Hedge Funds vs. Traditional Investments: Insights for Boston Analysts

Hedge Funds vs. Traditional Investments: Insights for Boston Analysts
Overview
Hedge funds stand apart from traditional investments primarily due to their unique investment strategies and regulatory environments. Hedge funds utilize diverse approaches, such as leverage and derivatives, to pursue absolute returns. In contrast, traditional investments typically emphasize long-term growth and are subject to more stringent regulations.
This flexibility in hedge funds presents a significant advantage: the potential for higher returns. However, it also introduces increased risk. Investors must grasp these distinctions to make informed decisions. Understanding the balance of risk and reward in hedge funds can empower you to tailor your investment strategy effectively.
In summary, while hedge funds offer opportunities for substantial gains, they require a careful assessment of risk. By recognizing these differences, investors can navigate the complexities of the investment landscape with greater confidence.
Introduction
The landscape of investment opportunities is evolving, with hedge funds and traditional investments standing at opposing ends of the spectrum. Hedge funds are characterized by their flexibility and complex strategies, which promise the allure of higher returns. However, they also come with heightened risks and substantial entry barriers. In contrast, traditional investments offer a more stable and regulated environment, appealing to risk-averse investors who seek consistent growth.
As analysts in Boston navigate these contrasting avenues, a critical question arises: how do the distinct characteristics and regulatory frameworks of these investment vehicles shape strategic decisions in an increasingly volatile market? Understanding these dynamics is essential for making informed investment choices.
Consider the features of hedge funds:
- Their ability to employ diverse strategies can lead to significant returns.
- Yet, the associated risks and barriers to entry may deter some investors.
On the other hand, traditional investments provide a sense of security and predictability, which can be particularly beneficial in uncertain economic climates.
Ultimately, the choice between these investment types hinges on individual risk tolerance and investment goals. As the market continues to evolve, staying informed about these options will empower investors to make strategic decisions that align with their financial objectives.
Define Hedge Funds and Traditional Investments
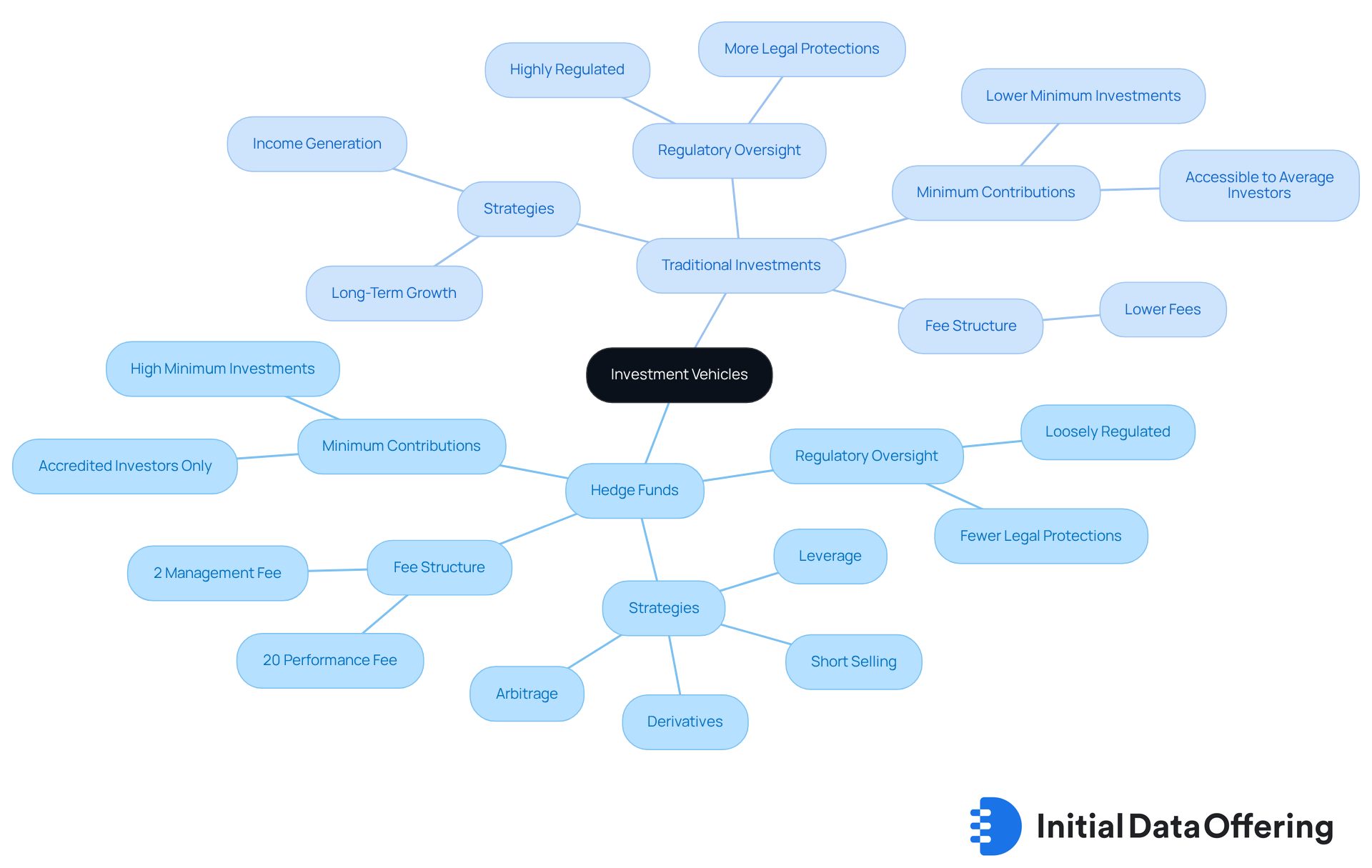
Hedge vehicles are private financial entities that pool capital from qualified investors, employing a diverse range of strategies, including leverage and derivatives, to enhance returns. Unlike conventional assets, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, alternative funds operate with reduced regulatory oversight. This flexibility allows them to adapt their strategies and engage with a broader array of financial instruments.
Traditional assets typically focus on long-term growth and income generation, adhering to a more conservative approach. They often require lower minimum contributions, making them more accessible to the average investor. In contrast, investment pools aim for absolute returns, frequently utilizing advanced strategies that can adjust to shifting market conditions. However, they usually necessitate substantial minimum contributions and come with a fee structure that includes approximately a 2% management fee and a 20% performance fee. This is notably different from the lower fees associated with conventional assets.
This distinction underscores the dynamic nature of hedge vehicles compared to the more stable and regulated environment of traditional assets. How might these differences influence your investment strategy? Understanding the characteristics of hedge funds in Boston can assist you in making informed decisions about where to allocate your capital.
Examine Hedge Fund Strategies and Risk Profiles
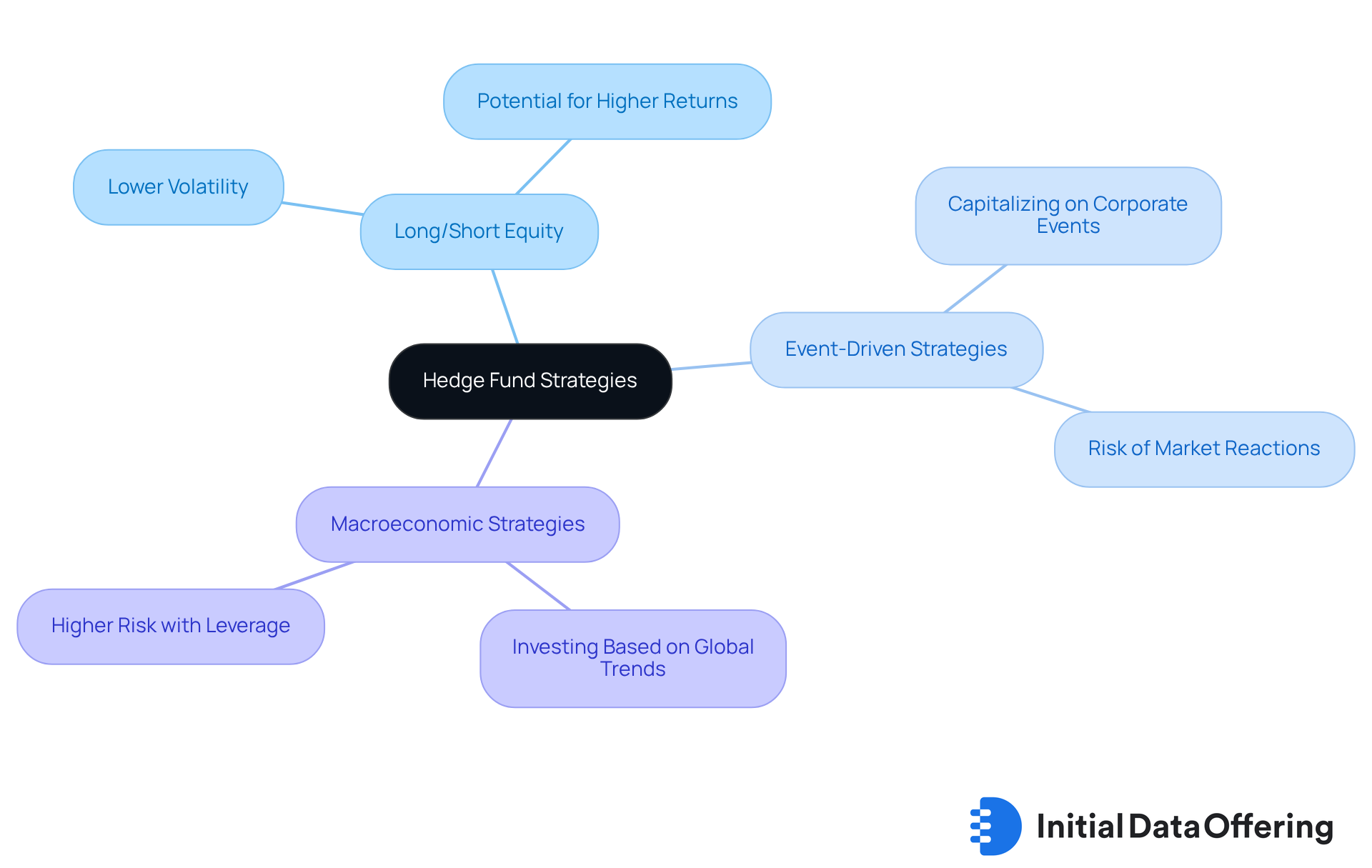
Hedge funds Boston utilize a variety of strategies to achieve their investment objectives. These strategies include:
- Long/short equity, where funds take long positions in undervalued stocks while shorting those that are overvalued.
- Event-driven strategies that capitalize on corporate events such as mergers.
- Macroeconomic strategies that invest based on global economic trends.
The risk profiles of these investment partnerships can vary significantly depending on their chosen strategies. For example, long/short equity vehicles typically exhibit lower volatility compared to those that employ high leverage or derivatives. However, it's important to note that the potential for higher returns often comes with increased risk. This makes hedge funds more suitable for sophisticated investors who can manage such volatility.
Have you considered how these strategies might align with your investment goals? Understanding the nuances of hedge funds Boston strategies can empower you to make informed decisions. By recognizing the balance between risk and reward, investors can better navigate the complexities of the market.
Analyze Traditional Investment Structures and Risks
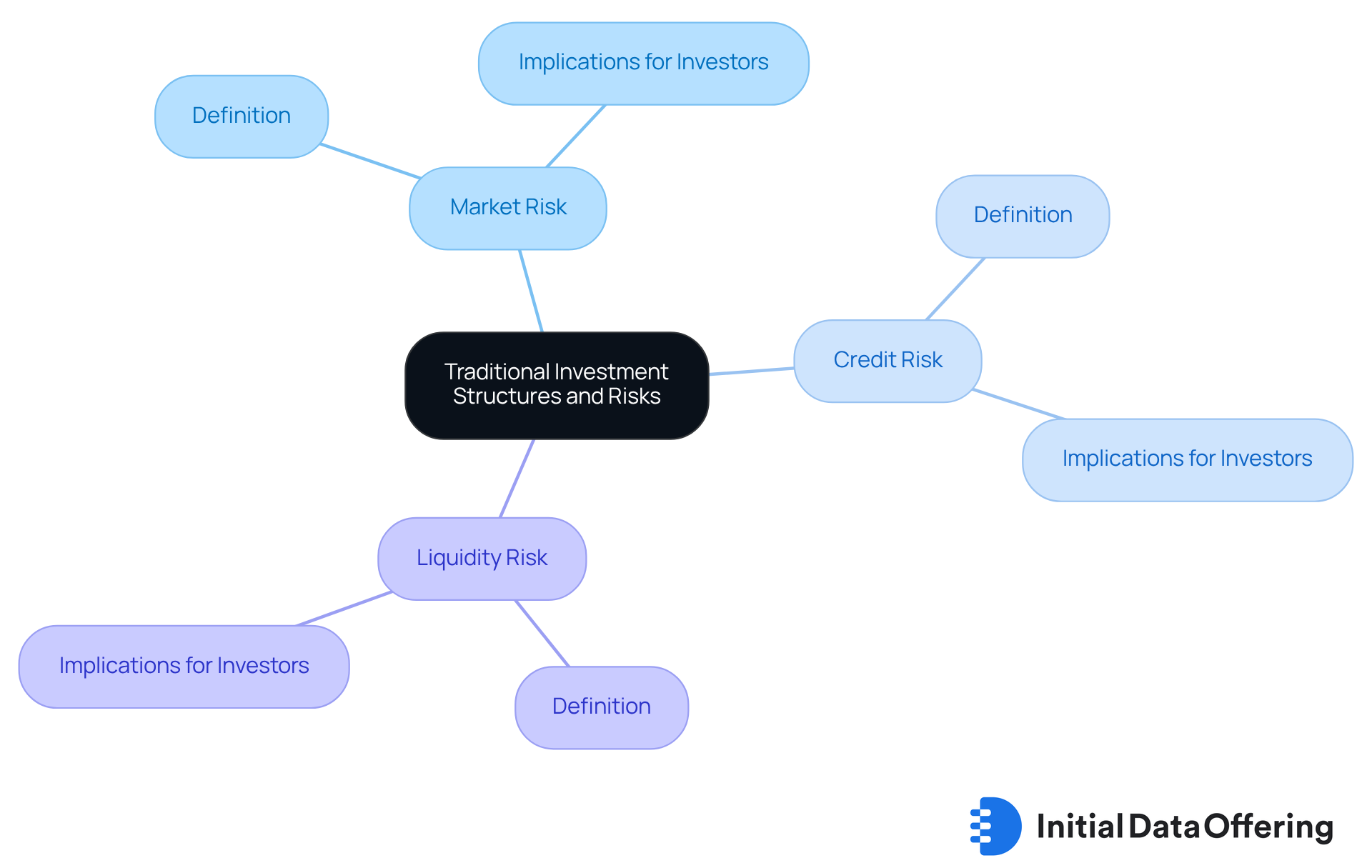
Conventional assets primarily consist of publicly traded securities, such as stocks and bonds, which are regulated by government entities to protect investors. These assets come with specific risks that are important to understand:
- Market Risk: The value of these assets can fluctuate based on market conditions.
- Credit Risk: This relates to the possibility of a borrower defaulting on a loan.
- Liquidity Risk: This concerns how easily an asset can be bought or sold without affecting its price.
While conventional assets generally offer lower returns compared to alternative investment strategies, they are often perceived as safer due to their regulatory oversight and established market practices. This makes them a reliable choice for risk-averse investors.
How do these factors influence your investment decisions? Understanding the balance between risk and return is crucial for making informed choices in your portfolio.
Compare Performance Metrics: Hedge Funds vs. Traditional Investments
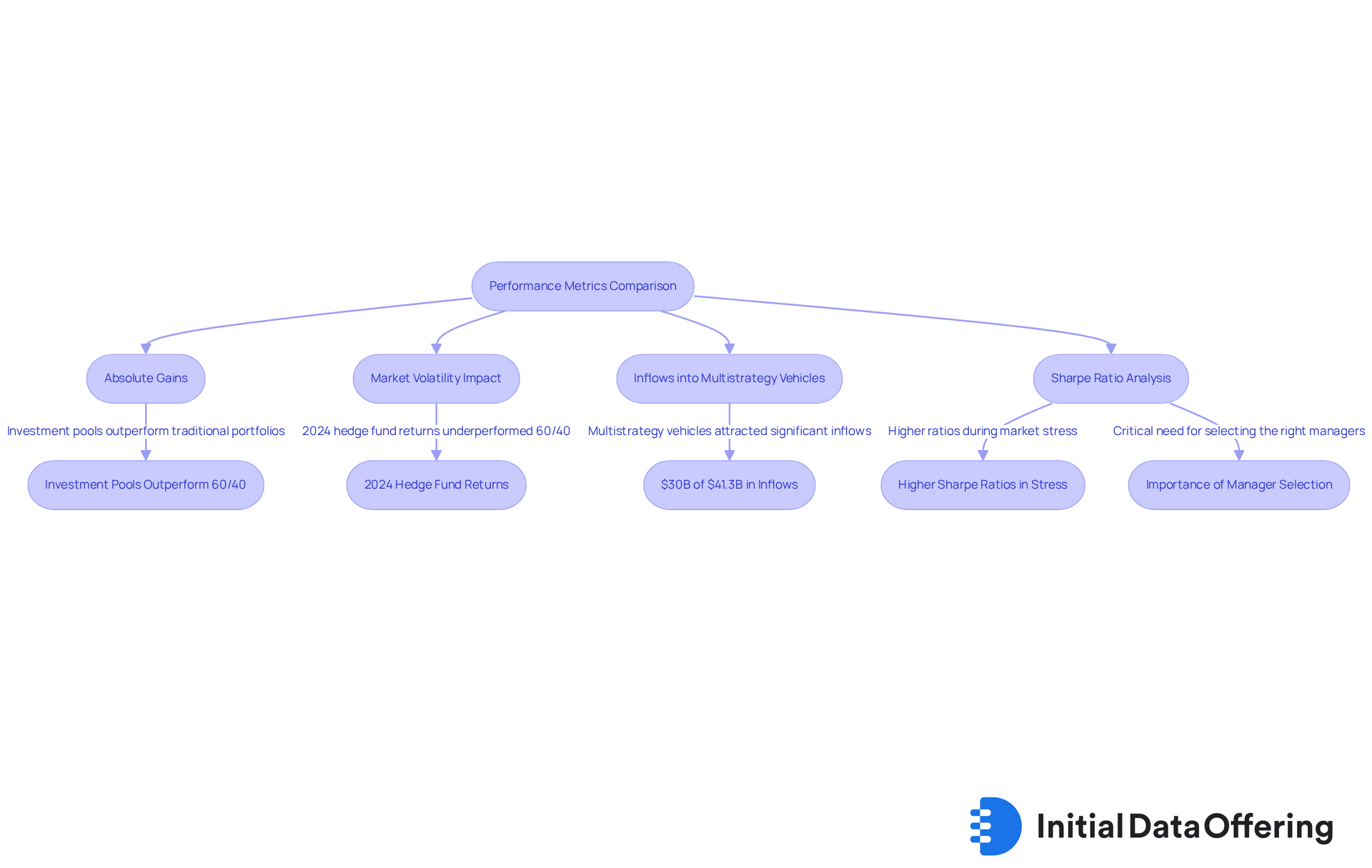
When analyzing performance metrics, investment firms often pursue absolute gains, which can lead to higher average profits compared to conventional investments, especially during unstable market conditions. For instance, investment pools have been shown to outperform traditional 60/40 portfolios across various periods, particularly in years marked by significant market volatility. In 2024, investment managers fell short of the 60/40 model, which yielded better returns, with Barclays estimating investor outcomes to be between 10% and 11%.
Despite this, the overall trend suggests that investment pools are gaining traction in volatile environments. This is evident from the $30 billion of the $41.3 billion in net inflows in 2025 attributed to multistrategy vehicles. While conventional assets typically exhibit lower volatility and more consistent outcomes—making them appealing to cautious investors—alternative strategies can provide enhanced performance indicators.
Performance metrics such as the Sharpe ratio, which assesses risk-adjusted returns, further illustrate the differences in performance between these asset types. Alternative funds often display higher ratios during periods of market stress. Declan Quilligan noted that investors are capitalizing on steady performance, as seen in the monthly inflows during Q3, underscoring the importance of manager selection and strategic allocation in navigating the complexities of the financial landscape.
Moreover, the increased variability in profits among investment vehicles emphasizes the critical need for selecting the right managers, particularly as the investment landscape becomes more intricate. How can investors leverage these insights to enhance their strategies?
Assess Regulatory Impacts on Hedge Funds and Traditional Investments
Hedge vehicles operate within a regulatory framework that is notably less stringent than that governing conventional assets, which are designed to safeguard retail investors. This regulatory flexibility enables hedge funds to utilize a broader array of financial strategies, such as leverage and derivatives. While these strategies can amplify returns, they also heighten risk exposure. In contrast, traditional assets benefit from stringent regulatory oversight that promotes transparency and bolsters investor protection, making them more accessible to the general public.
Recent regulatory changes, particularly those affecting disclosure requirements and investor qualifications, have further shaped the landscape for both investment types. For instance, the introduction of registration requirements for investment managers aims to enhance oversight and investor protection, allowing regulators to gain a clearer understanding of these entities' activities. This shift has led to a more organized environment where investment groups must navigate compliance challenges while maintaining their strategic flexibility.
Statistics reveal that investment pools, despite being less regulated, have seen a notable increase in profit dispersion compared to traditional asset categories. This underscores the importance of careful manager selection. Notably, investment pools recorded gains in the fourth quarter of 2023, fueled by rising stocks and bonds, showcasing their potential for positive returns even amid market fluctuations. As the investment management sector evolves, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.3% in the multi-manager space over the past six years, balancing regulatory compliance with strategic innovation remains crucial. This balance influences how investors allocate their capital across these distinct investment avenues.
Moreover, the complexity of the investment management sector has increased, with new access points like separately managed accounts and co-investments becoming more prevalent. This evolution presents both opportunities and challenges, particularly concerning transparency and compliance, as investment firms adapt to the changing regulatory landscape. As Elizabeth Burton, a Client Investment Strategist, noted, the current environment necessitates that limited partner allocators assess and develop their investment programs differently today. Overall, grasping these regulatory impacts is vital for market research analysts as they navigate the intricate dynamics of hedge funds and traditional investments.
Conclusion
Hedge funds and traditional investments represent two distinct approaches to capital allocation, each with unique characteristics, strategies, and risk profiles. Understanding these differences is crucial for investors aiming to optimize their portfolios.
Features:
Hedge funds are known for their flexibility and aggressive strategies, targeting absolute returns. However, this comes with heightened risks, making them suitable primarily for sophisticated investors. In contrast, traditional investments emphasize long-term growth and stability, appealing to those who prioritize safety and regulatory oversight.
Advantages:
The article explores various strategies employed by hedge funds, such as long/short equity and event-driven approaches, which can yield significant returns in volatile markets. It also highlights the structured and regulated nature of traditional investments, emphasizing their relative safety and accessibility. Performance metrics indicate that while hedge funds may outperform traditional portfolios during market turbulence, they also exhibit increased variability, underscoring the importance of manager selection and strategic allocation.
Benefits:
As analysts and investors navigate the complex investment landscape, weighing the benefits and risks associated with each option becomes essential. Staying informed about current trends and regulatory impacts empowers investors to make strategic decisions that align with their financial goals. Embracing a balanced approach that considers both hedge funds and traditional investments could lead to a more resilient and adaptable investment strategy in 2025 and beyond.
How can you leverage these insights to enhance your investment strategy? By understanding the unique features and benefits of each investment type, you can make informed choices that align with your risk tolerance and financial objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are hedge funds and how do they differ from traditional investments?
Hedge funds are private financial entities that pool capital from qualified investors, using diverse strategies like leverage and derivatives to enhance returns. Unlike traditional investments, which focus on long-term growth and income generation with lower minimum contributions, hedge funds aim for absolute returns and often require substantial minimum investments along with higher fees.
What are the typical fees associated with hedge funds?
Hedge funds usually charge approximately a 2% management fee and a 20% performance fee, which is notably higher than the lower fees associated with conventional assets.
What strategies do hedge funds commonly employ?
Hedge funds commonly utilize strategies such as long/short equity, event-driven strategies that capitalize on corporate events, and macroeconomic strategies that invest based on global economic trends.
How do the risk profiles of hedge funds compare to traditional investments?
The risk profiles of hedge funds can vary significantly based on their strategies. For instance, long/short equity funds typically exhibit lower volatility, while funds that employ high leverage or derivatives may present higher risk. This increased potential for returns often comes with greater risk, making hedge funds more suitable for sophisticated investors.
Who are hedge funds primarily suitable for?
Hedge funds are primarily suitable for sophisticated investors who can manage the volatility and risks associated with advanced investment strategies.