10 Cyber Security Strategies Every Business Should Implement

10 Cyber Security Strategies Every Business Should Implement
Introduction
In an era where digital threats are more prevalent than ever, businesses are tasked with the critical responsibility of protecting their sensitive information from a variety of cyberattacks. Implementing effective cybersecurity strategies is not merely a necessity; it is a strategic imperative that can significantly influence an organization's survival. This article delves into ten essential cybersecurity practices that every business should adopt to strengthen their defenses, enhance resilience, and mitigate risks.
But with a multitude of options available, how can organizations prioritize their efforts to ensure they are genuinely safeguarded against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats? By understanding the features, advantages, and benefits of these practices, businesses can make informed decisions that bolster their security posture.
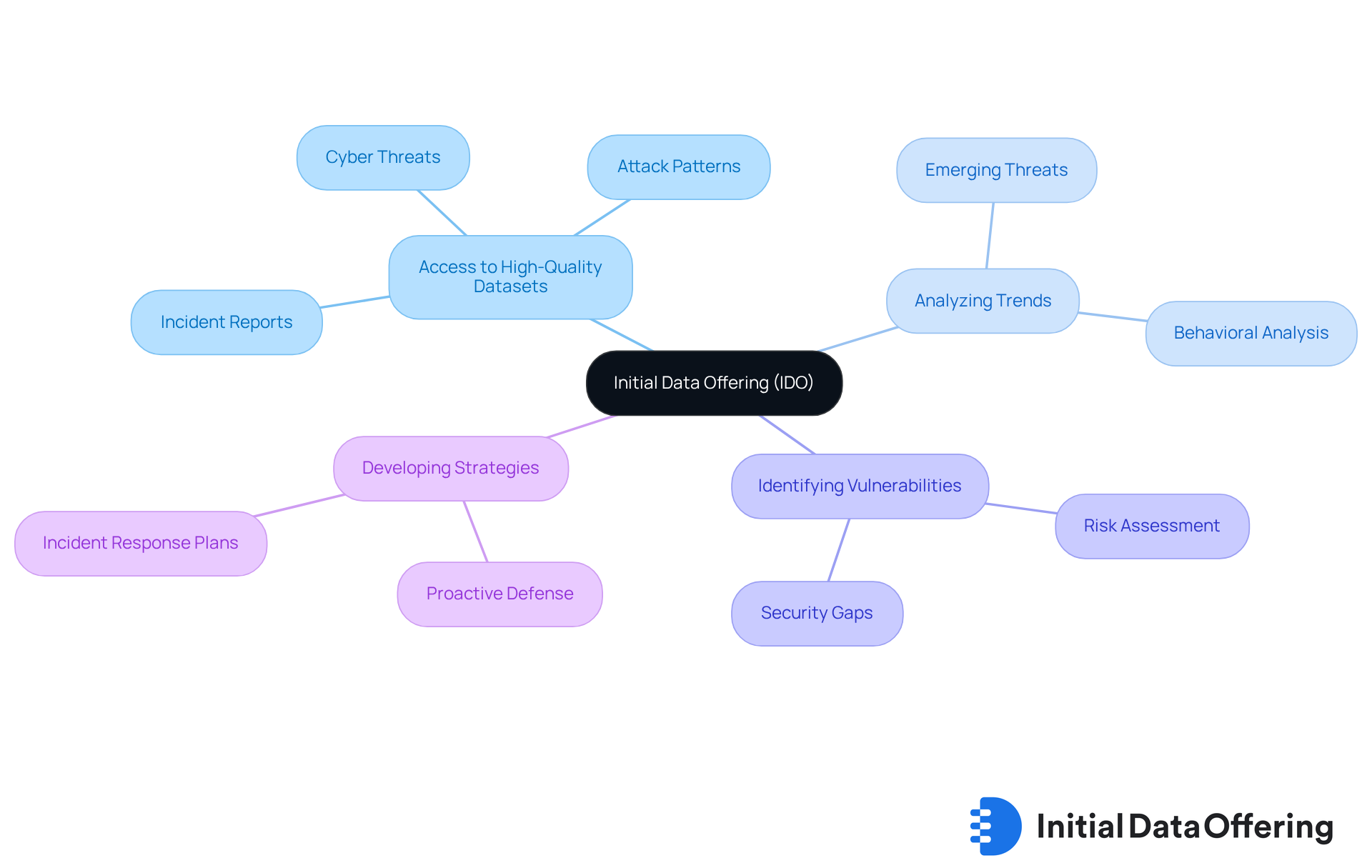
Initial Data Offering: Access High-Quality Datasets for Cybersecurity Insights
Initial Data Offering (IDO) serves as a vital asset for enterprises aiming to bolster their security protocols. By providing access to high-quality datasets, IDO enables organizations to analyze emerging trends, identify vulnerabilities, and develop informed strategies. For instance, datasets detailing cyber threats, attack patterns, and incident reports allow businesses to tailor their defenses and proactively mitigate potential risks.
What if your organization could leverage these insights for data-driven decision-making? By applying the knowledge gained from these datasets, cyber security businesses can significantly enhance their overall security posture. As organizations increasingly adopt data analytics, cyber security businesses can help them refine their security strategies, ensuring resilience against evolving threats.
In summary, the integration of IDO not only empowers enterprises with critical information but also fosters a proactive approach to security. This shift towards data-centric strategies is essential in today’s rapidly changing threat landscape.
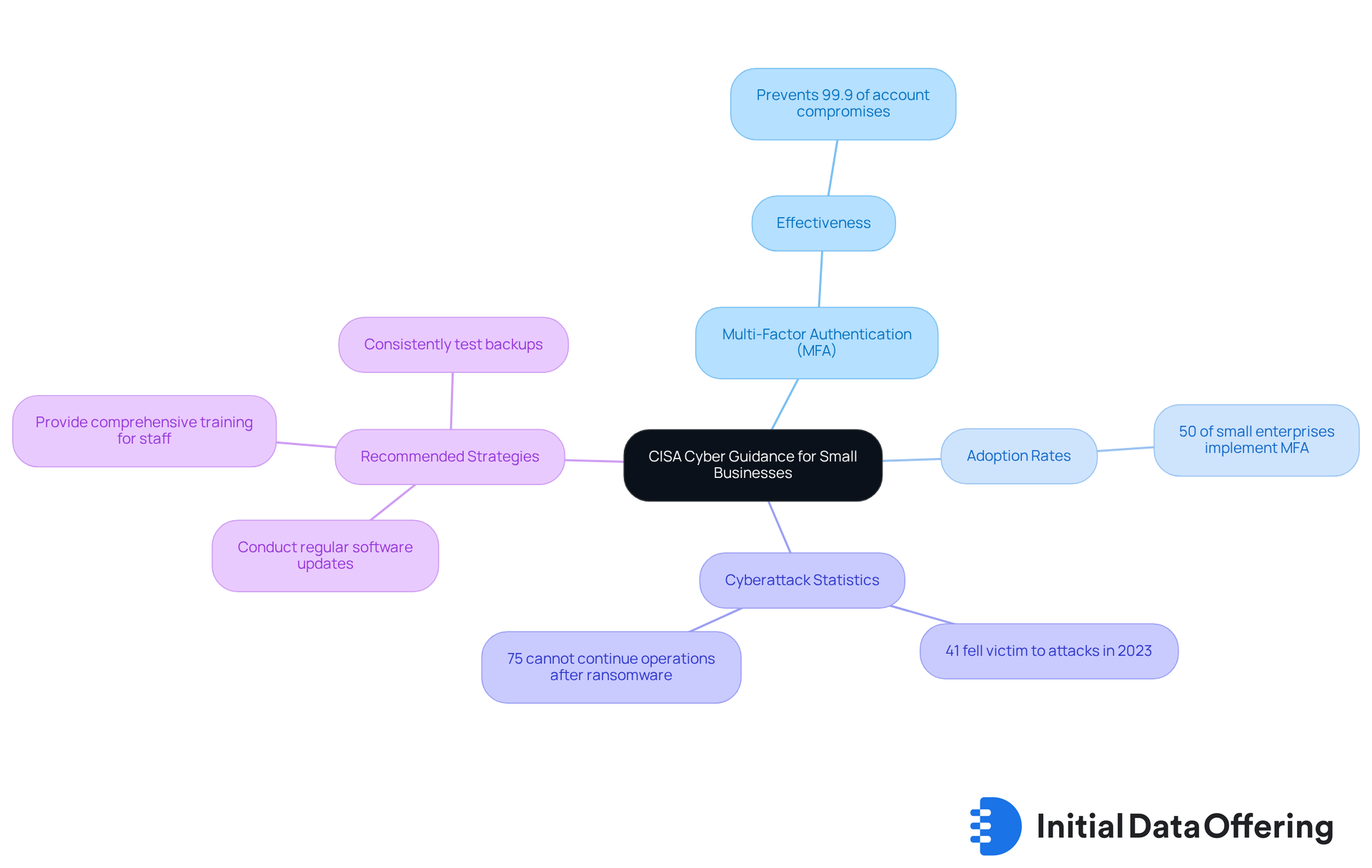
CISA Cyber Guidance: Tailored Strategies for Small Business Cybersecurity
CISA provides targeted strategies to bolster cybersecurity for small enterprises, placing a strong emphasis on the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA). This security measure is essential, as it significantly diminishes the risk of unauthorized access. Organizations that adopt MFA can effectively mitigate the impact of cyberattacks; studies indicate that MFA can prevent up to 99.9% of account compromise attacks.
However, despite its effectiveness, the current adoption rates of MFA among small enterprises remain low, with only about 50% implementing it. Alarmingly, 41% of small enterprises fell victim to a cyberattack in 2023, highlighting the urgent need for MFA adoption. Furthermore, 75% of SMBs reported they could not continue operations if struck by ransomware, underscoring the serious consequences of inadequate online security practices.
CISA advises small enterprises to not only implement MFA but also to:
- Conduct regular software updates
- Provide comprehensive training for staff to recognize phishing attempts
- Consistently test backups to ensure data recovery after an attack
Together, these strategies create a robust security framework tailored to the unique vulnerabilities and operational constraints faced by smaller organizations. By following CISA's recommendations, small enterprises can significantly enhance their security posture and reduce the likelihood of cyber incidents.
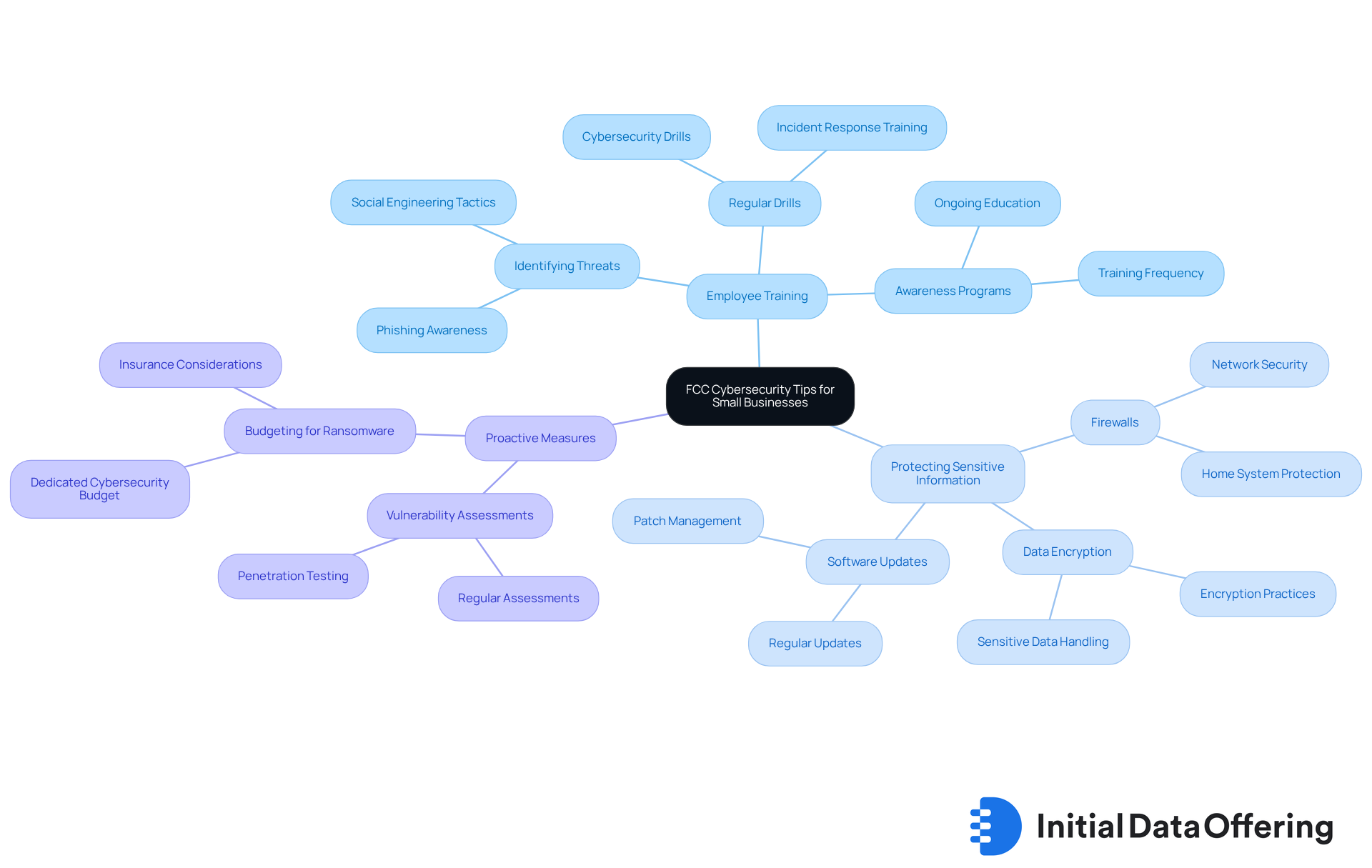
FCC Cybersecurity Tips: Essential Practices for Small Business Protection
The FCC outlines essential cybersecurity strategies for small enterprises, emphasizing the necessity of comprehensive employee training in security protocols vital for cyber security businesses. This training is crucial, as human error accounts for a significant percentage of breaches. Studies indicate that 68% of all SMB breaches involve non-malicious errors or social engineering tactics. By equipping workers with the knowledge to identify threats like phishing and social engineering, organizations can greatly diminish their susceptibility to cyberattacks. Notably, 43% of cyber breaches globally involve small enterprises, highlighting the need for cyber security businesses to address their increased vulnerability.
In addition to training, protecting sensitive information is paramount. Small enterprises should implement robust practices such as utilizing firewalls to prevent unauthorized access and ensuring that all sensitive data is encrypted. Regularly updating software and conducting vulnerability assessments are also essential steps in safeguarding digital assets.
Instances of small enterprises successfully improving their security through employee training abound. For instance, companies that have instituted regular cybersecurity drills and awareness programs report a marked decrease in incidents related to human error. According to Mohammed Khalil, a Cybersecurity Architect at DeepStrike, "The financial impact is worsened by the fact that many small enterprises don’t have a dedicated budget to cover ransomware expenses, so they have to pay the ransom to return to operations." These proactive measures not only bolster security but also foster a culture of vigilance among employees.
Integrating these FCC-suggested practices can greatly enhance the online security stance of cyber security businesses. This ensures they are more equipped to confront the changing environment of cyber dangers. Moreover, with 60% of small enterprises that encounter a serious breach unable to continue functioning, the significance of effective security measures cannot be overstated.
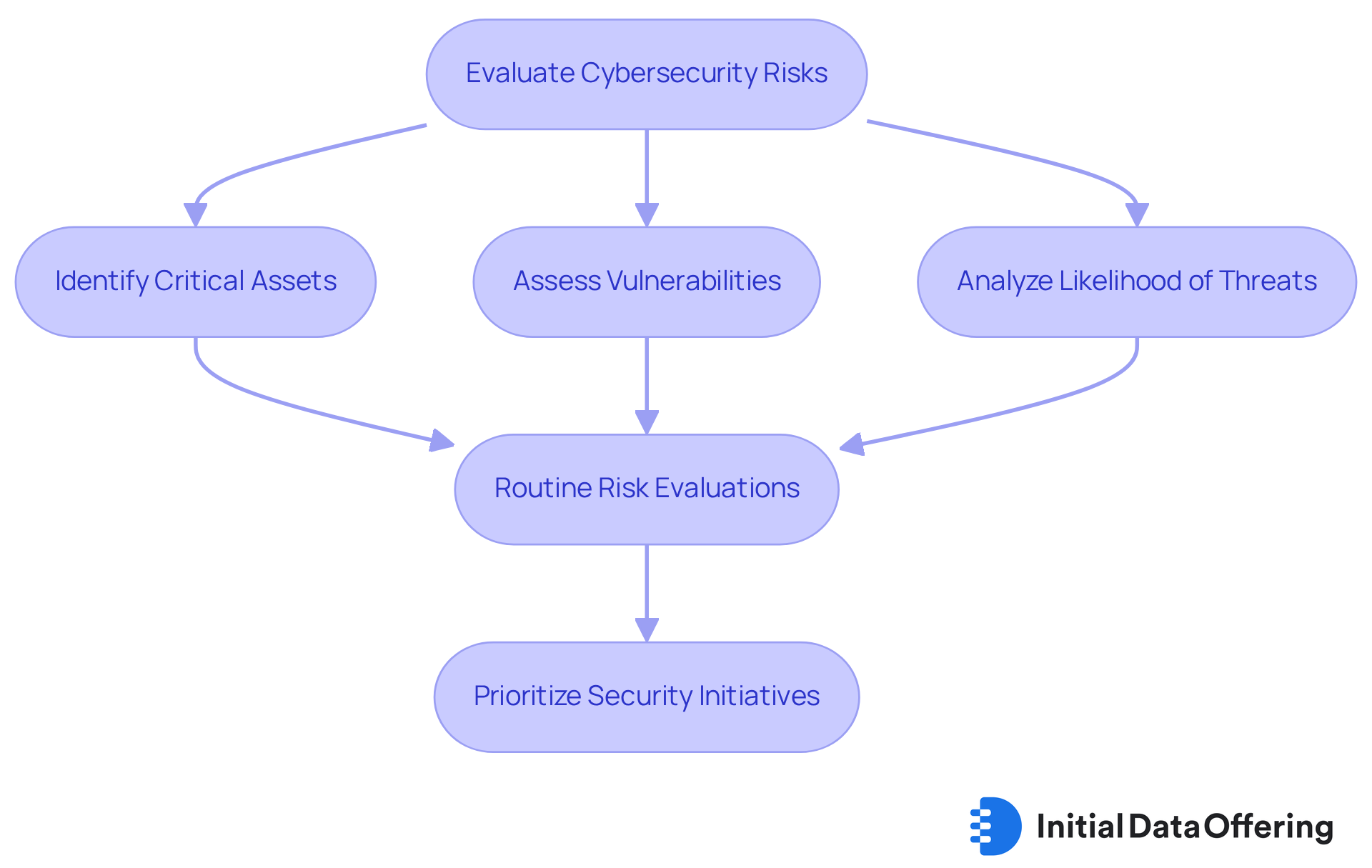
Cybersecurity Guide: Evaluate Risks and Understand Threats to Your Business
A thorough security plan necessitates a comprehensive assessment of risks and an awareness of potential threats to the organization. This process begins with:
- Identifying critical assets
- Assessing vulnerabilities
- Analyzing the likelihood of various cyber threats
Routine risk evaluations allow organizations to prioritize their security initiatives and allocate resources effectively, ensuring that the most pressing risks are addressed. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining a resilient cybersecurity posture, particularly as 70% of companies are currently using or planning to implement AI in their risk management programs.
Moreover, experts stress the importance of simulating worst-case scenarios to prepare for potential disruptions. Notably, 61% of companies have already conducted such simulations. However, only 28% report an increase in technology spending for risk management, revealing a significant gap between awareness and action. By adopting these strategies, cyber security businesses can strengthen their defenses against increasingly sophisticated and targeted cyber threats. As Diana Kelley from Noma Security points out, "red team testing becomes essential to identify emergent behaviors and security vulnerabilities before deployment."
Furthermore, the average cost of a breach in 2025 is projected to reach $10.22 million for U.S. firms, underscoring the financial repercussions of inadequate risk evaluations. Interestingly, 68% of organizations rate their cybersecurity capabilities as high, suggesting a perceived effectiveness that may not correspond with actual preparedness. How prepared is your organization to face these evolving threats? By recognizing these insights and implementing robust risk management strategies, cyber security businesses can enhance their cybersecurity posture and mitigate potential losses.
Understanding Cyber Threats: Key Types Every Business Should Know
Businesses face a myriad of cyber threats, with phishing attacks and ransomware being among the most prevalent. Phishing schemes often exploit employees, tricking them into revealing sensitive information. In contrast, ransomware can lock critical data, demanding hefty payments for its release. In 2024, phishing attacks increased significantly, with an estimated 3.4 billion phishing emails dispatched daily. Over 90% of companies worldwide reported encountering a phishing attack. This alarming trend underscores the necessity for cyber security businesses to implement robust training programs and security measures.
To combat these threats, organizations should adopt targeted strategies such as:
- Email filtering
- Endpoint protection
- Partnering with cyber security businesses
Effective incident response relies on a well-informed workforce; thus, training employees to recognize phishing attempts is crucial. Cybersecurity experts emphasize that a breach isn't the disaster-mismanagement of the incident is. Moreover, ransomware payments have nearly doubled to $1.5 million over the past year, and the average payout for small businesses affected by ransomware is around $5,900. This highlights the financial burden even minor breaches can impose. The FBI recommends against paying ransoms, as it does not ensure information recovery.
Real-world examples of ransomware prevention strategies include:
- Maintaining immutable, offsite backups
- Conducting regular security awareness training, such as the program offered by Huntress
These proactive measures not only safeguard sensitive data but also support cyber security businesses by fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness within the organization. Ultimately, this approach reduces the risk of falling victim to cybercriminals.
How prepared is your organization to handle these threats? By implementing these strategies, businesses can not only protect their data but also enhance their overall security posture.
Mitigating Vulnerabilities: Strategies for Small Business Cybersecurity
To effectively mitigate vulnerabilities, small businesses must implement several essential strategies. These include regular software updates, robust password policies, and thorough vulnerability assessments.
-
Regular software updates are crucial. They ensure that protection patches are applied swiftly, significantly reducing the risk of exploitation. In fact, unpatched software was responsible for
60%of data breaches worldwide in2023, according to the Ponemon Institute. This statistic underscores the importance of timely updates for safeguarding sensitive information. -
Establishing strong password policies is another vital strategy. Incorporating multi-factor authentication (MFA) can greatly enhance security by making unauthorized access more challenging. Present trends indicate that
58%of small enterprises have adopted antivirus software, while49%have implemented firewalls. This reflects a growing awareness of the necessity for comprehensive digital security measures. -
Furthermore, conducting regular vulnerability assessments allows organizations to identify and address potential weaknesses in their systems. This proactive approach fortifies defenses against cyber threats. It is also essential for companies to enable automatic updates for critical software and security patches to maintain their security posture.
-
Utilizing a cybersecurity health checklist can further assist organizations in assessing their cybersecurity practices. This tool ensures resilience against potential threats. How prepared is your business to face these challenges? By implementing these strategies, small businesses can significantly enhance their cybersecurity and protect their valuable data.
Employee Training: Building a Cybersecurity-Aware Workforce
Establishing a cybersecurity-conscious workforce is essential for organizations today. Strong employee training initiatives play a crucial role in this effort, focusing on key subjects such as identifying phishing attempts, understanding information protection, and adhering to secure practices when handling sensitive data.
Features: Effective training should not be a one-time event; it must be an ongoing process. This includes regular sessions and interactive elements, like simulated phishing exercises.
Advantages: These simulations have shown remarkable effectiveness, with organizations reporting a 70% reduction in successful phishing attacks when employees receive adequate training.
Benefits: By fostering an environment where employees feel safe to report suspicious activities without fear of repercussions, organizations can significantly enhance their overall security posture.
Integrating these practices into workplace culture not only strengthens defenses against cyber threats but also addresses the financial implications of data breaches. With the average cost of a data breach reaching $4.88 million globally, investing in comprehensive training programs is not just beneficial - it's essential. Tailored training programs for specific industries, such as healthcare and finance, can further enhance the relevance and effectiveness of these initiatives.
As one cybersecurity trainer noted, "Recognizing phishing attempts is not just about awareness; it's about creating a proactive culture where employees feel empowered to act." How can your organization implement these strategies to foster a more secure environment?
Firewall Security: Protecting Your Business Network from Cyber Attacks
Establishing strong firewall protection is essential for safeguarding corporate networks against cyber threats. Firewalls serve as a critical line of defense, monitoring both incoming and outgoing traffic. They block unauthorized access while allowing legitimate communication to flow freely. This dual function not only protects sensitive data but also ensures operational continuity.
Why is this important? Companies must consistently assess and revise their firewall settings. This ongoing evaluation guarantees that the configurations align with current protection policies and adapt to evolving threat environments. By doing so, organizations can stay one step ahead of potential breaches, enhancing their overall security posture.
Moreover, integrating intrusion detection systems can significantly boost firewall effectiveness. These systems provide real-time alerts on suspicious activities, allowing for immediate responses to potential threats. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also fosters a culture of vigilance within the organization.
In conclusion, investing in robust firewall protection and complementary systems is not just a technical necessity; it’s a strategic imperative. How does your organization ensure its firewall settings are up to date? Consider the implications of neglecting this critical aspect of cybersecurity.
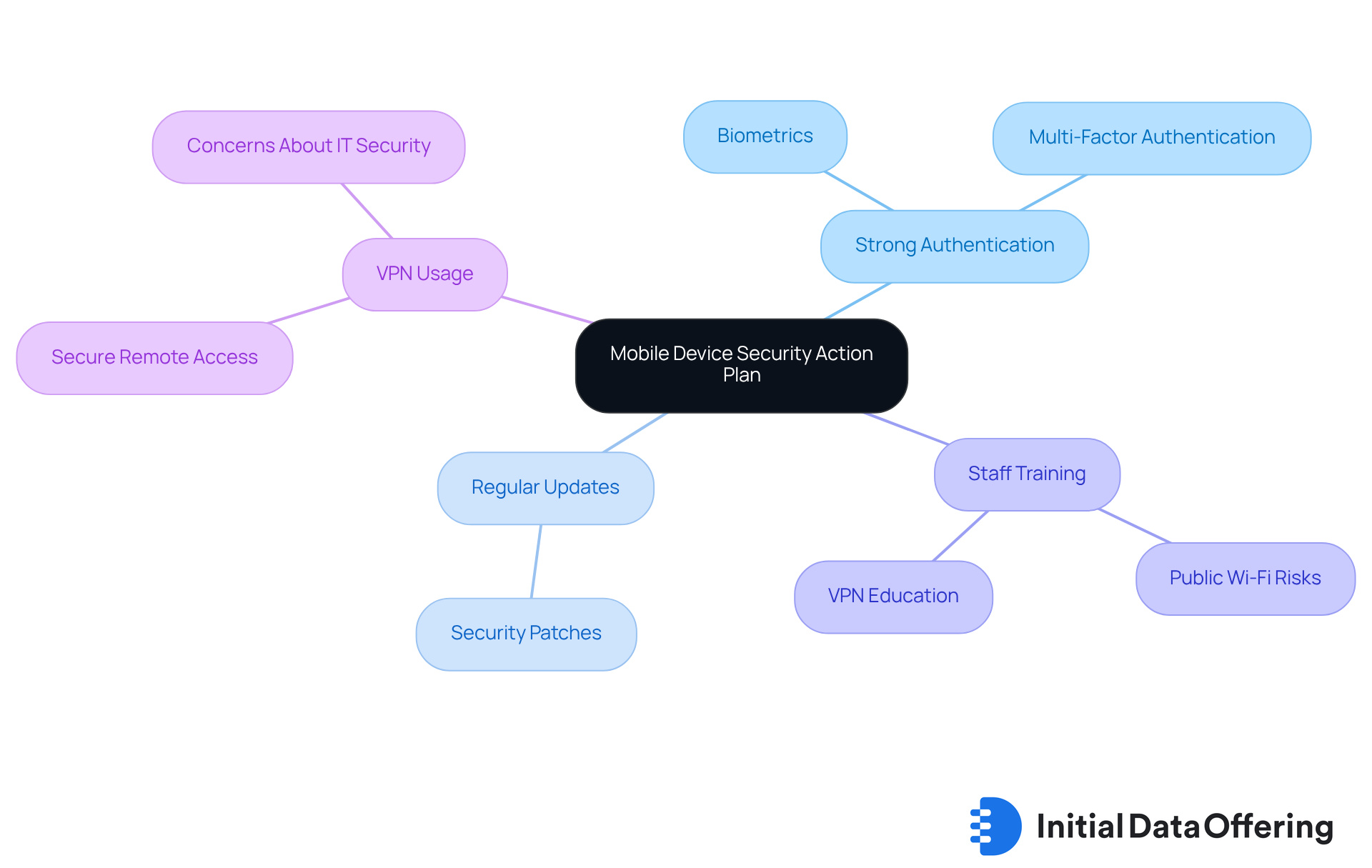
Mobile Device Security: Action Plan for Protecting Business Data
To protect business data on mobile devices, organizations must adopt a robust mobile device protection action plan. This plan should prioritize strong authentication methods, such as biometrics and multi-factor authentication (MFA). These features significantly enhance security by ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive information. Regular updates with the latest security patches are essential to mitigate vulnerabilities that cybercriminals could exploit. Notably, banking trojans account for 27% of mobile malware, underscoring the specific threats organizations face.
Furthermore, companies should actively instruct staff on secure mobile practices. This includes advising against using public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions and promoting virtual private networks (VPNs) for remote access to company resources. With 70% of organizations utilizing VPNs primarily for secure remote access, it’s crucial that employees understand how to leverage these tools effectively. However, it’s important to note that 91% of respondents expressed concerns about VPNs potentially undermining their IT protection environment, highlighting the dual nature of VPNs as both a protective tool and a possible vulnerability.
Examples of businesses successfully enforcing strong authentication methods include those that have implemented MFA across their platforms, which has significantly reduced unauthorized access incidents. Current approaches for implementing these methods involve incorporating user-friendly authentication solutions that simplify the login process while maintaining high safety standards. By fostering a culture of security awareness and applying these strategies, organizations can better safeguard their information on mobile devices.
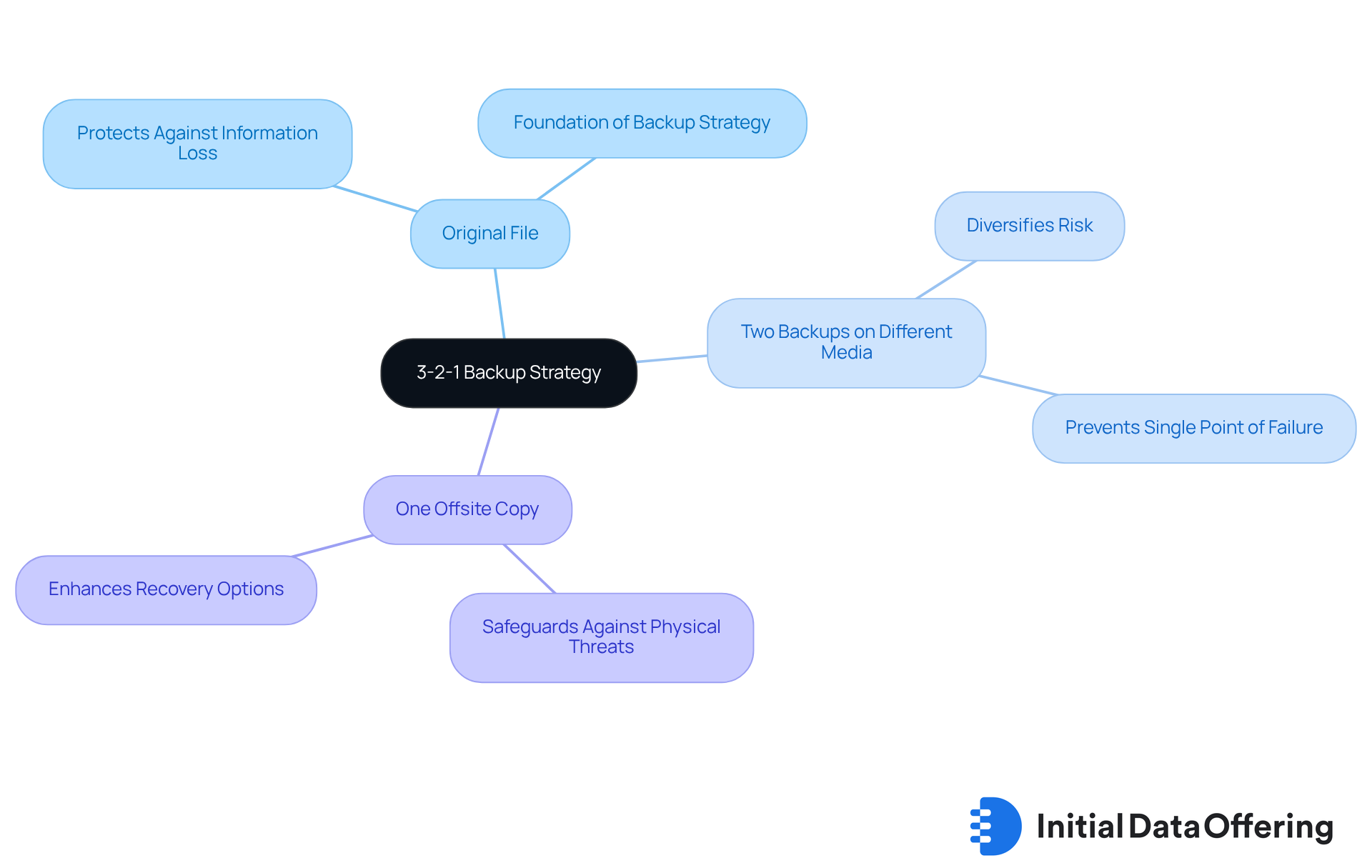
Data Backup Best Practices: Ensuring Business Continuity in Cybersecurity
Implementing strong backup practices is essential for maintaining business continuity amid increasing cyber threats. One effective method is the 3-2-1 backup strategy, which advocates for three copies of files: the original, two backups stored on different media, and one copy kept offsite. This approach not only protects against information loss but also enhances recovery options in the event of a cyber incident.
Why is this important? Routine examination of backup systems is equally crucial. It ensures that information can be recovered quickly and reliably, reducing downtime and safeguarding vital organizational functions. As emphasized by industry specialists, the 3-2-1 strategy is widely regarded as a best practice. Many organizations recognize the effectiveness of cyber security businesses in mitigating risks associated with breaches and ransomware attacks.
In fact, a significant portion of businesses now prioritize this strategy, reflecting a growing awareness of the need for comprehensive data protection measures. By adopting the 3-2-1 strategy, cyber security businesses can significantly bolster their defenses against potential cyber threats.
Conclusion
Implementing robust cybersecurity strategies is critical for businesses of all sizes in today's digital landscape. This article highlights ten essential practices that organizations should adopt to safeguard their data and maintain operational integrity. These strategies include:
- Leveraging high-quality datasets for informed decision-making
- Establishing strong employee training programs aimed at fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness
- Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) to reduce unauthorized access risks
- Conducting regular software updates to mitigate vulnerabilities
- Performing comprehensive risk assessments to help prioritize security initiatives
- Adopting effective data backup practices
- Utilizing firewalls to protect sensitive information
- Ensuring mobile device security
- Enhancing incident response plans
- Engaging in continuous monitoring of security systems
Key insights discussed include the importance of multi-factor authentication (MFA) in reducing unauthorized access risks. Regular software updates are necessary to mitigate vulnerabilities, while comprehensive risk assessments help prioritize security initiatives. Effective data backup practices, along with the role of firewalls and mobile device security, are also crucial in protecting sensitive information. Each of these elements contributes to a more resilient cybersecurity posture, enabling organizations to better respond to evolving threats.
In conclusion, the significance of adopting a proactive approach to cybersecurity cannot be overstated. As cyber threats continue to grow in sophistication, businesses must prioritize these strategies to protect their assets and ensure continuity. By investing in these practices, organizations not only enhance their security measures but also foster a culture of vigilance that empowers employees to contribute to a safer digital environment. Embracing these cybersecurity best practices is essential for safeguarding the future of any business.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Initial Data Offering (IDO) and how does it benefit enterprises?
The Initial Data Offering (IDO) provides access to high-quality datasets that help enterprises analyze emerging trends, identify vulnerabilities, and develop informed security strategies, thereby enhancing their overall security posture.
How can organizations leverage insights from IDO for cybersecurity?
By applying knowledge gained from IDO datasets, organizations can make data-driven decisions that significantly improve their security measures and resilience against evolving cyber threats.
What key strategies does CISA recommend for small business cybersecurity?
CISA recommends implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), conducting regular software updates, providing comprehensive staff training on recognizing phishing attempts, and consistently testing backups for data recovery.
Why is multi-factor authentication (MFA) important for small enterprises?
MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and can prevent up to 99.9% of account compromise attacks. Despite its effectiveness, only about 50% of small enterprises currently implement it.
What are the consequences of inadequate cybersecurity practices for small businesses?
In 2023, 41% of small enterprises experienced a cyberattack, and 75% reported they could not continue operations if struck by ransomware, highlighting the serious risks of poor online security.
What essential cybersecurity practices does the FCC recommend for small enterprises?
The FCC emphasizes comprehensive employee training, protecting sensitive information with firewalls and encryption, regularly updating software, and conducting vulnerability assessments.
How can employee training impact cybersecurity for small businesses?
Employee training can significantly reduce the likelihood of breaches caused by human error, as 68% of all SMB breaches involve non-malicious errors or social engineering tactics.
What is the financial impact of cybersecurity incidents on small enterprises?
Many small enterprises lack a dedicated budget for ransomware expenses, which often forces them to pay ransoms to regain access to their operations, worsening the financial impact of cyber incidents.
How can small enterprises create a culture of vigilance against cyber threats?
By integrating regular cybersecurity drills and awareness programs, small enterprises can foster a culture of vigilance among employees, leading to a decrease in incidents related to human error.