?
The Initial Data Offering (IDO) is a centralized hub for information exchange that provides a diverse array of datasets tailored for various sectors, enhancing data manipulation capabilities for analysts.
How can IDO benefit data professionals?
By leveraging unique datasets from IDO, data professionals can extract actionable insights that inform decision-making and strategic planning across different sectors.
What is the significance of alternative datasets in decision-making?
Research shows that 41% of companies rely on the Highest Paid Person's Opinion (HiPPO) for business strategies instead of data-driven insights, highlighting the importance of alternative datasets in today’s decision-making landscape.
What is the INSERT command in SQL?
The INSERT command in SQL is a fundamental data manipulation language command that facilitates the addition of new records to a database table using the syntax: INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2) VALUES (value1, value2).
How can the INSERT command improve database management?
The INSERT command streamlines database management processes, allowing for efficient addition of both single and multiple rows, which can save time and reduce errors compared to manual entry techniques.
What are the advantages of using the UPDATE command in SQL?
The UPDATE command is crucial for modifying existing records in a database, ensuring data accuracy and relevance, with approximately 70% of analysts relying on it to maintain information integrity.
What precautions should be taken when using the UPDATE command?
It is important to use the SQL UPDATE statement with a WHERE clause to avoid unintended changes across all rows in a table, which can lead to significant data inaccuracies.
How do advancements in SQL techniques enhance the INSERT and UPDATE commands?
Recent advancements such as indexing, batch updates, and transactions enhance the efficiency of the INSERT and UPDATE operations, allowing for more complex and targeted modifications to improve data management capabilities.