10 Essential Insights on Manufacturing Data for Analysts

10 Essential Insights on Manufacturing Data for Analysts
Overview
The article titled "10 Essential Insights on Manufacturing Data for Analysts" provides critical insights and practices that analysts must grasp to effectively utilize manufacturing data. It highlights the features of data accessibility, integration, and quality management, which serve as foundational elements in enhancing decision-making processes. The advantages of prioritizing these factors are evident, as they significantly boost operational efficiency within the manufacturing sector. Ultimately, the benefits extend beyond mere data handling; they empower analysts to make informed decisions that can lead to substantial improvements in productivity and performance.
How can these insights transform your approach to manufacturing data? By understanding and implementing these practices, analysts can unlock the full potential of the data at their disposal.
Introduction
Manufacturing data is rapidly emerging as the backbone of operational excellence in today’s competitive landscape. Analysts are now faced with the challenge of harnessing a wealth of information that can drive efficiencies, enhance quality, and optimize supply chains. Yet, with the increasing complexity of data sources and the pressing need for accurate insights, how can analysts effectively navigate these challenges? This article explores ten essential insights designed to empower analysts in leveraging manufacturing data for strategic decision-making and operational success.
Initial Data Offering: A Hub for Discovering Manufacturing Datasets
The Initial Data Offering (IDO) serves as a vital centralized hub for accessing a diverse array of manufacturing data. By meticulously curating high-quality information, IDO streamlines the process for analysts seeking valuable insights. The platform features manufacturing data that address essential aspects of production, including:
- Efficiency
- Supply chain metrics
- Quality control information
This improved accessibility is crucial, as 86% of production leaders believe that smart factory solutions, which rely on manufacturing data accessibility, will enhance competitiveness over the next five years. Furthermore, around 74% of evaluators utilize centralized information hubs to extract insights from manufacturing data that guide their decision-making processes.
By offering a user-friendly interface and up-to-date information, IDO enables analysts to leverage the latest trends and insights, ultimately promoting informed decision-making within the industry. How can these datasets transform your approach to production challenges? Subscribing to the Initial Data Offering grants you premium access to unique collections and keeps you informed of daily discoveries, thereby enhancing your ability to make well-informed choices.
OMAC and ei³ Manufacturing Data Governance Guide: Best Practices for Data Management
The OMAC (Open Modular Architecture Controls) and ei³ (Electronic Industry Initiative) frameworks provide essential guidelines for effective manufacturing data governance. A key feature is the establishment of clear information ownership, which is crucial for accountability and decision-making. This clarity enhances the advantage of implementing standardized formats, facilitating interoperability across systems.
Furthermore, adhering to industry regulations significantly boosts the integrity of information management processes. Research indicates that individuals spend 60% to 80% of their time trying to locate information, underscoring the productivity decline associated with ineffective information management and ownership. By adhering to these principles, analysts can significantly improve information quality and reliability, leading to more precise insights and informed decision-making in production operations.
As emphasized by industry leaders, a robust information governance strategy not only streamlines operations but also fosters a culture of analytics-informed decision-making, which is vital for navigating the complexities of modern production. Additionally, integrating the FAIR principles (Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, Reusability) can enhance the efficiency of information management practices.
However, challenges such as inadequate infrastructure and privacy concerns must be addressed to fully leverage the benefits of these governance frameworks.
Evolution of Data Collection in Manufacturing: Adapting to New Technologies
The development of information collection in manufacturing data has been significantly influenced by technological progress, particularly through the incorporation of IoT devices and automation. Conventional manual information entry techniques have largely been replaced by automated capture systems, enabling manufacturers to gather manufacturing data in real-time that substantially enhances operational efficiency. For instance, the adoption of IIoT-enabled production visibility has resulted in a remarkable increase in equipment utilization, climbing from 20% to 60%, as reported by MachineMetrics. This transformation not only streamlines processes but also fosters proactive decision-making, allowing manufacturers to swiftly respond to market demands.
As producers increasingly rely on IoT technologies, statistics reveal that approximately 62% of manufacturers have integrated IoT into their operations, underscoring the growing significance of manufacturing data in information gathering. Moreover, automation in production has been shown to improve product quality by reducing defects through heightened consistency and precision, as evidenced by various case studies. How might your organization benefit from these advancements?
Technology leaders highlight the essential role of these innovations. For example, the global industrial safety market, which encompasses IoT technology, is projected to expand from $6.2 billion in 2024 to $8.9 billion by 2030, according to P&S Intelligence. This growth reflects the increasing dependence on smart sensors and wearables to enhance safety and efficiency in operations.
Additionally, McKinsey indicates that the worldwide market for digital twin technology is expected to grow at an annual rate of 60% until 2027, emphasizing the critical importance of digital twins in manufacturing data collection. What implications does this have for your operational strategy?
In conclusion, the shift to automated information collection through IoT devices represents a fundamental transformation that enables manufacturers to optimize their operations and leverage manufacturing data to maintain a competitive edge in an ever-evolving market landscape. To capitalize on these advancements, manufacturers should consider integrating IoT solutions and automation technologies into their manufacturing data collection processes.
Types of Manufacturing Data: Key Categories Every Analyst Should Know
Manufacturing data can be classified into several key types:
- Operational information
- Quality information
- Supply chain information
- Financial information
Operational information features metrics related to manufacturing data, which provide insights into efficiency and effectiveness. Quality information, on the other hand, focuses on manufacturing data regarding product standards and defect rates, which are crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and compliance. Manufacturing data within supply chain information offers advantages by providing insights into inventory levels and logistics, allowing for better resource management. Lastly, financial information encompasses manufacturing data, cost analysis, and profitability metrics, which are vital for strategic decision-making. Understanding these categories benefits professionals by enabling them to focus their analysis effectively and make informed decisions that drive organizational success.
How can each type of information be leveraged in your specific role to enhance operational performance?
Key Methods for Data Collection in Manufacturing: Strategies for Analysts
Analysts in the manufacturing sector can utilize a variety of information collection methods, including:
- Surveys
- Interviews
- Direct observations
- Automated manufacturing data capture systems
Each of these methods offers unique features that contribute to effective data collection. Surveys and interviews are essential for gathering qualitative information, enabling analysts to examine nuanced perspectives from stakeholders. As Hilary Mason highlights, curiosity is fundamental to analysis, facilitating deeper comprehension and significant insights.
Direct observations provide real-time information on production processes, allowing for a deeper understanding of operational dynamics. Automated systems, such as IoT sensors, enable ongoing collection of manufacturing data, ensuring that analysts have access to the most current details available. As Prashanth Southekal notes, success in information management revolves around understanding rather than mere information gathering. This underscores the importance of integrating these techniques.
This integration not only enhances the robustness of the information collected but also aligns with the growing trend of utilizing automated systems, which have been shown to improve efficiency in information gathering by up to 30%. By merging qualitative and quantitative methods, professionals can obtain more thorough insights from manufacturing data, ultimately enhancing strategic planning and decision-making in production. Furthermore, addressing the disjointed nature of the data marketplace is essential, as it presents challenges that professionals must navigate to effectively collect and analyze data.
Production Metrics: Essential Indicators for Manufacturing Analysts
Key production metrics, which include Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), cycle time, yield rates, defect rates, and other manufacturing data, should be monitored by every analyst. OEE assesses the efficiency of production processes and is determined as the product of availability, performance, and quality. A world-class OEE score is regarded as 85% or above; however, most production organizations generally attain scores nearer to 55-60%, emphasizing the typical challenges encountered by producers. For instance, a leading automotive parts manufacturer improved its OEE from 65% to 82% by addressing long setup times and frequent small stops, resulting in an additional $2 million in annual revenue. This improvement underscores the importance of targeted strategies in enhancing OEE performance.
Cycle time, which indicates the duration required to produce a single unit, is another vital metric. Average cycle times can vary significantly across industries, with electric vehicle battery manufacturers aiming for an ideal output of 48 batteries per 8-hour shift. By examining cycle times, specialists can identify inefficiencies and optimize production processes. How can your organization benefit from monitoring cycle times closely?
Yield rates reflect the percentage of products that meet quality standards, while defect rates highlight areas needing improvement. For example, a chemical plant achieved a 30% reduction in quality-related losses after implementing OEE improvements, showcasing the direct correlation between effective metrics analysis and enhanced product quality. What steps can you take to improve your yield rates?
As the saying goes, 'In the realm of production, what you don’t measure, you can’t improve.' By systematically analyzing the manufacturing data and these metrics, analysts can identify bottlenecks, optimize production processes, and ultimately drive better operational outcomes. Are you ready to take your production metrics to the next level?
Data Accuracy and Quality: Overcoming Challenges in Manufacturing Analysis
Ensuring information accuracy and quality in manufacturing data analysis presents significant challenges. These challenges arise primarily from human error, equipment malfunctions, and inconsistent entry practices. Notably, a staggering 25-30% of information becomes inaccurate each year. Furthermore, poor quality information costs U.S. businesses approximately $600 billion annually, underscoring the critical need for robust management strategies.
To mitigate these challenges effectively, analysts must implement:
- Rigorous information validation processes
- Regular audits
- Systems for capturing manufacturing data
For example, organizations that have implemented automated systems in production have reported enhanced efficiency and decreased human error. This has led to better information quality and improved operational results, as demonstrated in the case study on manufacturing data and its role in Automation in Manufacturing.
To further improve information quality, analysts should adopt best practices such as:
- Standardizing formats
- Employing deduplication techniques to remove redundant entries
Consistent practice in information management techniques can greatly decrease mistakes during information handling. Moreover, performing comprehensive audits is crucial for detecting quality concerns. By emphasizing information quality, analysts can enhance the trustworthiness of their insights and suggestions. This ultimately promotes better decision-making and nurtures an analytics-driven culture within their organizations.
As Veda Bawo, director of information governance at Raymond James, stresses, good information quality is vital for effective analytics. Therefore, it is essential to tackle these issues proactively to sustain a competitive edge in the production sector.

Integration Considerations: Merging Data Sources for Comprehensive Analysis
Incorporating manufacturing data from various sources, including ERP systems, production databases, and external market insights, is vital for achieving comprehensive analysis in manufacturing. Analysts must prioritize compatibility and standardization while leveraging integration tools to streamline this process. For instance, a global electronics producer enhanced its supply chain visibility by standardizing inventory tracking information, leading to a 15% decrease in lead times and reduced excess inventory expenses. Furthermore, standardized information practices have demonstrated a 25% decrease in unplanned downtime in a chemical facility, further highlighting the advantages of standardization in production. This emphasizes how combining various information sources can provide a comprehensive perspective on manufacturing performance and market dynamics, ultimately leading to more informed strategic decisions based on manufacturing data.
How can organizations leverage these insights? SavvyIQ's AI-driven APIs support this integration by providing high-quality business identity and intelligence solutions, allowing organizations to automate workflows and remove manual information tasks. As the sector progresses, the significance of information standardization practices keeps increasing, requiring frequent evaluations and improvements to adjust to advancing technologies and market requirements. This adaptability enables organizations to utilize the full capacity of their information resources.
Maximizing Data Value: Leveraging Insights for Strategic Planning
To unleash the full potential of manufacturing data, analysts must prioritize transforming insights into actionable strategies. This process begins with identifying key trends and forecasting future performance, which are vital for aligning insights with overarching business goals. A recent survey indicates that 78% of manufacturing executives consider manufacturing data and predictive analytics essential for maintaining a competitive advantage, a notable increase from 47% in 2018. This underscores the growing acknowledgment of data-driven decision-making in the industry.
Organizations that effectively leverage information can drive innovation and boost operational efficiency. For instance, General Motors' predictive maintenance program anticipates equipment failures with over 85% accuracy, leading to a significant reduction in unplanned downtime by 30-50% and a decrease in maintenance costs by 10-40%. Similarly, BMW's Zero-Defect Production Initiative utilizes real-time information analysis to minimize quality-related rework, achieving a 31% reduction in its first year. These examples illustrate how information can lead to substantial improvements in production processes.
Business leaders emphasize the importance of translating information findings into practical strategies. As John Coykendall, US Industrial Products & Construction leader at Deloitte, highlights, organizations need to integrate predictive analytics into their operations to secure ongoing performance enhancements. Nonetheless, challenges such as organizational silos between IT and OT teams complicate the implementation of these capabilities. By adopting a customer-centric approach to forecasting and integrating various information sources through concepts like 'data lakes,' manufacturers can more effectively anticipate market changes and optimize resource allocation, ultimately fortifying their competitive position.
In conclusion, the strategic application of manufacturing insights not only fosters innovation but also equips organizations to adeptly navigate the complexities of today's market landscape.
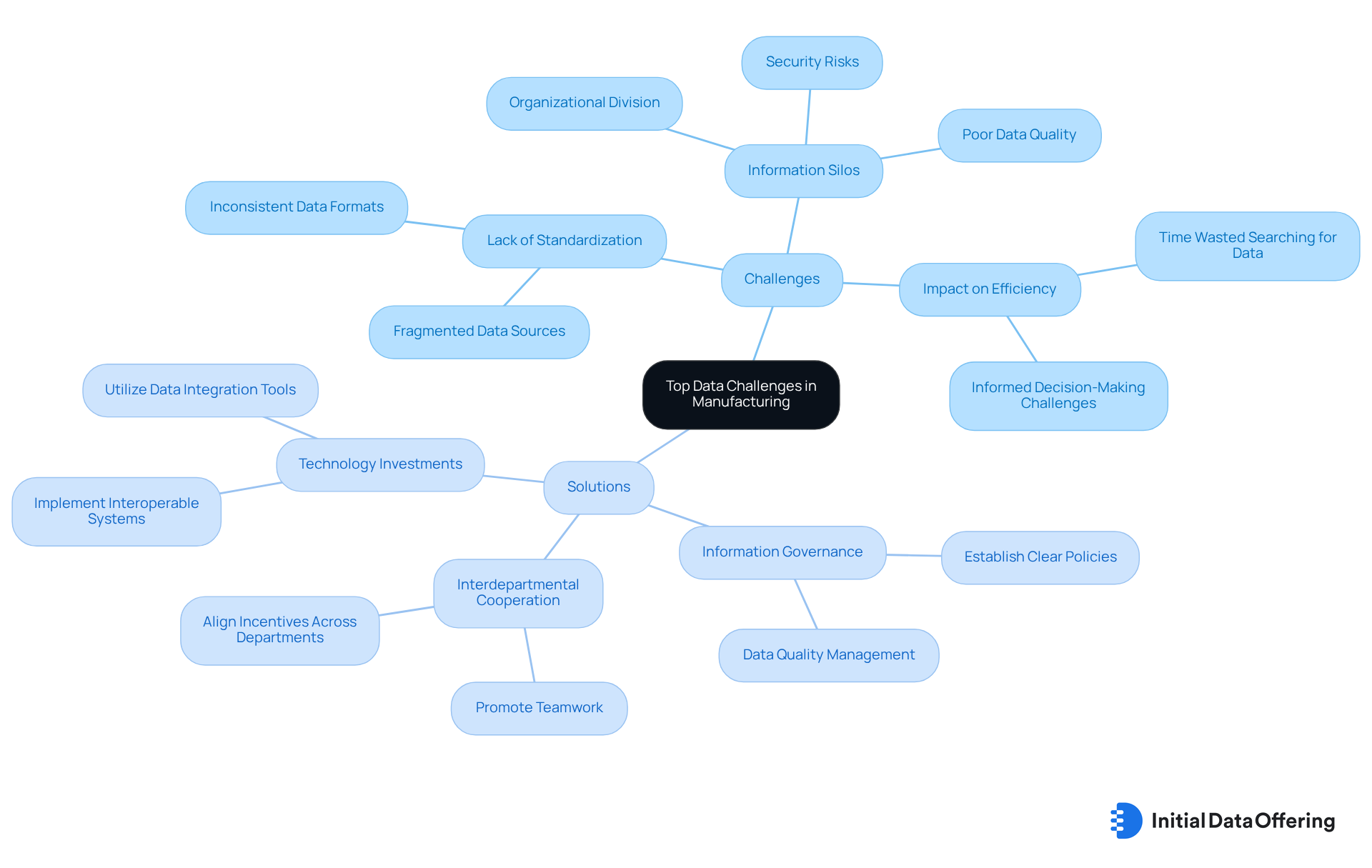
Top Data Challenges in Manufacturing: Insights for Analysts
Manufacturing data analysts encounter significant challenges that can hinder effective information analysis and decision-making. Among these challenges are information silos and a lack of standardization, which obstruct access to essential knowledge. For instance, information silos may lead to organizational separation, resulting in diminished information quality and inefficiencies. Employees can lose as much as 30% of their weekly work hours searching for information due to fragmented systems. Moreover, a staggering 70% of organizations with information silos reported experiencing a breach in the past 24 months, underscoring the risks associated with these issues.
To address these challenges, analysts should advocate for robust information governance frameworks that establish clear policies and procedures for information management. This includes promoting interdepartmental cooperation, which is vital for breaking down barriers and enhancing information visibility. Organizations that have successfully tackled these issues often implement interoperable systems and standardize formats, facilitating seamless integration and improving overall operational efficiency. A case study on dismantling information barriers in manufacturing illustrates how companies centralized their management and invested in analytics to unlock the potential of their assets. By cultivating a culture of collaboration and aligning incentives across departments, these organizations enhanced their decision-making processes and resource utilization.
Industry experts emphasize the importance of information literacy, noting that it is essential for employees to understand the relevance of information to their roles. As Jordan Marrow, VP and Head of Analytics, stated, "Information literacy starts with curiosity, creativity, and critical thinking," highlighting the need for organizations to empower their workforce to utilize information effectively.
In conclusion, addressing the challenges of information silos and standardization in manufacturing data requires a strategic approach that includes investing in technology, fostering collaboration, and promoting information governance. Organizations should consider starting with small integration efforts, focusing on specific use cases before scaling up. By adopting this approach, analysts can significantly enhance the quality and accessibility of manufacturing data, ultimately resulting in better outcomes for their organizations.
Conclusion
The exploration of manufacturing data reveals its critical role in enhancing operational efficiency and strategic decision-making within the industry. By leveraging centralized data hubs like the Initial Data Offering, analysts can access diverse datasets that inform their actions and ultimately drive competitiveness. The integration of robust data governance frameworks, adherence to best practices, and the utilization of advanced technologies such as IoT and automation further empower analysts to extract valuable insights from manufacturing data.
Key insights discussed throughout this article include:
- The importance of standardized data collection methods
- The categorization of manufacturing data types
- The necessity of monitoring essential production metrics
The challenges of data accuracy and integration were also highlighted, emphasizing the need for rigorous management strategies to ensure high-quality information. By addressing these challenges and embracing innovative data practices, organizations can unlock the full potential of their manufacturing data.
In summary, the effective use of manufacturing data not only promotes informed decision-making but also paves the way for innovation and improved operational outcomes. Analysts are encouraged to prioritize data governance, leverage technology, and foster collaboration across departments to overcome barriers and enhance data accessibility. The journey towards maximizing the value of manufacturing data is ongoing, and organizations that commit to these practices will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly data-driven landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Initial Data Offering (IDO)?
The Initial Data Offering (IDO) is a centralized hub that provides access to a variety of high-quality manufacturing datasets, focusing on aspects such as efficiency, supply chain metrics, and quality control information.
Why is the accessibility of manufacturing data important?
Accessibility is crucial because 86% of production leaders believe that smart factory solutions, which depend on accessible manufacturing data, will enhance competitiveness in the next five years. Additionally, 74% of evaluators use centralized information hubs to extract insights that inform their decision-making.
How does IDO support analysts in the manufacturing industry?
IDO offers a user-friendly interface and up-to-date information, allowing analysts to leverage the latest trends and insights, which promotes informed decision-making within the industry.
What guidelines do OMAC and ei³ provide for data management?
OMAC and ei³ provide guidelines for effective manufacturing data governance, emphasizing clear information ownership, standardized formats for interoperability, and adherence to industry regulations to improve information management and decision-making.
What challenges exist in implementing data governance frameworks?
Challenges include inadequate infrastructure and privacy concerns that must be addressed to fully leverage the benefits of governance frameworks like OMAC and ei³.
How has data collection in manufacturing evolved with technology?
Data collection has evolved through the adoption of IoT devices and automation, replacing manual entry with real-time data capture, which enhances operational efficiency and allows for proactive decision-making.
What impact does IoT integration have on manufacturing?
Approximately 62% of manufacturers have integrated IoT into their operations, leading to improved equipment utilization and product quality by reducing defects through enhanced consistency and precision.
What is the projected growth of the industrial safety market and digital twin technology?
The global industrial safety market, which includes IoT technology, is projected to grow from $6.2 billion in 2024 to $8.9 billion by 2030. The market for digital twin technology is expected to grow at an annual rate of 60% until 2027.
What should manufacturers consider to optimize their operations?
Manufacturers should consider integrating IoT solutions and automation technologies into their data collection processes to capitalize on advancements in manufacturing data collection and maintain a competitive edge.